- 4,4'-Methylenedianiline
-
4,4'-Methylenedianiline 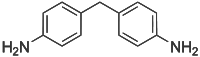 Bis(4-aminophenyl)methaneOther names4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane; 4,4'-Methylenebisbenzenamine; MDA
Bis(4-aminophenyl)methaneOther names4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane; 4,4'-Methylenebisbenzenamine; MDAIdentifiers CAS number 101-77-9 
PubChem 7577 UNII GG5LL7OBZC 
EC number 202-974-4 KEGG C14288 
ChEMBL CHEMBL85728 
RTECS number BY5425000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1cc(N)ccc1Cc2ccc(N)cc2
- InChI=InChI=1/C13H14N2/c14-12-5-1-10(2-6-12)9-11-3-7-13(15)8-4-11/h1-8H,9,14-15H2
Properties Molecular formula C13H14N2 Molar mass 198.26 g mol−1 Density 1.05 g/cm3 (100°C) Melting point 89 °C, 362 K, 192 °F
Boiling point 398-399 °C, 671-672 K, 748-750 °F
Solubility in water 0.125 g/100 ml (20 °C)  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4,4'-Methylenedianiline (MDA) is a suspected carcinogen.[1] It is included in the "substances of very high concern" list of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA)[2]. The compound was involved in an accidental mass poisoning in the vicinity of Epping, Essex, United Kingdom during 1965 during which 84 individuals were poisoned through accidental contamination of flour used to make bread[3].
Contents
Synthesis
In the industrial production, MDA is synthesised by reaction of formaldehyde and aniline in the presence of hydrochloric acid[4].
Uses
MDA is used primarily for making polyurethane foams in which case it is first reacted with phosgene to create 4,4 ́-methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) prior to polymerization with a polyol.[1][2] Lower quantities are used as hardeners in epoxy resins and adhesives, as well as in the production of high-performance polymers[4].
References
- ^ a b ToxFAQs for 4,4'-Methylenedianiline, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
- ^ a b Background document for 4,4’-Diaminodiphenylmethane (MDA)[1]
- ^ The Epping jaundice outbreak: a 24 year follow up.[2]
- ^ a b Data on manufacture, import, export, uses and release of 4-4’ diaminodiphenylmethane as well as ... [3]
External links
- International Labor Organisation icsc1111
- European Union Risk Assessment Report
- J.H. Petersen, S.K. Mortensen, G.A. Pedersen, Memorandum for the Danish Veterinary and Food Administration on An acute case of primary aromatic amines migrating from cooking utensils, Danish Institute for Food and Veterinary Research, 12 October 2004

This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
