- Downstream-peptide motif
-
Downstream-peptide RNA 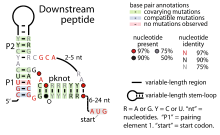
Consensus secondary structure of Downstream-peptide RNAs Identifiers Symbol Downstream-peptide Rfam RF01704 Other data RNA type Cis-regulatory element Domain(s) Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus The Downstream-peptide motif refers to a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in the cyanobacterial genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and one phage that infects such bacteria.[1] It was also detected in marine samples of DNA from uncultivated bacteria, which are presumably other species of cyanobacteria.
Downstream-peptide RNAs are found upstream of short open reading frames (ORFs) that are predicted to encode short peptides (usually between 17 and 100 amino acids). One of the ORFs is apparently down-regulated when cells are grown with an insufficient supply of nitrogen sources.[2] Downstream-peptide RNAs overlap a predicted non-coding RNA called yfr6 that is over 200 nucleotides in length,[2] but it was proposed that only the upstream region (corresponding to the Downstream-peptide motif) functions as an RNA structure.[1] A distinct predicted non-coding RNA called yfr14[3] overlaps both yfr6 and Downstream-peptide RNAs. However, no experimental data has been published to resolve the question of which and how many of these RNAs are functional.
The Downstream-peptide motif has a structural resemblance to a different candidate RNA structure called the glnA RNA motif.[1] The most striking similarity is the nucleotide conservation within the P1 stem of both motifs, and this and other similarities was discussed previously.[1]
It was hypothesized that Downstream-peptide RNAs correspond to riboswitches, based on multiple lines of evidence.[1] First, glnA RNAs are often located in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of multiple classes of genes involved in nitrogen metabolism. This, and other evidence, suggests that glnA RNAs are riboswitches, and their structural similarity to Downstream-peptide RNAs in turn suggests that Downstream-peptide RNAs are also riboswitches. Second, Downstream-peptides are consistently positioned in a place that is consistent with a cis-regulatory role in regulating the downstream ORFs, although the biological role of the ORFs is unknown. Third, the pseudoknot structure has a moderate complexity that is typical of riboswitches. Finally, the observation of regulation of a downstream ORF by nitrogen available also suggests a cis-regulatory role of the element. The subsequent determination that both Downstream-peptide RNAs and glnA RNAs selectively bind glutamine supports these hypotheses.[4]
References
- ^ a b c d e Weinberg Z, Wang JX, Bogue J, et al. (March 2010). "Comparative genomics reveals 104 candidate structured RNAs from bacteria, archaea and their metagenomes". Genome Biol 11 (3): R31. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r31. PMC 2864571. PMID 20230605. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2864571.
- ^ a b Axmann IM, Kensche P, Vogel J, Kohl S, Herzel H, Hess WR (2005). "Identification of cyanobacterial non-coding RNAs by comparative genome analysis". Genome Biol. 6 (9): R73. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-9-r73. PMC 1242208. PMID 16168080. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1242208.
- ^ Steglich C, Futschik ME, Lindell D, Voss B, Chisholm SW, Hess WR (August 2008). Matic, Ivan. ed. "The challenge of regulation in a minimal photoautotroph: non-coding RNAs in Prochlorococcus". PLoS Genet. 4 (8): e1000173. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000173. PMC 2518516. PMID 18769676. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2518516.
- ^ Ames TD, Breaker RR (January 2011). "Bacterial aptamers that selectively bind glutamine". RNA Biol 8 (1). PMID 21282981.
External links
Categories:- Cis-regulatory RNA elements
- Riboswitch
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
