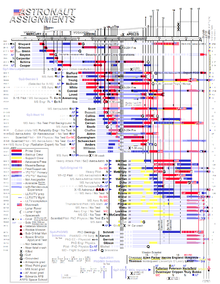
- NASA Astronaut Group 2
-
NASA's Astronaut Group 2, also known as The New Nine, was the second group of astronauts selected by NASA in September 1962. The group was required to augment the original Mercury 7 with the announcement of the Gemini program and leading to the Apollo program. While the Original 7 had been selected to accomplish the simpler task of orbital flight, the new challenges of rendezvous and lunar landing led to the selection of candidates with advanced engineering degrees (for four of the New Nine) as well as test pilot experience. Two of this group had been candidates for the original 7, but were not selected then for medical reasons. In addition, Group 2 became the first group with civilian test pilots in the group; one flew for General Electric, while another flew the X-15 research plane for NASA.
- Neil A. Armstrong, ex-USN
- Gemini 8, Apollo 11
- First U.S. civilian to fly in space; Commander, first docking (Gemini ATV) in space and first mission abort from earth orbit; Commander, first manned lunar landing; first person to walk on the Moon.
- Frank F. Borman, Jr, USAF
- Gemini 7, Apollo 8
- Commander, first 14 day manned mission; Commander, first mission to orbit the Moon.
- Charles Conrad, Jr, USN (1930–1999)
- Gemini 5, Gemini 11, Apollo 12, Skylab 2
- Pilot, first 8 day manned mission and first re-boost to set record for human earth orbit altitude record; Commander, second manned lunar landing; third man to walk on the Moon. Commander, first successful US space station mission and space endurance record of 28 days. Conrad was a candiate for the original 7, but disqualified himself when he refused to complete what he considered to be invasive medical tests.[1]
- James A. Lovell, Jr, USN
- Gemini 7, Gemini 12, Apollo 8, Apollo 13
- Pilot, first 14 day manned mission; Command Module Pilot (navigator), first mission to orbit the Moon. First man to travel to vicinity of the Moon twice. Commander, first mission abort beyond earth orbit aboard Apollo 13. Absolute human altitude record. Lovell was a candidate for the original 7, but was not selected due to a high bilirubin blood count.[2]
- James A. McDivitt, USAF
- Gemini 4, Apollo 9
- Commander, first American EVA mission. Commander, first manned test of Lunar Module. First Roman Catholic to fly into Space.
- Elliot M. See, Jr, ex-USN (1927–1966)
- Slated to command Gemini 9, but died in a plane crash before the mission.
- Thomas P. Stafford, USAF
- Gemini 6A, Gemini 9A, Apollo 10, Apollo-Soyuz Test Project.
- Pilot, first United States orbital rendezvous; Commander, lunar landing test mission; Commander, first joint US-USSR space mission.
- Edward H. White, II, USAF (1930–1967)
- Gemini 4
- Pilot, first American EVA mission; conducted first American EVA. Slated to be the Prime Crew Senior Pilot for first Apollo mission, but died in the Apollo 1 fire.
- John W. Young, USN
- Gemini 3, Gemini 10, Apollo 10, Apollo 16, STS-1, STS-9
- Pilot, first mission to change orbit plane; Commander, first mission to rendezvous with two different craft ("Gemini ATV") in Earth orbit. Command Module Pilot, lunar landing test mission; first person to orbit the Moon solo and orbit the Moon twice; Commander, fifth lunar landing; ninth person to walk on the Moon; Commander, first Space Shuttle mission; first person to travel into space six times.
References on television
The episode "Can We Do This?" from the HBO miniseries, From the Earth to the Moon depicts the first meeting of the New Nine.
References
- ^ Conrad, Nancy and Klausner, Howard. Rocketman: Astronaut Pete Conrad's Incredible Ride to the Moon and Beyond (NAL 2005), pp. 113-118.
- ^ .Kluger, Jeffrey; Jim Lovell (July 1995). Lost Moon: The Perilous Voyage of Apollo 13 (First Pocket Books printing ed.). New York: Pocket Books. pp. 188-196. ISBN 0-671-53464-5.
External links
NASA Astronaut Group 2, "The New Nine, The Next Nine, The Nifty Nine", 1962 NASA Astronaut Groups · NASA Astronaut Corps Categories:- NASA astronauts
- Human spaceflight
- Lists of astronauts
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.