- German torpedoboats of World War II
-
The German torpedoboats of World War II were armed principally, if not exclusively, with torpedoes and varied widely in size. They should not be confused with the larger destroyers, nor with the smaller, torpedo-armed Schnellboote (known to the Allies as E-boats).
Contents
Classes
Raubvogel (1923) and Raubtier (1924)

Raubtier-class torpedo boatsClass overview Operators:  Kriegsmarine
KriegsmarineIn commission: 1926 - 1944 Completed: 12 General characteristics Type: Raubvogel (1923) & Raubtier (1924) Torpedo boat Displacement: 1923: 923 tons (standard)
1,290 tons (full load)
1924: 932 tons (standard)
1,298 tons (full load)Length: 1923: 87.7 m
1924: 92.6 mBeam: 1923: 8.25 m
1924: 8.65 mDraught: 1923: 3.65 m
1924: 3.52 mPropulsion: 1923:
2 shaft geared steam turbines (all Blohm & Voß, except Albatros - Schichau), 3 boilers, 24,000 shp
1924:
2 shaft geared steam turbines (from Brown, Boveri & Cie, Vulcan and Schichau), 3 boilers, 25,500 shpSpeed: 1923: 33.6 kn (62.2 km/h)
1924: 35.2 knots (65.2 km/h)Range: 1923: 1,700 nmi (3,100 km) at 17 knots (31 km/h)
1924: 2,000 nmi (4,000 km) at 17 knots (31 km/h)Complement: 120 - 129 Armament: 3 × 10.5 cm L/45 (3x1)
2 × 2 cm Flak L/65 (1×1) (4 or 7 from 1940)
6 × 500 (533 from 1931) mm torpedo tubes (2×3)
30 minesThe six Raubvogel (German:"Bird of prey") class torpedo boats were developed from earlier designs shortly after World War I and came into service in 1926 and 1927. They were the first to use electrical welding for hull construction to reduce displacement and they also introduced geared turbines. During the Second World War these ships were referred to as the Möwe class by the Royal Navy.
Despite the innovations, and unlike contemporary German destroyers, the Raubvogels were successful sea-boats, although limited to coastal waters, and most remained in service until 1944, by which time all had been lost. Well before this time, however, the deficiencies of their concentration on torpedoes became apparent: their anti-aircraft weaponry was wholly deficient, and had to be upgraded, and their guns were also minimal.
The immediately following six ships of Raubtier ("predator") class had been intended to mount 12.7 cm guns but, instead, received updated 10.5 cm weapons. Speed and range were improved. Otherwise, they displayed the same good and bad points as the Raubvogels and experienced similar operational conditions and upgrades.
They entered service in 1927 and 1928 and all but one had been lost before mid 1942.
During the St. Nazaire Raid ("Operation Chariot"), the destroyer HMS Campbeltown was altered by the Royal Navy to look like a Raubvogel class torpedo boat.
All twelve vessels were built at Reichsmarinewerft Wilhelmshaven
Type 23 (Raubvogel)
Name Launched Completed Fate Möwe (Seagull) 1926 1926 Sunk by bombing in Le Havre 14 June 1944 Falke (Falcon) 1926 1926 Sunk by bombing in Le Havre 14 June 1944 Greif (Griffon) 1926 1927 Torpedoed by aircraft 24 May 1944 Kondor (Condor) 1926 1927 Mined 23 May 1944, decommissioned 1 August 1944 Albatros 1926 1928 Wrecked by accidental grounding on 10 April 1940 during the invasion of Norway Seeadler (Sea Eagle) 1926 1927 Sunk by British MTBs 14 May 1942 while escorting the auxiliary cruiser Stier Type 24 (Raubtier)
Name Launched Completed Fate Wolf 1927 1928 Mined 8 January 1941 near Dunkirk Iltis (Polecat) 1927 1928 Sunk by British MTBs 14 May 1942 while escorting the auxiliary cruiser Stier Jaguar 1928 1929 Bombed 14 June 1944 Leopard 1928 1929 Wrecked in collision 30 April 1940 Luchs (Lynx) 1928 1929 Torpedoed by HM Submarine Thames 26 July 1940 Max Schultz 25 September 1939 Torpedoboot 1935 and 1937
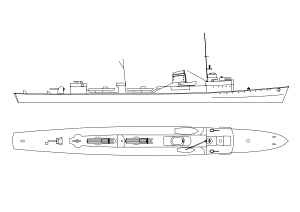
Torpedoboot 1935Class overview Operators:  Kriegsmarine
KriegsmarineCompleted: 21 General characteristics Type: 1935 and 1937 Torpedo boat Displacement: 1935: 844 tons (standard), 1,088 tons (full load)
1937: 1,098 tons (full load)Length: 1935: 84.30 m
1937: 85.20 mBeam: 1935: 8.62 m
1937: 8.87 mDraught: 1935: 2.94 m
