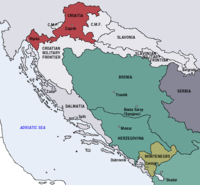
- Croatian–Hungarian Settlement
-
Croatian–Hungarian Settlement
Hrvatsko-ugarska nagodba
Horvát–magyar kiegyezés
The part of the Settlement regarding Rijeka is shown "patched"Created 1868 Purpose A document that governed Croatia's political status in the Hungarian-ruled part of Austria-Hungary Croatian–Hungarian Settlement (Croatian: Hrvatsko-ugarska nagodba, Hungarian: Horvát–magyar kiegyezés, German: Kroatisch-Ungarischer Ausgleich) was a pact signed in 1868, that governed Croatia's political status in the Hungarian-ruled part of Austria-Hungary.[1] It had lasted until the end of World War I, when the Croatian Parliament, as the representative of the historical sovereignty of Croatia, on October 29, 1918 adopted a decision on the cessation of all state and legal ties with the old Austria-Hungary.[2]
Contents
Background
Before the Revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas and the notable actions of Croatian Ban Josip Jelačić, the northern Croatian lands were divided into the Kingdom of Croatia and the Kingdom of Slavonia as separate Habsburg crown lands, recognized as Lands of the Crown of St. Stephen and under the jurisdiction of the Kingdom of Hungary, but effectively functioned a single kingdom subordinate to the central government in Vienna. After 1849, Slavonia and Croatia continued to function in the same capacity.[3] Imperial officials referred to this kingdom simply as the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia.[4]
The southern Croatian land, the Kingdom of Dalmatia, was formed from the southern parts of the Illyrian Provinces that the Habsburg Monarchy conquered from the French Empire in 1815 and it remained a separate administrative division of the Austrian part of Monarchy.
When the Ausgleich, or Compromise, of 1867 created the Austro-Hungarian Dual Monarchy, the Habsburg crownlands of Croatia and Slavonia were effectively merged and placed under Hungarian jurisdiction. Levin Rauch became the acting ban of Croatia, replacing Josip Šokčević.
Ban Rauch prepared a new electoral law that was imposed by the king on October 20, 1867, that reduced the number of elected representatives to 66 and increased the number of unelected ones (the so-called virilist members).[5] In the subsequent election, held from November 19 to December 23, 1867, the People's Party won only 14 seats, and Rauch's Unionist Party had obtained a majority in the Sabor. Although many Croats who sought full autonomy for the South Slavs of the empire objected to that arrangement, that questionable session of Sabor confirmed the subordination of Croatia to Hungary by accepting the Nagodba on the 24th of September 1868.[1]
Description
An agreement was reached between the Parliament of Hungary on the one hand and the Parliament of Croatia on the other hand, with regard to composing by a joint enactment the constitutional questions at issue between them. After the settlement was confirmed, enforced and sanctioned by His Imperial and Apostolic Royal Majesty, it was thereby inarticulated as a joint fundamental law of Hungary and of Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia.[6]
With this compromise the parliament of personal union (in which Croatia-Slavonia had only twenty-nine deputies) controlled the military, the financial system, legislation and administration, Sea Law, Commercial Law, the law of Bills of Exchange and Mining Law, and generally matters of commerce, customs, telegraphs, Post Office, railways, harbors, shipping, and those roads and rivers which jointly concern Hungary and Croatia-Slavonia.[7]
Following the Settlement, the Croatian kingdom was referred to using the name Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia. It claimed also to include Dalmatia, but Dalmatia remained part of Cisleithania.
Status of Rijeka (Fiume)
The Settlement was produced in a manner that left the issue of the port of Rijeka unresolved. Croatia saw it as part of its territory, but Hungary saw it as Corpus separatum.
See also
- Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia
- Timeline of Croatian history
References
- ^ a b Britannica 2009 Nagodba
- ^ Dragutin Pavličević, Short overview of the political and cultural history of the Republic of Croatia
- ^ "Hrvatska pravna povijest 1790. - 1918." (in Croatian). Library of the Supreme Court of Croatia. http://www.vsrh.hr/EasyWeb.asp?pcpid=44. "Zemaljsko-zakonski i vladni list za Krunovinu Horvatsku i Slavoniu 1850.-1859."
