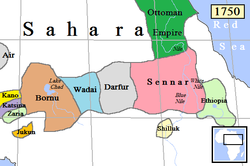
- Sultanate of Darfur
-
Sultanate of Darfur ← 
1603–1874  →
→[[Coat of arms of Darfur|A kaskara sword]]
Sultanate of Darfur and surrounding states in 1750. Capital Al Fasher after 1790 Language(s) Fur Religion Sunni Islam Government Absolute monarchy Sultan - 1603-1637 Suleiman Solon - 1873 Ibrahim Historical era Early Modern Period - Established 1603 - Disestablished 1874 The Sultanate of Darfur was a pre-colonial East African state in what is today Sudan. It functioned independently from 1603 to October 24, 1874.
Contents
Origins
Darfur is composed mostly of semi-arid plains that cannot support a dense population. The one exception is the area in and around the Jebal Marra mountains. It was from bases in these mountains that a series of groups expanded to control the region. The Daju and the 14th century migrants the Tunjur were the earliest powers in Darfur according to written records. The transition of power from the Daju to the Tunjur was facilitated through marriage.
Eventually the Tunjur began marrying amongst the Fur people producing Sultan Dali, a celebrated figure in Darfur histories, who was on his mother's side a Fur, and thus brought the dynasty closer to the people it ruled. Dali divided the country into provinces, and established a penal code, which, under the title of Kitab Dali or Dali's Book, is still preserved, and differs in some respects from Quranic law. His grandson Suleiman (or "Sulayman", usually distinguished by the Fur epithet Solon, meaning "the Arab" or "the Red") reigned from 1603 to 1637, and was a great warrior and a devoted Muslim. Suleiman Solon is considered as the founder of the Keira dynasty and the sultanate of Darfur.
Islam and Prosperity in Darfur
The Tunjur introduced Islam to Darfur via their experience in the Muslim empires of Kanem and Ouaddai. Soleiman's grandson, Ahmed Bukr (c.1682-c.1722), made Islam the religion of the state, and increased the prosperity of the country by encouraging immigration from Bornu and Bagirmi. His rule extended east of the Nile as far as the banks of the Atbara.
Civil War (1722-1786)
The death of Bukr initiated a long running conflict over the succession. On his death bed Bukr stated that each of his many sons should rule in turn. Once on the throne each of his sons instead hoped to make their own son heir, leading to an intermittent civil war that lasted until 1785/6 (AH 1200) Due to these internal divisions Darfur declined in importance and engaged in wars with Sennar and Wadai.
Mohammed II Tairab
One of the most capable of the monarchs during this period was Sultan Mohammed Terab, one of Ahmad Bukr's sons. He led a number of successful campaigns. In 1785/6 (AH 1200) he led an army against the Funj, but got no further than Omdurman. Here he was stopped by the Nile, and found no means of getting his army across the river. Unwilling to give up his project, Terab remained at Omdurman for months and the army began to grow disaffected. According to some stories Tayrab was poisoned by his wife at the instigation of disaffected chiefs, and the army returned to Darfur. While he tried to have his son succeed him, the throne instead went to his brother Abd al-Rahman.
Abd-er-Rahman the Just
Abd-er-Rahman established a new capital at Al Fashir, meaning "the capital", in 1790. The capital had formerly been moved from place to place then at another location called Kobb. During his reign Abd-er-Rahman, surnamed el-Rashid or the Just, Napoleon Bonaparte was campaigning in Egypt. In 1799 Abd-er-Rahman wrote to congratulate the French general on his defeat of the Mamluks. Bonaparte replied by asking the sultan to send him by the next caravan 2000 black slaves upwards of sixteen years old, strong and vigorous.
Mohammed-el-Fadhl
Mohammed-el-Fadhl, his son, was for some time under the control of an energetic eunuch, Mohammed Kurra, but he ultimately made himself independent, and his reign lasted till 1838, when he died of leprosy. He devoted himself largely to the subjection of the semi-independent Arab tribes who lived in the country, notably the Rizeigat, thousands of whom he slew. In 1821 he lost the province of Kordofan to the Egyptians under Mehemet Ali, who planned to conquer the Sudan. The Keira dispatched an army but it was routed by the Egyptians near Bara on 19 August 1821. The Egyptians had been intending to conquer the entirety Darfur, but their difficulties consolidating their hold on the Nile region forced them to abandon these plans. Al-Fadl died in 1838 and of his forty sons, the third, Mohammed Hassan, was appointed his successor. Hassan is described as a religious but avaricious man. In 1856 he went blind and for the rest of his reign his sister Zamzam, the iiry bassi, was the de facto ruler of the sultanate.
Conquest
In 1856 a Khartoum businessman, al-Zubayr Rahma, began operations in the land south of Darfur. He set up a network of trading posts defended by well-armed forces and soon had a sprawling state under his rule. This area known as the Bahr el Ghazal had long been the source of the goods that Darfur would trade to Egypt and North Africa, especially slaves and ivory. The natives of Bahr el Ghazal paid tribute to Darfur, and these were the chief articles of merchandise sold by the Darfurians to the Egyptian traders along the road to Asyut. Al-Zubayr redirected this flow of goods to Khartoum and the Nile.
Sultan Hassan died in 1873 and the succession passed to his youngest son Ibrahim, who soon found himself engaged in a conflict with al-Zubayr. After earlier conflicts with the Egyptians, Al-Zubayr had become their ally and in cooperation with them agreed to conquer Darfur. The war resulted in the destruction of the kingdom. Ibrahim was slain in battle in the autumn of 1874, and his uncle Hassab Alla, who sought to maintain the independence of his country, was captured in 1875 by the troops of the khedive, and removed to Cairo with his family.
See also
References
Sahelian kingdoms Categories:- Former countries in Africa
- States and territories established in 1603
- States and territories disestablished in 1874
- Sahelian kingdoms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.