- Coggabata
-
Coordinates: 54°55′37″N 3°08′53″W / 54.927°N 3.148°W
Concavata 
Site of Concavata at Drumburgh. The fortified farmhouse of Drumburgh Castle is built with Roman wall stones.
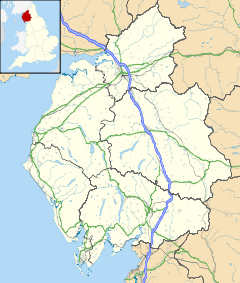
 Concavata shown within Cumbria
Concavata shown within CumbriaOS grid reference NY265598 List of places: UK • England • Cumbria Coggabata, or Congavata / Concavata, (with the modern name of Drumburgh) was a Roman fort on Hadrian's Wall, between Aballava (Burgh by Sands) to the east and Mais (Bowness on Solway) to the west. It was built on a hill commanding views over the flatter land to the east and west and to the shore of the Solway Firth to the north. Its purpose was to guard the southern end of two important Solway fords, the Stonewath and the Sandwath.
The Notitia Dignitatum gives the name of the fort as 'Congavata', but the Rudge Cup gives the name as 'Coggabata'.
Contents
Description
The fort was an oblong and built of stone, with the Wall running along its northern side, and measured 270 feet (82 m) north to south by 316 feet (96 m) east to west, occupying an area of just less than 2 acres (8,100 m2). The Wall at this point is nine feet seven inches wide, and is made of stone. It was constructed on the foundations of the levelled turf Wall. There were gates on each side, with the north gate giving access beyond the wall.
Two miles south of the fort a Roman road was uncovered linking the western end of the Stanegate to Kirkbride to the west.
There is a manor house, Drumburgh Castle, lying across the line of the north wall of the fort, built entirely of Roman stones.
Garrison
The Notitia Dignitatum gives the garrison as the Second Cohort of Lingones but only a detachment could be accommodated in such a small fort.
Excavations
The site was excavated in 1899, when the stone fort was revealed. A buttressed granary was found within the north-west angle of the fort.
Excavations in 1947 revealed that the stone fort was built within a slightly larger fort with levelled clay ramparts. It is presumed that the earthwork fort had been added to the turf Wall, and that the stone fort replaced it when the turf Wall was re-built in stone. This would date the stone fort at about 160 A.D.
No sign of a vicus has yet been detected near to the fort.
References
- J. Collingwood Bruce, Roman Wall (1863), Harold Hill & Son, ISBN 0-90046-332-5
- Frank Graham, The Roman Wall, Comprehensive History and Guide (1979), Frank Graham, ISBN 0-85983-140-X
External links
- Concavata at www.Roman-Britain.org
- iRomans website showing Coggabata objects in the Tullie House Museum collection
Wall Forts (East to West) Segedunum • Pons Aelius • Condercum • Vindobala • Onnum • Cilurnum • Procolita • Vercovicium • Aesica • Magnis • Banna • Camboglanna • Uxelodunum • Aballava • Coggabata • MaiaOutpost Forts Stanegate Forts Corstopitum • Newbrough • Vindolanda • Haltwhistle Burn • Magnis • Throp • Nether Denton • Castle Hill Boothby • Brampton Old Church • LuguvaliumSupply Forts Categories:- Forts of Hadrian's Wall
- Roman forts in England
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.