- Klang (music)
-
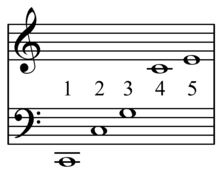
In music, Klang (German: sound) is the, "chord of nature", so called because it is built from the first five partials of the overtone series[1] (which if built on C produces: CC'G'C"E", a C major chord). The Klang is the abstracted referential sonority, the tonic triad, in Riemannian theory, the dualistic music theory of Hugo Riemann.[2]
According to Heinrich Schenker, "The musical sonority as it exists in Nature is a triad" [Der Klang in der Natur ist ein Dreiklang][3] ("drei" = three).
See also
- Linear progression
Sources
- ^ Ayotte, Benjamin (2003). Heinrich Schenker: A Research and Information Guide, p. 182. ISBN 0415940710.
- ^ Riemann, Heinrich (1893). Vereinfachte Harmonielehre, oder die Lehre von den Tonalen Funktionen der Akkorde. Augener's Edition. London: Augener & Co.; New York: G. Schirmer. Cited in Lerdahl, Fred (1989) "Atonal Prolongational Structure", p. 74, Music and the Cognitive Sciences. McAdams, Stephen and Irene Deliege, eds. ISBN 3718649535.
- ^ Schenker, Heinrich (1994). The Masterwork in Music: A Yearbook, Volume 1, 1925, Cambridge Studies in Music Theory and Analysis 4, edited by William Drabkin, translated by Ian Bent (Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press), p. 3 n2. ISBN 0521455413.
Chords By type Major · Minor · Dominant · Dominant seventh flat five · Diminished · Half-diminished · Diminished major · Minor-major · Augmented major · Augmented minor · Nondominant · Harmonic seventh chordAdded
/ omittedBy function SecondaryWith names Elektra chord · Farben chord · Hendrix chord · Mu chord · Mystic chord · Northern lights chord · Petrushka chord · Power chord · Psalms chord · So What chord · Spider chord · Tristan chord · Viennese trichord · Dream chordOther Common chord (music) · Mixed interval · Open chord · Polychord · Primary triad · Quartal and quintal · Slash chord · Subsidiary chord · Synthetic chord · Tone clusterCategories:- Chords
- Schenkerian analysis
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.