- Milkymist
-
Milkymist One 
Manufacturer Qi Hardware Release date December 27, 2010 (early developer kit), September 28, 2011 (final version) Introductory price 380 EUR (early developer kit), 499 USD (final version) Operating system RTEMS, Linux CPU LatticeMico32 in a Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA Storage capacity 32 MB built-in NOR flash, memory card Memory 128 MB DDR SDRAM Display SVGA up to 140MHz pixel clock (1280x1024) Input USB keyboard and mouse Camera External (CVBS digitizer) Connectivity DMX512, MIDI, OpenSoundControl, AC97 audio, Ethernet, RC-5 infrared, USB, GPIO Dimensions 172 x 145 x 45 mm Weight 465 g The Milkymist project is an informal organization of people and companies who develop, manufacture and sell a comprehensive open source solution for the live synthesis of interactive visual effects for VJs. The project goes great lengths to apply the open source principles at every level possible, and is best known for the Milkymist system-on-chip (SoC) which is among the first commercialized system-on-chip designs with free HDL source code.
As a result, several Milkymist technologies have been reused in applications unrelated to video synthesis. For example, NASA's Communication Navigation and Networking Reconfigurable Testbed (CoNNeCT) experiment uses the memory controller that was originally developed for the Milkymist system-on-chip[1] and published under the GNU GPL.
The project was presented at several open source and hacker conferences such as the Chaos Communication Congress,[2] FOSDEM[3], Libre Software Meeting[4], and Libre Graphics Meeting 2011[5][6]. It was also featured on the Make Magazine blog[7] and included in their "ultimate open source hardware gift guide 2010".[8]
Contents
Milkymist SoC
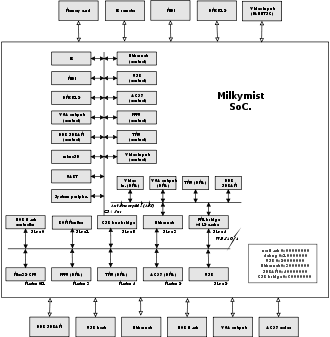
The Milkymist system-on-chip uses the LatticeMico32 (LM32) core as a general purpose processor. It is a RISC 32-bit big endian CPU without a memory management unit (MMU). It is supported by the GCC compiler and can run RTEMS and uClinux. There is also an experimental back-end for LLVM targeting this microprocessor.
The LM32 microprocessor is assisted by a texture mapping unit and a programmable floating point VLIW coprocessor which are used by the Flickernoise video synthesis software. It is also surrounded by various peripheral cores to support every I/O device of the Milkymist One. The system-on-chip interconnect uses three bridged buses and mixes the Wishbone protocol with two custom protocols used for configuration registers and high performance DMA with the SDRAM.
The architecture of the Milkymist system-on-chip is largely documented in the project founder's Master thesis report.[1] Most components of the system-on-chip, except the LatticeMico32 core, were custom developed and placed under the GNU GPL license.
The QEMU emulator can be used to run and debug Milkymist SoC binaries[9] on another computer.
Milkymist One
The Milkymist One video synthesizer and reconfigurable computer is the main product released by the project. It is manufactured by Qi Hardware, a start-up founded by former Openmoko employees.[10] It was first sold at the Chaos Communication Congress in 2010,[11] as an "early developer kit" for interested hackers, open source activists and pioneers who could stand the remaining software and FPGA design bugs. The hardware still came with a warranty against manufacturing defects. Moreover, the Milkymist project has plans to level the Milkymist One up to a general (non-technical) public device marketed at clubs, music bands and VJs.
The technical specifications of the Milkymist One[12] are as follows:
- Multi-standard video input (PAL/SECAM/NTSC)
- Two DMX512 (RS485) ports
- MIDI IN and MIDI OUT ports
- SVGA output, 24bpp, up to 140 MHz pixel clock (about 1280x1024)
- AC97 audio
- XC6SLX45 Spartan-6 FPGA supporting the open source Milkymist SoC
- 128MB 32-bit DDR400 SDRAM
- 32MB parallel flash
- 10/100 Ethernet
- Memory card
- Two USB host connectors
- RC-5 compatible infrared receiver
- RS232 debug port
Following the open source principles that guide the project, the design files of the printed circuit board and the CAD files of the case were released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike license.
Flickernoise
Flickernoise is the video synthesis software that runs on the Milkymist One. It is heavily inspired by MilkDrop and uses a similar, and largely compatible, scripting language to define and program the visual effects. However, while MilkDrop is designed to run automatically in a music player, Flickernoise puts the accent on the interactivity of the visuals and live performance uses. The software supports the programming of visual effects that transform a live video stream coming from a camera connected to the Milkymist One, as well as input from OpenSoundControl, DMX512 and MIDI controllers.
Flickernoise runs on the RTEMS real-time operating system, and uses many POSIX software libraries that were ported to this operating system such as libpng, libjpeg, jbig2dec, openjpeg, Freetype, MuPDF and liblo for OpenSoundControl support. The streamlined hardware platform along with the use of a real-time operating system allows the system to have a lower response time than an equivalent PC based setup.
Flickernoise is also free software, released under the GNU GPL.
References
- ^ a b Bourdeauducq, Sebastien (2010-06). "A performance-driven SoC architecture for video synthesis". KTH. http://kth.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:370883. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "26C3 schedule". http://events.ccc.de/congress/2009/Fahrplan/events/3350.en.html. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "Milkymist : Pushing further the limits of electronics openness". http://m.fosdem.org/event/milkymist. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "Milkymist : a free System-on-Chip for real-time video". http://2010.rmll.info/Milkymist-a-free-System-on-Chip-for-real-time-video.html?lang=fr. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "Milkymist One video synthesizer shown at 6th Libre Graphics Meeting in Montreal". http://en.qi-hardware.com/wiki/Press_Release:_Milkymist_One_video_synthesizer_shown_at_6th_Libre_Graphics_Meeting_in_Montreal. Retrieved 2011-05-14.
- ^ "Milkymist One Shown at Libre Graphics Meeting". http://fabricatorz.com/2011/05/milkymist-one-video-synthesizer-shown-at-6th-libre-graphics-meeting-in-montreal/. Retrieved 2011-05-14.
- ^ "Make: Online: Milkymist :: Interactive VJ Station". http://blog.makezine.com/archive/2010/08/milkymist-interactive-vj-station.html. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "Make: Online: The Ultimate Open Source Hardware Gift Guide 2010". http://blog.makezine.com/archive/2010/12/the-ultimate-open-source-hardware-g.html. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "QEMU development mailing list". http://lists.nongnu.org/archive/html/qemu-devel/2011-04/msg00239.html. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "OpenMoko Layoffs Lead to New Open Hardware Venture". http://www.linux.com/news/embedded-mobile/mids/29263-openmoko-layoffs-lead-to-new-open-hardware-venture. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "First Milkymist One Early Developer Kits are coming!". http://hackable-devices.org/news/post/john/2010/12/first-milkymist-one-early-developer-kits-are-c/. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- ^ "Milkymist official website: Milkymist One". http://www.milkymist.org/mmone.html. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
Categories:- Consumer electronics brands
- Open hardware electronic devices
- Video art
- Video hardware
- Visual effects
- Visual music
- Visualizations
- Open microprocessors
- Open hardware organizations and companies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.