- Cis–trans isomerism
-
In organic chemistry, cis/trans isomerism or geometric isomerism or configuration isomerism or E/Z isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism describing the orientation of functional groups within a molecule. In general, such isomers contain double bonds, which cannot rotate, but they can also arise from ring structures, wherein the rotation of bonds is greatly restricted. Cis and trans isomers occur both in organic molecules and in inorganic coordination complexes.
The terms cis and trans are from Latin, in which cis means "on the same side" and trans means "on the other side" or "across". The term "geometric isomerism" is considered an obsolete synonym of "cis/trans isomerism" by IUPAC.[1] It is sometimes used as a synonym for general stereoisomerism (e.g., optical isomerism being called geometric isomerism); the correct term for non-optical stereoisomerism is diastereomerism.
Contents
In organic chemistry
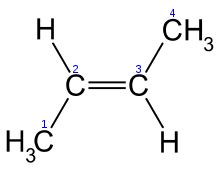
When the substituent groups are oriented in the same direction, the diastereomer is referred to as cis, whereas, when the substituents are oriented in opposing directions, the diastereomer is referred to as trans. An example of a small hydrocarbon displaying cis/trans isomerism is 2-butene.
Alicyclic compounds can also display cis/trans isomerism. As an example of a geometric isomer due to a ring structure, consider 1,2-dichlorocyclohexane:
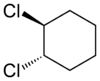
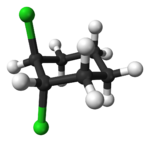
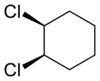
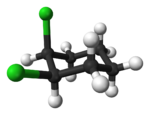
trans-1,2-dichlorocyclohexane cis-1,2-dichlorocyclohexane Comparison of physical properties
Cis and trans isomers often have different physical properties. Differences between isomers, in general, arise from the differences in the shape of the molecule or the overall dipole moment.
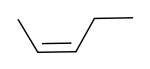
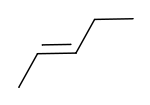
cis-2-pentene trans-2-pentene 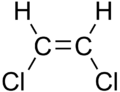
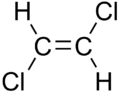
cis-1,2-dichloroethene trans-1,2-dichloroethene 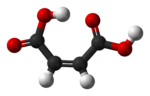
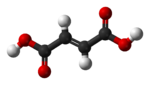
cis-butenedioic acid
(maleic acid)trans-butenedioic acid
(fumaric acid)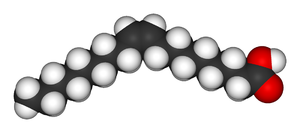
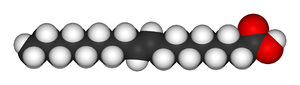
Oleic acid Elaidic acid These differences can be very small, as in the case of the boiling point of straight-chain alkenes, such as 2-pentene, which is 37°C in the cis isomer and 36°C in the trans isomer.[2] The differences between cis and trans isomers can be larger if polar bonds are present, as in the 1,2-dichloroethenes. The cis isomer in this case has a boiling point of 60.3°C, while the trans isomer has a boiling point of 47.5°C.[3] In the cis isomer the two polar C-Cl bond dipole moments combine to give an overall molecular dipole, so that there are intermolecular dipole–dipole forces (or Keesom forces) which add to the London dispersion forces and raise the boiling point. In the trans isomer on the other hand, this does not occur because the two C-Cl bond moments cancel and the molecule is non-polar.
The two isomers of butenedioic acid have such large differences in properties and reactivities that they were actually given completely different names. The cis isomer is called maleic acid and the trans isomer fumaric acid. Polarity is key in determining relative boiling point as it causes increased intermolecular forces, thereby raising the boiling point. In the same manner, symmetry is key in determining relative melting point as it allows for better packing in the solid state, even if it does not alter the polarity of the molecule. One example of this is the relationship between oleic acid and elaidic acid; oleic acid, the cis isomer, has a melting point of 13.4 degrees Celsius, making it a liquid at room temperature, while the trans isomer, elaidic acid, has the much higher melting point of 43 degrees Celsius, due to the straighter trans isomer being able to pack more tightly, and is solid at room temperature.
Thus, trans-alkenes, which are less polar and more symmetrical, have lower boiling points and higher melting points, and cis-alkenes, which are generally more polar and less symmetrical, have higher boiling points and lower melting points.
In the case of geometric isomers that are a consequence of double bonds, and, in particular, when both substituents are the same, some general trends usually hold. These trends can be attributed to the fact that the dipoles of the substituents in a cis isomer will add up to give an overall molecular dipole. In a trans isomer, the dipoles of the substituents will cancel out[citation needed] due to their being on opposite site of the molecule. Trans isomers also tend to have lower densities than their cis counterparts.[citation needed]
March[4] observes that trans alkenes tend to have higher melting points and lower solubility in inert solvents, as trans alkenes, in general, are more symmetrical than cis alkenes.
