- Molossians
-
For the micronation of Molossia, see Republic of Molossia.
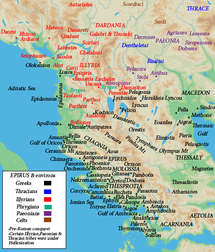
The Molossians (Greek: Μολοσσοί, Molossoi) were an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited the region of Epirus since the Mycenaean era.[1] On their northeast frontier they had the Chaonians and to their southern frontier the kingdom of the Thesprotians, to their north were the Illyrians. The Molossians were part of the League of Epirus until they sided against Rome in the Third Macedonian War (171 BC-168 BC). The result was disastrous with the vengeful Romans enslaving 150,000 of its inhabitants and annexing the region into the Roman Empire.
Contents
Mythology
According to Greek mythology, the Molossians were the descendants of Molossus, one of the three sons of Neoptolemus, son of Achilles and Deidamia. Following the sack of Troy, Neoptolemus and his armies settled in Epirus where they joined with the local population. Molossus inherited the kingdom of Epirus after the death of Helenus, son of Priam and Hecuba of Troy, who had married his erstwhile sister-in-law Andromache after Neoptolemus' death. Plutarch tells us that according to some historians their first king was Phaethon, one of those who came into Epirus with Pelasgus. Plutarch also says, that Deucalion and Pyrrha, having set up the worship of Zeus at Dodona, settled there among the Molossians.[2]
Ancient sources
Strabo tells us that the Molossians, along with the Chaonians and Thesprotians, were the most famous among the fourteen tribes of Epirus, who once ruled over the whole region. The Chaonians ruled Epirus at an earlier time and afterwards the Thesprotians and Molossians controlled the region. Plutarch[2] tells us that the Thesprotians, the Chaonians and the Molossians were the three principal clusters of Greek-speaking tribes that had emerged from Epirus and were the most powerful among all other tribes.
The Molossians were also renowned for their vicious hounds, which were used by shepherds to guard their flocks. This is where the canine breed Molossoid, native to Greece, got its name. Virgil tells us that in ancient Greece the heavier Molossian dogs were often used by the Greeks and Romans for hunting (canis venaticus) and to watch over the house and livestock (canis pastoralis). "Never, with them on guard," says Virgil, "need you fear for your stalls a midnight thief, or onslaught of wolves, or Iberian brigands at your back."
Strabo records that the Thesprotians, Molossians, and Macedonians referred to old men as πελιοί pelioi and old women as πελιαί peliai (<PIE *pel-, 'grey'). Cf. Ancient Greek πέλεια peleia, "pigeon", so-called because of its dusky grey color. Ancient Greek πελός pelos meant "grey".[3] Their senators were called Peligones, similar to Macedonian Peliganes.
Molossian royalty
The most famed member of the Molossian dynasty was Pyrrhus, who became famous for his Pyrrhic victory over the Romans. According to Plutarch, Pyrrhus was the son of Aeacides of Epirus and a Greek woman from Thessaly named Phthia, the daughter of a war hero in the Lamian War. Pyrrhus was a second cousin of Alexander the Great. In the 4th century BC, they had adopted the term for office of prostatai (Greek: προστάται)[4] literally meaning "protectors" like most Greek tribal states at the time. Other terms for office were grammateus (Greek: γραμματεύς) meaning "secretary", demiourgoi (Greek: δημιουργοί) literally meaning "creators", hieromnemones (Greek: ἱερομνήμονες) literally meaning "of the sacred memory" and synarchontes (Greek: συνάρχοντες) literally meaning "co-rulers"[5] An inscription from the 4th century stated (referring to Alexander I of Epirus):[6]
“ When King was Alexandros when of Molossoi prostatas was Aristomachos Omphalas secretary was Menedamos Omphalas resolved by the assembly of the Molossoi; Kreston is benefactor hence to give citizenship to Kteson and descent line ” Dodona was used for the display of public decisions.[7] Despite having a monarchy, the Molossians sent princes[8] to Athens to learn of democracy as they did not consider monarchy and certain aspects of democracy as opposite concepts.[9]
Olympias, the mother of Alexander the Great, was a member of this celebrated sovereign house.
War
In 385 BC, the Molossians were attacked by Illyrians instigated and aided by Dionysius of Syracuse to place Alcetas that was a refugee in his court to the throne.[10] Dionysius planned to control all the Ionian Sea. Sparta intervened[11] as soon as the events became known and expelled[12] the Illyrians who were led by Bardyllis.[13] Despite being aided by 2000 Greek hoplites and 500 suits of Greek armour, the Illyrians were defeated by the Spartans (led by Agesilaus) but not before ravaging the region and killing 15,000 Molossians.[13]
In another Illyrian attack in 360 BC, the Molossian king Arymbas (or Arybbas) evacuated his non-combatant population to Aetolia and let the Illyrians loot freely. The stratagem worked and the Molossians fell upon the Illyrians now encumbered with booty and defeated them.[13][14]
List of Molossians
- Neoptolemus son of Achilles and Deidamia (Aeacid dynasty till 231 BC).
- Molossus son of Neoptolemus and Andromache.
