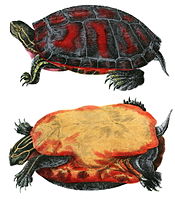
- Chicken turtle
-
Chicken turtle 
Conservation status Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Testudines Family: Emydidae Subfamily: Deirochelyinae Genus: Deirochelys Species: D. reticularia Binomial name Deirochelys reticularia
(Latreille, 1801)The Chicken turtle (Deirochelys reticularia), is a cold-blooded uncommon freshwater turtle found in the southeast of the United States. It is in the monotypic genus Deirochelys.
The name "Chicken" turtle refers to the taste of their meat, which used to be popular in southern markets.
Contents
Description
They are similar in appearance to the eastern painted turtle (Chrysemys picta picta), but have an unusually long, striped neck that is close to the length of the shell, with a yellow stripe on both the forelegs and rear legs. It has a distinguishable net-like pattern on its carapace. The carapace is pear-shaped, and is an olive to dark brown. Females are usually larger than the males, and males have a longer, thicker tail. Males also have longer front claws. At birth, Chicken turtles are one inch in diameter, and adults reach from 10.2-25.4 cm. They are medium in size compared to other turtles.
Behavior
Chicken turtles are regularly encountered on land, migrating between aquatic habitats or seeking areas to burrow into the soil and escape dry conditions. Males generally travel around farther than females. They are social, spending much of their time basking on logs and rocks and swim in small groups. Chicken turtles hibernate in the soft mud, but only in the northern part of their range, and vegetation of bodies of water. They are known to be timid and if caught they generally will bite very easily.
Lifespan
Wild chicken turtles have been recaptured up to 15 years old after their first capture. Some reached the maximum ages of 20 to 24 years.
Range
Chicken turtles, made up of three subspecies, are found in suitable habitat throughout the southeastern United States. Deirochelys reticularia is found in the coastal areas of Virginia to Texas and northward Oklahoma and Arkansas. The Florida subspecies, D. r. chrysea, is limited to peninsular Florida. The Eastern, D. r. reticularia, and Western, D. r. miaria, subspecies of chicken turtles are separated by Mississippi River. It is a basking turtle, and is often found wandering far from water.
Habitat
Chicken turtles are semi-aquatic turtles, found both in water and on land. They prefer quiet still bodies of water: Shallow ponds and lakes, ditches, marshes, cypress swamps, and Carolina Bays. They prefer water with dense vegetation and soft substrate. Chicken turtles are tolerant of ephemeral aquatic habitats and readily travel onto land to burrow into the soil and escape dry conditions. They've been found at depths of a few centimeters to more than 2 m.
Reproduction
Males reproduce with female chicken turtles by vibrating the fore-claws against the female's face. Once the female is receptive, copulation occurs. Chicken turtles are different from most other North American turtles because they nest in either fall or winter. In South Carolina, there are two-egg laying seasons; from winter to early spring (February to may) and fall to early winter (August to November). Females excavate cylindrical nest on land in a variety of soil types, from sandy to heavy soils. Females lay 2 to 19 clutches of eggs. Chicken turtle embryos go through a period of dispause in the late gastrula stage. They must experience a period of cool temperatures before development proceeds. Eggs hatch in 152 days at 29 Celsius, some eggs may overwinter in the nest before hatching. Incubation temperature influences the sex of the embryos, with a 25 degrees Celsius incubation temperature resulting in all males. Warmer temperatures result in an increase in female embryos, with only 11 percent becoming males at incubation temperatures of 30 degrees Celsius. +
Diet
Chicken Turtles are omnivorous, eating crayfish, fish, fruits, insects, invertebrates, frogs, tadpoles and plants. During the first year of their life they are almost completely carnivorous. As though they are mostly carnivorous at birth they will still eat plants. Chicken turtles use their well-developed hyoid apparatus to create suction that pulls food items into their throat, its very unique.
Conservation status
Chicken turtle populations are currently considered stable throughout their range, although they do face potential threats. The eastern chicken turtle species is listed as state threatened in Virginia.[1] Habitat destruction reduces suitable habitat for foraging, migration, and hibernation. Chicken turtles are sometimes killed on roads as they migrate between habitats. Hunting for food impacts populations of chicken turtles as well.
Subspecies
There are three distinct sub-species of Chicken turtle:
- Eastern chicken turtle (Deirochelys reticularia reticularia)
- Florida chicken turtle (Deirochelys reticularia chrysea)
- Western chicken turtle (Deirochelys reticularia miaria)
References
Order Testudines (turtles) Kingdom: Animalia · Phylum: Chordata · Class: Reptilia · Subclass: Anapsida · Order: Testudines Suborder SuperfamilySubfamily
Cryptodira Chelydra · MacrochelysCaretta · Chelonia · Eretmochelys · Lepidochelys · NatatorDermochelysDermatemydidaeDermatemysStaurotypinaeClaudius · StaurotypusBatagur · Cuora · Cyclemys · Geoclemys · Geoemyda · Hardella · Heosemys · Leucocephalon · Malayemys · Mauremys · Melanochelys · Morenia · Notochelys · Orlitia · Pangshura · Rhinoclemmys · Sacalia · Siebenrockiella · VijayachelysAldabrachelys · Astrochelys · Chelonoidis · Chersina · Cylindraspis · Geochelone · Gopherus · Homopus · Indotestudo · Kinixys · Malacochersus · Manouria · Psammobates · Pyxis · Stigmochelys · TestudoTrionychiaCarettochelyidaeCarettochelysTrionychinaePleurodira ChelidinaeChelodininaeHydromedusinaePelomedusa · PelusiosPhylogenetic arrangement based on turtles of the world 2010 update: annotated checklist. Extinct turtles not included.
See also List of Testudines families
 Portal ·
Portal ·  WikiProjectCategories:
WikiProjectCategories:- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Deirochelys
- Monotypic reptile genera
- Animals described in 1801
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.