- n-Butylamine
-
n-Butylamine 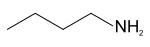 butan-1-amineOther namesNBA; Monobutylamime; 1-Butanamine; 1-Aminobutane
butan-1-amineOther namesNBA; Monobutylamime; 1-Butanamine; 1-AminobutaneIdentifiers CAS number 109-73-9 
PubChem 8007 ChemSpider 7716 
UNII N2QV60B4WR 
UN number UN 1125 DrugBank DB03659 ChEBI CHEBI:43799 
ChEMBL CHEMBL13968 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - NCCCC
Properties Molecular formula C4H11N Molar mass 73.14 g mol−1 Appearance Colorless liquid Density 0.74 g/cm3 Melting point -49 °C, 224 K, -56 °F
Boiling point 77 °C, 350 K, 171 °F
Solubility in water Miscible Acidity (pKa) 10.59[1] Viscosity 0.5 mPa.s at 20 °C Hazards MSDS JT Baker R-phrases R11 R35 R20 R21 R22 S-phrases S3 S16 S26 S29 S45 S36 S37 S39 Main hazards Corrosive, if touched, can cause smelling and taste problems and Highly flammable Flash point -14 °C Related compounds Related compounds sec-butylamine
tert-butylamine
isobutylamine
butane
n-butanol (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references n-Butylamine is an organic compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2. This colourless liquid is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being sec-butylamine, tert-butylamine and isobutylamine. At standard temperature and pressure, n-butylamine is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents.
Uses
This compound is used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides (such as thiocarbazides), pharmaceuticals, and emulsifiers. It is also a precursor for the manufacture of N,N'-dibutylthiourea, a rubber vulcanization accelerator, and n-butylbenzenesulfonamide, a plasticizer of nylon.
References
- ^ Hall, H.K. (1957). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (20): 5441. doi:10.1021/ja01577a030.
Categories:- Amines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
