- Königsberg class cruiser (1927)
-

KarlsruheClass overview Name: K Operators: Reichsmarine, Kriegsmarine General characteristics Type: light cruiser Displacement: 6,650 tons full load Length: 174 m Beam: 15.3 m Draught: 6.28 m Propulsion: 2 steam turbines, 6 boilers, + 2 MAN diesel, 2 shafts, 69,800 shp Speed: 32 knots Range: 7,300 nm at 17 knots Complement: 610 Armament: 3 × 3 15 cm SK C/25 guns
4 × 3 533 mm torpedoes
3 × 2 8.8 cm Flak 18 anti-aircraft guns
4 × 2 3.7 cm Flak 18 anti-aircraft guns
8 20 mm anti-aircraft gunsAircraft carried: 2 seaplanes (Arado Ar 196 or Heinkel He 60) Notes: Ships in class include: Königsberg, Karlsruhe, Köln The Königsberg class was a class of light cruisers of the German Reichsmarine and Kriegsmarine, consisting of three ships named after German cities: Königsberg, Karlsruhe, Köln. It's also referred to as K class, as all three ships' names began with that letter.
Contents
History
The class was designed in the 1920s, adhering to the 6,000 ton limit for cruisers imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles. To stay within this limit, 85% of the ships' joints were welded instead of bolted. This led to problems, as the welding did not withstand the stress of long sea journeys as well as had been hoped. One unit had to interrupt a cruise to undergo significant repairs at San Diego. In addition, the ships suffered major stability problems which, along with the structural ones, led to their being confined to the home waters of the North Sea and Baltic during World War II and precluded their use as commerce raiders.
Armament
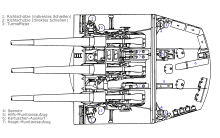
The main battery was grouped in three triple-turrets, one forward and two aft. This unconventional placement was because the K class were designed as scouting cruisers with the intention that they would "hit and run." This allowed two thirds of their firepower to be directed astern at pursuing vessels. In order to increase firepower ahead, the aft turrets were not placed on the centerline of the ship. The aftermost turret was positioned on the starboard side, the middle turret was positioned on the port side of the ship. This allowed the middle turret to train further forward at targets to port, while the aftermost turret could train further forward at targets to starboard. This shrank the area in which only one turret would be available. The off-centre arrangement also assisted the engine-room layout.
Propulsion
The ships had both steam turbine and diesel engines, the former to be used for high speed, the latter for fuel-economical cruising. The two power plants could not be used simultaneously.
Ships
Königsberg and Karlsruhe were lost during the invasion of Norway in World War II- Karlsruhe after being torpedoed at Kristiansand and Königsberg, bombed at Bergen. Köln was used as a training ship for most of the war, before being bombed and sunk in the shallow water of Wilhelmshaven harbor in March 1945. She remained in action, however, and shelled advancing Allied forces.
Followup
The "K class" ships were followed by a modified two-ship class composed of the Leipzig and the Nürnberg which differed from them principally in terms of having only one funnel instead of two, and having the two aft turrets on the centerline, as well as somewhat different machinery (but retaining the dual propulsion concept). These ships suffered from the same defects of structural weakness and instability as the "K class", and were likewise confined to the Baltic and North Sea during World War II for these reasons.
See also
 Media related to Königsberg class light cruiser at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Königsberg class light cruiser at Wikimedia CommonsKönigsberg · Karlsruhe · Köln
List of Kriegsmarine ships Aircraft carriers Capital Ships - Scharnhorst
- Bismarck
- HX
- OX
Pre-dreadnought battleships Heavy cruisers Light cruisers Destroyers - Type 1934
- Type 1934A
- Type 1936
- Type 1936A / 1936A (Mob) / Narvik
- Type 1936B
Torpedo boats U-boats (submarines) Other - S-boats
- R Boats
- M class minesweepers
- Fleet Escorts
- Auxiliary cruisers
- Vorpostenboot
- Marinefährprahm
- Siebel ferry
- S — Single ship of class
- X — Cancelled
- V — Conversions
Categories:- Cruiser classes
- German K class cruisers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.