- ^ Constitution of Union between Croatia-Slavonia and Hungary
- ^ Horvat, Rudolf (1906). Najnovije doba hrvatske povijesti. Zagreb: Matica hrvatska.
- ^ The Hungaro-Croatian Compromise of 1868
- ^ Constitution of Union between Croatia-Slavonia and Hungary
External links
- HRVATSKO-UGARSKA NAGODBA (1868)
- (Croatian) Tekst Hrvatsko-ugarske nagodbe iz 1868. Text in Croatian
- (Hungarian) 1868. évi XXX. törvénycikk, 1000ev.hu Text in Hungarian
Treaties of Hungary 9th-10th century (age of Magyars) Legend of the white horse (894) · Magyar-East Frankish Treaty (899) · First Magyar-Italian Treaty (900) · Treaty of Bergamo (904) · Third Magyar-Italian Treaty (924) · Magyar-Holy Roman Treaty (927) · First Magyar-Byzantine Treaty (934) · Second Magyar-Byzantine Treaty (943) · Third Magyar-Byzantine Treaty (948)
 1000-1301 (Árpád dynasty)
1000-1301 (Árpád dynasty)Treaty of Strigonium (1031) · First Hungarian-Holy Roman Treaty (1043) · Second Hungarian-Holy Roman Treaty (1058) · Second Hungarian-Holy Roman Treaty (1058) · Treaty of Serdica (1058) · Hungarian-Byzantine Treaty (1971) · Hungarian-Byzantine Treaty (1971) · Hungarian-Kievan Rus' Treaty (1092) · Hungarian-Venetian Treaty (1097) ·
Personal union of Hungary and Croatia (1102) · Third Hungarian-Holy Roman Treaty (1108) · Hungarian-Czech Treaty (1126) · Hungarian-Bavarian Treaty (1127) · Treaty of Branitshevo (1129) · Hungarian-Byzantine Treaties (1153-1167) · First Hungarian-Venetian Truce (1187) · Second Hungarian-Venetian Truce (1190) · Hungarian-Polish Treaty (1193) · Hungarian-Novgorodian Treaty (1219-1221) · Treaty of Graz (1225) · Hungarian-Austrian Treaty (1235) · Treaty of Galas (1244) · Treaty of Buda (1254) · Treaty of Vienna (1261) · Treaty of Pressburg (1271) · Treaty of Hainburg (1291)










1302-1526 (Middle ages to Tripartition)Treaty of Bruck (1328) · Treaty of Enns (1336) · Hungarian-Lithuanian Treaty (1351) · Hungarian-Neapolitan Treaty (1352) · Treaty of Zara (1358) · Treaty of Brunn (1364) · Treaty of Torino (1381) · Treaty of Iglo (1397) · Treaty of Lubowla (1412) · Truce of Eger (1437) · Peace of Szeged (1444) · Truce of Radkersburg (1447) · Hunyadi-Frederick pact (1450) · Peace Treaty of Wiener Neustadt (1463) · Treaty of Ófalu (1474) · Treaty of Korneoburg-Gmunden (1477) · Treaty of Brno (1478) · Treaty of Piotrków (1479) · Treaty of Olomouc (1479) · Treaty of Pressburg (1491) · First Congress of Vienna (1515)Dual reign, Ottoman vassalship,
reconquest and Napoleonic Wars
(1526-1848)Franco-Hungarian alliance (1526) · Treaty of Grosswardein (1538) · Confessio Pentapolitana (1549) · Treaty of Speyer (1571) · Treaty of Szatmár (1711)
_1526-1848_ 1526-1848
1526-1848  (Royal Hungary to Independence)Truce of Adrianople (1547) · Treaty of Adrianople (1568) · Treaty of Vienna (1606) · Peace of Zsitvatorok (1606) · Peace of Szőny (1627) · Peace of Vasvár (1664) · Holy League (1684) · Diploma Leopoldium (1690) · Treaty of Karlowitz (1699) · Treaty of Passarowitz (1718) · Pragmatic Sanction (1723) · Treaty of Belgrade (1739) · Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748) · First Partition of Poland (1772) · Treaty of Sistova (1791) · Treaty of Campo Formio (1797) · Treaty of Schönbrunn (1809) · Congress of Vienna (1815)