1937: 3.14 mPropulsion: 1935:
2 shaft geared Wagner turbines, 31,000 shp
1937:
2 shaft geared Wagner turbines, 34,110 shpSpeed: 1935: 35 kn (65 km/h)
1937: 36.6 knots (67.8 km/h)Range: 1935: 1,070 nmi (1,980 km) at 19 knots (35 km/h)
1937: 1,400 nmi (2,590 km) at 19 knots (35 km/h)Complement: 1935: 119
1937: 119-155Armament: (as for T1):
1 × 10.5 cm L/45 (3×1)
512 × 2 cm MG L/65
6 × 533 mm torpedo tubes (2×3)
30 minesMain article: Torpedo boat type 35The 1935 design was unsuccessful and the 1937 was little better. These ships were designed as a larger more seaworthy torpedo vessel rather than a more balanced mini destroyer.
The requirements for the 1935 class included a maximum "declared" displacement of around 600 tons in order to come within a clause in the Washington Naval Treaty, and higher speeds than the older 1923 and 1924 classes. In reality these ships came in overweight at around 900 tons standard displacement. To achieve this, high pressure turbines were used but these were unreliable and difficult to repair and maintain in the restricted space of the hull. The low displacement made them unseaworthy which was only partially resolved by 1940 and this reduced the effectiveness of the class as minelayers. There was an even greater concentration on torpedoes, with a single 10.5 centimetre gun and minimal anti-aircraft protection.
The 1937s incorporated some modifications, including lower pressure turbines, but with little real improvement. They displayed the same limitations as their predecessors and the reasons for persisting with such a poor design are unclear.
Twelve 1935s and nine 1937s were built at Schichau Elbing and all except two survived until the late war or post-war. This survivability reflects their unsuitability as warships and they were either withdrawn into reserve or used as training ships.
Type 1935
Name Launched Completed Fate T1 19 February 1938 2 December 1939 sunk 9 April 1945 T2 7 April 1938 9 December 1939 bombed and sunk in Bremen 29 July 1944, salvaged and scrapped 1946 T3 23 June 1938 3 April 1940 mined and sunk 14 March 1945 near Danzig T4 15 April 1938 27 May 1940 transferred to Denmark and scrapped Feb 1952 without seeing further service T5 22 Nov 1937 23 Jan 1940 mined and sunk 14 March 1945 near Danzig T6 16 December 1937 30 April 1940 mined and sunk 7 Nov 1940 off the East coast of England T7 18 June 1938 20 Dec 1939 scrapped between 1947-1949 T8 10 Aug 1938 8 Oct 1939 scuttled 3 May 1945 near Kiel T9 3 November 1938 4 July 1940 scuttled 3 May 1945 near Kiel T10 6 August 1940 6 August 1940 destroyed 18 December 1944, by bombing in dry dock Gotenhafen (note 1 date is likely wrong) T11 1 March 1939 7 May 1940 transferred to the French Navy as war reparation, renamed Bir Hakeim, scrapped October 1951 T12 12 Apr 1939 3 July 1940 transferred to the USSR as war reparation, served as the Podvischny until the 1960s. sunk in deep water 1991 Type 1937
Name Launched Completed Fate T13 15 June 1939 31 May 1941 sunk 10 April 1945 by RAF bombing T14 20 July 1939 14 June 1941 transferred to France as the Dompaire scrapped 1951 T15 16 September 1939 26 June 1941 sunk 13 December 1943 in Kiel by bombing T16 23 November 1938 24 July 1941 decommissioned 13 April 1945 T17 13 March 1940 28 August 1941 transferred to the USSR as the Poryvistyy, scrapped after 1960 T18 1 June 1940 22 November 1941 sunk 17 September 1944, by Soviet aircraft rockets near the Åland Islands T19 20 July 1940 18 December 1941 transferred to USA, then to Denmark and scrapped February 1952 T20 12 September 1940 5 June 1942 transferred to France as the Baccarat, scrapped 1951 T21 21 November 1940 11 July 1942 scuttled by the US Navy in the Skagerak 10 June 1946 Flottentorpedoboot 1939 (Elbing class)
Main article: Elbing class torpedo boatThe Elbings "Fleet torpedo boats" were a radical design departure from their predecessors, larger and with a more balanced weapons mix. They were comparable with British destroyers of the period. The ships were unnamed, but numbered T22 to T36.
