- Cinereous Vulture
-
- Aegypius redirects here. For the hero, see Aegypius (mythology)
Cinereous Vulture 
Conservation status Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: Falconiformes (or Accipitriformes, q.v.) Family: Accipitridae Subfamily: Aegypiinae Genus: Aegypius
Savigny, 1809Species: A. monachus Binomial name Aegypius monachus
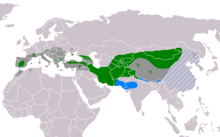
(Linnaeus, 1766)- Green: Current resident breeding range.
- Green ?: May still breed.
- Green R: Re-introduction in progress.
- Blue: Winter range; rare where hatched blue.
- Dark grey: Former breeding range.
- Dark grey ?: Uncertain former breeding range.
The Cinereous Vulture (Aegypius monachus) is also known as the Black Vulture, Monk Vulture, or Eurasian Black Vulture. It is a member of the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors such as kites, buzzards and harriers.
This bird is an Old World vulture, and is only distantly related to the New World vultures, which are in a separate family, Cathartidae, of the same order. It is therefore not directly related to the American Black Vulture despite the similar name and coloration.
It breeds across southern Europe and Asia from Portugal to Korea, but is endangered throughout its European range. It is resident except in those parts of its range where hard winters cause limited movement.[2][page needed][3][page needed]
Contents
Description and natural history
The Cinereous Vulture is believed to be the largest true bird of prey in the world. The Himalayan Griffon Vulture is slightly longer overall but is believed to be marginally surpassed in weight and wingspan by the Cinereous.[4] The condors, slightly larger, are now generally considered unrelated to the true raptors. This huge bird measures 98–120 cm (39–47 in) long with a 2.5–3.1 m (8.2–10 ft) wingspan and a weight of 7–14 kg (15–31 lb), and is thus one of the world's heaviest flying birds.[4] It breeds in high mountains and large forests, nesting in trees or occasionally on cliff ledges. The birds use sticks and twigs as building materials, and males and females cooperate in rearing young.[5]
It has all dark blackish-brown plumage, and even at a distance can be distinguished from the Griffon Vulture by its evenly broad "barn door" wings. It has the typical vulture unfeathered bald head (actually covered in fine down), and dark markings around the eye give it a menacing skull-like appearance. The beak is brown, with a blue-grey cere, and the legs and feet are grey.[2][page needed]
It is on average larger than mostly sympatric Griffon Vulture. Among the vultures in its range, the Eurasian Black Vulture is best equipped to tear open tough carcass skins, using its powerful bill. The cinereous vulture feeds on carrion ranging from large mammals to fish and reptiles.[5] It is dominant over other vultures at carcasses.[2][page needed]
It can fly at a very high altitude. It has a specialised haemoglobin alphaD subunit of high oxygen affinity which makes it possible to take up oxygen efficiently despite the low partial pressure in the upper troposphere.[6]
Status and conservation
The Cinereous Vulture has declined over most of its range in the last 200 years due to poisoning by eating poisoned bait put out to kill dogs and other predators, and to higher hygiene standards reducing the amount of available carrion; it is currently listed as near threatened. The decline has been the greatest in the western half of the range, with extinction in many European countries (France, Italy, Austria, Poland, Slovakia, Romania) and northwest Africa (Morocco, Algeria). More recently, protection and deliberate feeding schemes have allowed some local recoveries in numbers, particularly in Spain, where numbers increased to about 1,000 pairs by 1992 after an earlier decline to 200 pairs in 1970. This colony have now spread its breeding grounds to Portugal ref 7. Elsewhere in Europe, very small but increasing numbers breed in Bulgaria and Greece, and a re-introduction scheme is under way in France. Trends in the small populations in Ukraine (Crimea) and European Russia, and in Asian populations, are not well recorded. In the former USSR, it is still threatened by illegal capture for zoos, and in Tibet by rodenticides.[2][page needed][3][page needed]
Etymology
The genus name Aegypius is a Greek word (αιγυπιος) for 'vulture', or a bird not unlike one; Aelian describes the aegypius as "halfway between a vulture (gyps) and an eagle". Some authorities think this a good description of a lammergeier; others do not. Aegypius is the eponym of the species, whatever it was.[7] The English name 'Black Vulture' refers to the plumage colour, while 'Monk Vulture', a direct translation of its German name Mönchsgeier, refers to the bald head and ruff of neck feathers like a monk's cowl. 'Cinereous Vulture' (Latin cineraceus, ash-coloured; pale, whitish grey), was a deliberate attempt to rename it with a new name distinct from the American Black Vulture.[8][page needed]
Gallery
Footnotes
- References
- BirdLife International (2008). "Aegypius monachus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2010.4. International Union for Conservation of Nature. http://www.iucnredlist.org/apps/redlist/details/144355. Retrieved 2011-05-31.
- Cited texts
- del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Sargatal, J., eds (1994). Handbook of the Birds of the World. 2. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. ISBN 84-87334-15-6.
- Ferguson-Lees, James; Christie, David A. (2001). Raptors of the World. Illustrated by Kim Franklin, David Mead, and Philip Burton. Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-618-12762-7. http://books.google.com/books?id=hlIztc05HTQC&lpg=PP1&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false. Retrieved 2011-05-26.
- Celoria, Francis, ed (1992). The Metamorphoses of Antoninus Liberalis : a translation with a commentary. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-06896-3.
- Sibley, Dr. Charles G.; Monroe, Burt L., Jr. (1991). Distribution and Taxonomy of Birds of the World. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-04969-5.
- Snow, David W.; Perrins, Christopher M. (1998). The Birds of the Western Palearctic (Consise ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-854099-X.
- Weber, Roy E.; Hiebl, Inge; Braunitzer, Gerhard (1988). "High Altitude and Hemoglobin Function in the Vultures Gyps rueppellii and Aegypius monachus". Biological Chemistry Hoppe-Seyler 369 (4): 233–240. doi:10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.1.233. PMID 3401328.
External links
Old World vultures (subfamily: Aegypiinae) Genus Aegypius Cinereous VultureGypaetus Gypohierax Gyps Griffon Vulture • White-rumped Vulture • Rüppell's Vulture • Indian Vulture • Slender-billed Vulture • Himalayan Griffon Vulture • White-backed Vulture • Cape VultureNecrosyrtes Neophron Sarcogyps Torgos Trigonoceps Categories:- IUCN Red List near threatened species
- Old World vultures
- Aegypiinae
- Genera of birds
- Birds of Europe
- Birds of Turkey
- Birds of Iran
- Birds of Asia
- Birds of Pakistan
- Birds of Japan
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.