(Royal Hungary to Independence)Truce of Adrianople (1547) · Treaty of Adrianople (1568) · Treaty of Vienna (1606) · Peace of Zsitvatorok (1606) · Peace of Szőny (1627) · Peace of Vasvár (1664) · Holy League (1684) · Diploma Leopoldium (1690) · Treaty of Karlowitz (1699) · Treaty of Passarowitz (1718) · Pragmatic Sanction (1723) · Treaty of Belgrade (1739) · Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748) · First Partition of Poland (1772) · Treaty of Sistova (1791) · Treaty of Campo Formio (1797) · Treaty of Schönbrunn (1809) · Congress of Vienna (1815) (1571–1711) (Principality of Transylvania)Alliance of Alba Iulia (1595) · Peace of Nikolsburg (1621) · Treaty of Vienna (1624) · Treaty of Pressburg (1626) · Treaty of Linz (1645) · Treaty of Nymwegen (1679) · Diet of Ónod (1707)
(1571–1711) (Principality of Transylvania)Alliance of Alba Iulia (1595) · Peace of Nikolsburg (1621) · Treaty of Vienna (1624) · Treaty of Pressburg (1626) · Treaty of Linz (1645) · Treaty of Nymwegen (1679) · Diet of Ónod (1707)Austria-Hungary 
to the end of World War I
(1848-1922)Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 · Croatian–Hungarian Settlement (1868) · League of the Three Emperors (1873) · Treaty of Bern (1874) · Reichstadt Agreement (1876) · Treaty of Berlin (1878) · Dual Alliance, 1879 · Triple Alliance (1882) · Boxer Protocol (1901) · Treaty of London (1913) · Armistice of Focşani (1917) · Treaty of Brest-Litovsk with Ukraine (1918) · Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (1918) · Treaty of Bucharest (1918) · Armistice of Villa Giusti (1918) Belgrade Convention (1919) · Treaty of Trianon (1920) · Armistice with Romania (1920) · Bill of dethronement (1921) · US–Hungarian Peace Treaty (1921) · Covenant of the League of Nations (1922)


 Modern age (1922-)Treaties of the Kingdom of Hungary (1922–1946) · Hungarian-Soviet Reparations Agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Czechoslovak population exchange agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Czechoslovak Reparations Agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Yugoslav Reparations Agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Yugoslav economic and cooperation treaty (1947) · Hungarian-Yugoslav Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance (1947) · Paris Peace Treaties, 1947 · Hungarian-Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance (1948) · Soviet weaponry supply agreement (1948) · Agreement of Štrbské Pleso (1949) · Treaties of the People's Republic of Hungary (1949–1989) · Treaties of the Third Republic of Hungary (1989–)Categories:
Modern age (1922-)Treaties of the Kingdom of Hungary (1922–1946) · Hungarian-Soviet Reparations Agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Czechoslovak population exchange agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Czechoslovak Reparations Agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Yugoslav Reparations Agreement (1946) · Hungarian-Yugoslav economic and cooperation treaty (1947) · Hungarian-Yugoslav Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance (1947) · Paris Peace Treaties, 1947 · Hungarian-Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance (1948) · Soviet weaponry supply agreement (1948) · Agreement of Štrbské Pleso (1949) · Treaties of the People's Republic of Hungary (1949–1989) · Treaties of the Third Republic of Hungary (1989–)Categories:- History of Croatia
- History of Hungary
- History of Montenegro
- History of Vojvodina
- Treaties of Austria-Hungary
- 1868 treaties
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.