- Domain (biology)
-
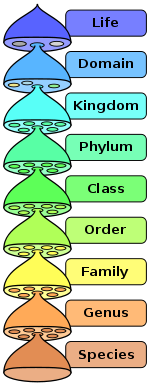
This article is about the "domain" rank in biological classification. For other uses, see Domain (disambiguation).The hierarchy of biological classification's eight major taxonomic ranks, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia. Life is divided into domains, which are subdivided into further groups. Intermediate minor rankings are not shown.

In biological taxonomy, a domain (also superregnum, superkingdom, empire, or regio) is the highest taxonomic rank of organisms, higher than a kingdom. According to the three-domain system of Carl Woese, introduced in 1990, the Tree of Life consists of three domains: Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya.[1] The arrangement of taxa reflects the fundamental differences in the genomes. Alternative classifications of life so far proposed include:
- The two-empire system or superdomain system, with top-level groupings of Prokaryota (or Monera) and Eukaryota.[2]
- The six-kingdom system with top-level groupings of Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.[3]
- The three-empire system (Eubacteria, Archaea, Eukarya) with five supergroups in the Eukarya (Unikonta, Excavata, Chromalveolata, Rhizaria and Archaeplastida)[2][4][5]
None of the three systems currently include non-cellular life.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ^ Woese C, Kandler O, Wheelis M (1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya.". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87 (12): 4576–9. Bibcode 1990PNAS...87.4576W. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. PMC 54159. PMID 2112744. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/reprint/87/12/4576. Retrieved 11 February 2010.
- ^ a b Mayr, Ernst (1998). "Two empires or three?.". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 (17): 9720–9723. Bibcode 1998PNAS...95.9720. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.17.9720. http://www.pnas.org/content/95/17/9720.full. Retrieved 5 Sept 2011.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith, T. (2004), "Only six kingdoms of life", Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 271: 1251–62, doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2705, PMC 1691724, PMID 15306349, http://www.cladocera.de/protozoa/cavalier-smith_2004_prs.pdf, retrieved 2010-04-29
- ^ Campbell, N. A., et al. (2008) "Biology." 8th edition. Person International Edition, San Francisco
- ^ Holt, Jack R. and Carlos A. Iudica, (2010) "Taxa of Life." Retrieved 09-03-2011.
Taxonomic ranks Magnorder Domain/Superkingdom Superphylum/Superdivision Superclass Superorder Superfamily Supertribe Superspecies Kingdom Phylum/Division Class Legion Order Family Tribe Genus Species Subkingdom Subphylum Subclass Cohort Suborder Subfamily Subtribe Subgenus Subspecies Infrakingdom/Branch Infraphylum Infraclass Infraorder Section Infraspecies Microphylum Parvclass Parvorder Series Variety Form Categories:- Scientific classification
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.