Vicinal coupling constants (3JHH), measured by NMR spectroscopy, are larger for trans– (range: 12–18 Hz; typical: 15 Hz) than for cis– (range: 0–12 Hz; typical: 8 Hz) isomers.[5]
Stability
Usually, trans isomers are more stable than cis isomers. This is due partly to their shape; the straighter shape of trans isomers leads to hydrogen intermolecular forces that make them more stable[citation needed]. According to Jerry March, trans isomers also have a lower heat of combustion, indicating higher thermochemical stability. In the Benson heat of formation group additivity dataset, cis isomers suffer a 1.10 kcal/mol stability penalty. Exceptions to this rule exist, such as 1,2-difluoroethylene, 1,2-difluorodiazene (FN=NF), and several other halogen- and oxygen-substituted ethylenes. In these cases, the cis isomer is more stable than the trans isomer.[6] This phenomenon is called the cis effect.[7]
E/Z notation
Main article: E-Z notationThe cis/trans system for naming isomers is not effective when there are more than two different substituents on a double bond. The E/Z notation should then be used. Z (from the German zusammen) means "together" and corresponds to the term cis; E (from the German entgegen) means "opposite" and corresponds to trans.
Whether a molecular configuration is designated E or Z is determined by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules; higher atomic numbers are given higher priority. For each of the two atoms in the double bond, it is necessary to determine the priority of each substituent. If both the higher-priority substituents are on the same side, the arrangement is Z; if on opposite sides, the arrangement is E.
Inorganic coordination complexes
In inorganic coordination complexes with octahedral or square planar geometries, there are also cis isomers in which similar ligands are closer together and trans isomers in which they are further apart.
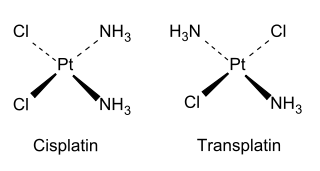
For example, there are two isomers of square planar Pt(NH3)2Cl2, as explained by Alfred Werner in 1893. The cis isomer, whose full name is cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II), was shown in 1969 by Barnett Rosenberg to have antitumor activity, and is now a chemotherapy drug known by the short name cisplatin. In contrast, the trans isomer (transplatin) has no useful anticancer activity. Each isomer can be synthesized using the trans effect to control which isomer is produced.
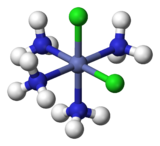
For octahedral complexes of formula MX4Y2, two isomers also exist. (Here M is a metal atom, and X and Y are two different types of ligands.) In the cis isomer, the two Y ligands are adjacent to each other at 90°, as is true for the two chlorine atoms shown in green in cis-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+, at left. In the trans isomer shown at right, the two Cl atoms are on opposite sides of the central Co atom.
A related type of isomerism in octahedral MX3Y3 complexes is facial-meridional (or fac/mer) isomerism, in which different numbers of ligands are cis or trans to each other.
See also
- E-Z notation
- Isomer
- Structural isomerism
- Chirality (chemistry)
- Trans fat
References
- ^ "IUPAC Gold Book - geometric isomerism". Goldbook.iupac.org. 2009-09-07. http://goldbook.iupac.org/G02620.html. Retrieved 2010-06-22.
- ^ "Chemicalland values". Chemicalland21.com. http://www.chemicalland21.com/info/Alkene%20Compound%20Boiling%20Points.htm. Retrieved 2010-06-22.
- ^ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 60th Edition (1979-80), p.C-298
- ^ Advanced organic Chemistry, Reactions, mechanisms and structure 3ed. page 111 Jerry March ISBN 0-471-85472-7
- ^ "Spectroscopic Methods in Organic Chemistry," Dudley H. Williams and Ian Fleming, 4th ed. revised, McGraw-Hill Book Company (UK) Limited, 1989.Table 3.27
- ^ The stereochemical consequences of electron delocalization in extended .pi. systems. An interpretation of the cis effect exhibited by 1,2-disubstituted ethylenes and related phenomena Richard C. Bingham J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1976; 98(2); 535-540 Abstract
- ^ Craig, N. C.; Chen, A.; Suh, K. H.; Klee, S.; Mellau, G. C.; Winnewisser, B. P.; Winnewisser, M. (1997). "Contribution to the Study of the Gauche Effect. The Complete Structure of theAntiRotamer of 1,2-Difluoroethane". Journal of the American Chemical Society 119: 4789. doi:10.1021/ja963819e.
External links
Categories:- Stereochemistry
- Isomerism
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.