- Chorismic acid
-
Chorismic acid 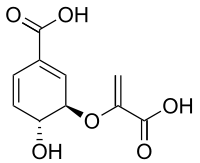 (3R,4R)-3-[(1-carboxyvinyl)oxy]-4-hydroxycyclohexa-1,5-diene-1-carboxylic acid
(3R,4R)-3-[(1-carboxyvinyl)oxy]-4-hydroxycyclohexa-1,5-diene-1-carboxylic acidIdentifiers CAS number 617-12-9 
ChemSpider 11542 
ChEBI CHEBI:17333 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)C1=C/[C@@H](O/C(C(=O)O)=C)[C@H](O)/C=C1
Properties Molecular formula C10H10O6 Molar mass 226.18 g mol−1 Melting point 140 °C, 413 K, 284 °F
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Chorismic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form chorismate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms. It is a precursor for:
- The aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine
- Indole, indole derivatives and tryptophan
- 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) used for enterobactin biosynthesis
- The plant hormone salicylic acid[1]
- Many alkaloids and other aromatic metabolites.
The name chorismic acid derives from a classical greek word, χωρίζω meaning "to separate",[2] because the compound plays a role as a branch-point in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis.[3]
Biosynthesis
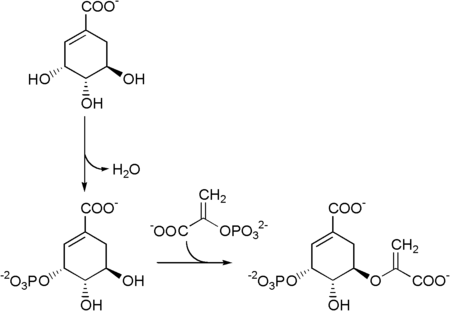
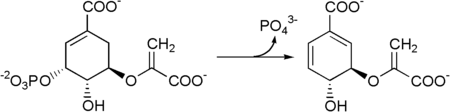
Shikimate → shikimate-3-phosphate → 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate → chorismate.
External links
References
- ^ Wildermuth MC, Dewdney J, Wu G, Ausubel FM (2001). "Isochorismate synthase is required to synthesize salicylic acid for plant defence". Nature 414 (6863): 562–5. doi:10.1038/35107108. PMID 11734859. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v414/n6863/full/414562a.html.
- ^ Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, Henry Stuart Jones and Roderick McKenzie. ISBN 0-19-864226-1.
- ^ Gibson, F. (1999). "The elusive branch-point compound of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis". Trends in Biochemical Sciences 24 (1): 36–38. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01330-9. PMID 10087921.
Categories:- Dicarboxylic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.