- Alcon (6th century BC) suitor of Agariste of Sicyon.
- Admetus, who gave asylum to Themistocles.
- Eidymmas prostates, secretary Amphikorios gave citizenship το Philista, wife of Antimachos from Arrhonos, under King Neoptolemos I 370-368 BC.[15]
- Tharyps theorodokos in Epidauros 365 BC.[16]
- Myrtale Olympias mother of Alexander the Great circa 376–316 BC.
- Arybbas winner in Tethrippon Olympics 344 BC.[17]
- Aristomachos prostates, secretary Menedamos gave citizenship to Simias of Apollonia, resident at Theptinon, under King Alexander I 342-330/329 BC.[18]
- Pyrrhus of Epirus (318-272 BC) most prominent Epirote king.
- Deidamia II of Epirus (died circa 233 BC) last surviving representative of the royal Aeacid dynasty.
- Kephalos, Antinoos sided with Perseus against the Romans (Third Macedonian War) circa 170 BC.[19]
See also
References
- ^ Lewis & Boardman 1994, pp. 430, 433–434; Wilkes 1995, p. 104; Errington 1990, p. 43; Borza 1992, pp. 62, 78, 98; Boardman & Hammond 1982, p. 284; Hammond 1998.
- ^ a b Plutarch. Parallel Lives, "Pyrrhus".
- ^ Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott - An Intermediate Greek-English Lexicon.
- ^ Horsley 1987, p. 243; Hornblower 2002, p. 199.
- ^ Lewis & Boardman 1994, p. 431.
- ^ Brock & Hodkinson 2000, p. 250.
- ^ Brock & Hodkinson 2000, p. 257.
- ^ Alcock & Osborne 2007, p. 392.
- ^ Brock & Hodkinson 2000, p. 256.
- ^ Hammond 1986, p. 479.
- ^ Hammond 1986, p. 470.
- ^ Diodorus Siculus. Library, 15.13.1.
- ^ a b c Lewis & Boardman 1994, p. 428.
- ^ Diodorus Siculus. Library. Books 14.92, 15.2, 16.2.
- ^ Cabanes, L'Épire 534,1.
- ^ IG IV²,1 95 Line 31.
- ^ Woodbury 1979, pp. 95–133.
- ^ Cabanes, L'Épire 540,4.
- ^ Smith 1844, p. 191: "ANTI'NOUS (Άντίνους), a chief among the Molossians in Epeirus, who became involved, against his own will, in the war of Perseus, king of Macedonia, against the Romans."
Sources
- Alcock, Susan E.; Osborne, Robin (2007). Classical Archaeology. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing Limited. ISBN 0631234187. http://books.google.com/books?id=RwVJ9QzNnQgC.
- Boardman, John; Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1982). The Cambridge Ancient History - The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries B.C., Part 3: Volume 3 (Second Edition). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521234476. http://books.google.com/books?id=0qAoqP4g1fEC.
- Borza, Eugene N. (1992). In the Shadow of Olympus: The Emergence of Macedon (Revised Edition). Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691008809. http://books.google.com/books?id=614pd07OtfQC.
- Brock, Roger; Hodkinson, Stephen (2000). Alternatives to Athens: Varieties of Political Organization. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198152205. http://books.google.com/books?id=HS-DAAAAMAAJ.
- Errington, Robert Malcolm (1990). A History of Macedonia. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. ISBN 0520063198. http://books.google.com/books?id=PYgkqP_s1PQC.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1986). A History of Greece to 322 B.C. Oxford, United Kingdom: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0198730969. http://books.google.com/books?id=KwHBQgAACAAJ.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1998). Philip of Macedon. London, United Kingdom: Duckworth. ISBN 0715628291. http://books.google.com/books?id=0XF5OwAACAAJ.
- Hornblower, Simon (2002). The Greek World, 479-323 BC. New York, New York and London, United Kingdom: Routledge. ISBN 0415163269. http://books.google.com/books?id=wvtyijSRcKUC.
- Horsley, G. H. R. (1987). New Documents Illustrating Early Christianity: A Review of the Greek Inscriptions and Papyri Published in 1979. Grand Rapids, Michigan: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. ISBN 0858375990. http://books.google.com/books?id=uVPSFtaE5H4C.
- Lewis, David Malcolm; Boardman, John (1994). The Cambridge Ancient History: The Fourth Century B.C.. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521233488. http://books.google.com/books?id=vx251bK988gC.
- Smith, William (1844). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology. I. London, United Kingdom: Taylor and Walton, Upper Gower Street. http://books.google.com/books?id=0CUBAAAAQAAJ.
- Wilkes, John (1995) [1992]. The Illyrians. Oxford, United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishers Limited. ISBN 0631198075. http://books.google.com/books?id=4Nv6SPRKqs8C.
- Woodbury, Leonard (1979). "Neoptolemus at Delphi: Pindar, "Nem." 7.30 ff.". Phoenix (Classical Association of Canada) 33 (2): 95–133. JSTOR 1087989.
Categories:- Alexander the Great
- Ancient Greece
- Ancient tribes in Epirus
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.