Flottentorpedoboot 1940
After the invasion of the Netherlands in 1940, the Dutch shipyards were almost undamaged. Therefore the German Navy contacted the Dutch shipbuilders to build some smaller vessels for the Kriegsmarine. The Flottentorpedoboot 1940 was more a destroyer than a torpedo boat and based on Dutch designs. Twenty four were ordered in 1940-1941, but only three were launched and in 1944 the incomplete ships were transferred to the Baltic Sea to be completed where they were either destroyed or captured by the Allies after the war.
Flottentorpedoboot 1941
The Flottentorpedoboot 1941 was an improvement of the Flottentorpedoboot 1939 class with more powerful engines and additional anti aircraft artillery was added. 15 of those boats were ordered in 1942-1944, but none of them was completed. At the end of the war, the few ships already launched were in different stages of construction, one of them, the T37 was very close to completion. Those ships which could be moved to the west were towed away from Elbing, but their construction was not continued.
Flottentorpedoboot 1944
The Flottentorpedoboot 1944 were planned after a radical change in torpedo boat tactics, they were designed to be able to operate with other fleet units in the North Atlantic. This class had the main focus of armament changed to anti aircraft artillery. Therefore the main armament were four 10,5 cm flak guns, plus an increased number of smaller antiaircraft guns, but those ships kept the torpedo and mine laying abilities of their predecessors. To enable those ships for ocean operations, their range had to be dramatically enlarged. As a technical innovation, all auxiliary machinery were electrical powered instead of the usual steam powered ones. Nine (T52-T60) were ordered but were cancelled shortly thereafter.
Torpedoboot Ausland
The Torpedoboot Ausland ("foreign torpedo boats") were small destroyers or large torpedo boats captured by Nazi Germany and incorporated into the Kriegsmarine. They were assigned a number beginning with TA. They numbered from TA 1 to TA 47, most never entered service for one reason or another.
See also
- Schnellboot German motor torpedo boats.
- German World War II destroyers
- Motor Torpedo Boat British MTBs
- Fairmile D motor torpedo boat British response to the E-boat
- Steam Gun Boat British E-boat hunter
- Torpedo boat general history
References
- Gröner, Erich (1990). German Warships: 1815–1945. Volume 1: Major Surface Warships. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-790-9.
- Rohwer, Jürgen (2005). Chronology of the War at Sea 1939-1945: The Naval History of World War Two (Third Revised ed.). Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-59114-119-2.
- Whitley, M. J. (1991). German Destroyers of World War Two. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-55750-302-8.
External links
- - page on Type 23 from German Navy.de
- - page on Type 24 from German Navy.de
- Classe: Raubtier (French)
Aircraft carriers Capital Ships - Scharnhorst
- Bismarck
- HX
- OX
Pre-dreadnought battleships Heavy cruisers Light cruisers Destroyers - Type 1934
- Type 1934A
- Type 1936
- Type 1936A / 1936A (Mob) / Narvik
- Type 1936B
Torpedo boats - Type: 1923 (Raubvogel)
- 1924 (Raubtier)
- 1935
- 1937
- Elbing
- Torpedoboot Ausland
U-boats (submarines) Other - S-boats
- R Boats
- M class minesweepers
- Fleet Escorts
- Auxiliary cruisers
- Vorpostenboot
- Marinefährprahm
- Siebel ferry
- S — Single ship of class
- X — Cancelled
- V — Conversions
Categories:- World War II naval ships of Germany
- Torpedo boats
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
