- North Pacific Fur Seal Convention of 1911
-
 The treaty was created to regulate hunting of the Northern fur seal, pictured here.
The treaty was created to regulate hunting of the Northern fur seal, pictured here.
The North Pacific Fur Seal Convention of 1911, formally known as the Convention between the United States and Other Powers Providing for the Preservation and Protection of Fur Seals, was an international treaty signed on July 7, 1911 designed to manage the commercial harvest of fur bearing mammals (such as Northern fur seals and sea otters) in the Pribilof Islands of the Bering Sea. The treaty, signed by the United States, Great Britain, Japan, and Russia, outlawed open-water seal hunting and acknowledged the United States' jurisdiction in managing the on-shore hunting of seals for commercial purposes. It was the first international treaty to address wildlife preservation issues.[1]
Contents
Terms of the treaty
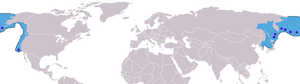 The fur seal's range. All pelagic sealing north of the 30th parallel in the Pacific Ocean was banned by the treaty.
The fur seal's range. All pelagic sealing north of the 30th parallel in the Pacific Ocean was banned by the treaty.
The two most significant terms of the treaty were the banning of pelagic seal hunting and the granting of jurisdiction to the United States in managing on-shore hunts. In exchange for granting jurisdiction to the United States, the other signatories to the treaties were guaranteed payments and/or minimum takes of seal furs while the treaty remained in effect, subject to certain conditions.[2]
The treaty also provided an exemption to aboriginal tribes which hunted seals using traditional methods and for non-commercial purposes including food and shelter. Aboriginal tribes specifically mentioned in the treaty include the Aleut and Aino (Ainu) peoples.[2]
Authorship and ratification
The treaty was co-authored by environmentalist Henry Wood Elliott and United States Secretary of State John Hay in 1905, although the treaty was not ratified for another six years. [1] The treaty was signed at Washington, D.C. on July 7, 1911, with ratifications by each signatory on the following dates:
- United States: Ratification advised by the Senate on July 24, 1911, and ratified by President William Howard Taft on November 24, 1911
- Great Britain: August 25, 1911
- Russia: October 22 / November 4, 1911
- Japan: November 6, 1911
Ratifications were then exchanged at Washington on December 12, 1911, and the treaty was proclaimed two days later on December 14. [2]
Enactment and legacy
Following ratification, the United States Congress enacted an immediate 5-year moratorium on hunting, to allow for recovery of the decimated herds. The treaty remained in effect until hostilities erupted among the signatories in World War II. However, the treaty set precedent for future national and international laws and treaties, including the Fur Seal Act of 1966 and the Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972.[1]
External links
- Full text of the treaty, as provided by the Edwin Ginn Library at The Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy, Tufts University
References
- ^ a b c "North Pacific Fur Seal Treaty of 1911". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. http://celebrating200years.noaa.gov/events/fursealtreaty/welcome.html#treaty.
- ^ a b c "Convention between the United States, Great Britain, Russia and Japan for the preservation and protection of fur seals". Edwin Ginn Library at The Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy, Tufts University. http://fletcher.tufts.edu/multi/sealtreaty.html.
Further reading
Oran R. Young, Gail Osherenko (1993) Polar politics: creating international environmental regimes Cornell studies in political economy Cornell University Press ISBN 0801480698, 9780801480690
C.H Townsend (1905) Notes on certain Pinnepeds with data respecting their present commercial importance Annual Report of the New York Zoological Society 15, 105-116
Categories:- Treaties of the United States
- Treaties concluded in 1911
- Treaties entered into force in 1911
- Treaties of the Russian Empire
- Treaties of the Empire of Japan
- 1911 in the environment
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
