- 1999 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
-
1999 North Indian Ocean cyclone season 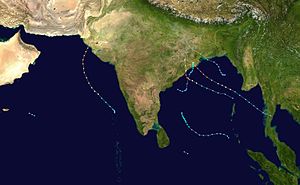
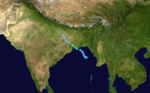
Season summary mapFirst storm formed: January 30, 1998 Last storm dissipated: December 10, 1998 Strongest storm: 05B – 912 hPa (mbar), 240 km/h (150 mph) (3-minute sustained) Depressions: 8 official, 1 unofficial Deep depressions: 6 official, 1 unofficial Cyclonic storms: 4 official, 1 unofficial Severe cyclonic storms: 4 Total fatalities: At least 15,780 Total damage: $5 billion (1999 USD) North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons
1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001IMD Tropical Cyclone
Strength Classification [1]Category Wind speed (3-min) Knots (km/h) Depression ≤27
(≤51)Deep Depression 28–33
(52–61)Cyclonic Storm 34–47
(62–87)Severe Cyclonic
Storm48–63
(88–117)Very Severe
Cyclonic Storm64–119
(118–221)Super Cyclonic Storm ≥120
(≥222)The 1999 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with peaks in May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Indian Ocean in the Northern Hemisphere, east of the Horn of Africa and west of the Malay Peninsula. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean - the Arabian Sea to the west of the Indian subcontinent, abbreviated ARB by the India Meteorological Department (IMD); and the Bay of Bengal to the east, abbreviated BOB by the IMD.
The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories. The tropical cyclone scale for this basin is detailed on the right. On average, 4 to 6 storms form in this basin every season.[2]
The season produced an average number of storms but there was an above average number of intense cyclones. In May, a Category 3 cyclone struck Pakistan, leaving at 700 people dead or missing. In October, two very intense cyclones struck eastern India within two weeks of each other, leaving over 10,000 people dead and causing more than $4.5 billion (1999 USD) in damages.
Contents
Storms
Five tropical cyclones were observed, making 1999 an average season. However, 4 reached Cyclone strength.
Cyclonic Storm BOB 01
Cyclonic Storm (IMD) Tropical storm (SSHS) 
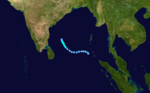
Duration February 2 – February 5 Intensity 95 km/h (60 mph) (3-min), 998 mbar (hPa) On January 30, an area of disturbed weather began to develop. Convection began to form around the center and a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert was issued the next day by the JTWC. Development of the storm stalled and the alert was cancelled. The next day, another TCFA was issued but was once more cancelled. Finally, on February 2, after the third TCFA was issued, the low pressure area developed into a tropical storm at 0900Z 370 nm west of Phuket, Thailand. The storm slowly intensified and reached its peak of 45 mph (1-min) on February 3. Shortly after peaking in intensity, vertical wind shear weakened the storm and the low became exposed by 1800Z the same day. The storm later dissipated on February 5 without making landfall.[3]
Very Severe Cyclonic Storm ARB 01 (02A)
Very severe cyclonic storm (IMD) Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
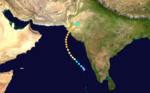
Duration May 16 – May 22 Intensity 195 km/h (120 mph) (3-min), 946 mbar (hPa) Main article: 1999 Pakistan cycloneAn area of disturbed weather in the Arabian Sea was monitored in early May for possible development. Over the next two weeks, strong convection would develop before sunrise but dissipate by sunset. By May 16, the convection had become constant and a TCFA was issued at 0100Z. The low became a tropical storm by 0900Z. Tropical Storm 02A intensified as it moved to the northwest and reached cyclone status on May 17 at 0600Z. At that time, a mid-latitude trough weakened the subtropical ridge, allowing 02A to curve into Pakistan. 02A continued to intensify and by May 19, it had reached its peak of 125 mph (205 km/h), just below Category four status on the SSHS. 02A made landfall on May 20 near Karachi, Pakistan at peak intensity. The storm began to dissipate as it continued inland over the Indus River Valley on May 21 and completely dissipated the next day.
The cyclone struck the same area which had been hit hard by Tropical Cyclone 03A, a category three as well, almost exactly a year prior. It proved to be very deadly with 700 people reported to be dead or missing. Damages totaled to $6 million (1999 USD).
02A was the strongest storm to ever form in the Arabian Sea until 2001, when cyclone 01A became the strongest storm to form in the Arabian Sea. It was itself surpassed in 2007 when Cyclone Gonu became the first category five to form in the Arabian Sea.[4]
Tropical Storm 03B
Tropical storm (SSHS) 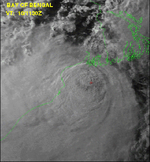
Duration June 8 – June 11 Intensity 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min), 997 mbar (hPa) On June 8, an area of low pressure formed 235 nm south of Chittagong, Bangladesh. The low slowly developed over the next two days while drifting to the west and northwest. On June 10, a TCFA was issued at 0830Z and the first warning on Tropical Storm 03B was issued at 1500Z the same day. The storm made landfall as a minimal tropical storm to the west of Calcutta, India later that day. 03B rapidly weakened due to vertical wind shear and the interaction with land and dissipated on June 11. No fatalities or damages have been associated with 03B.[5]
Deep Depression BOB 02
Deep depression (IMD) 
Duration June 17 – June 17 Intensity 55 km/h (35 mph) (3-min), 986 mbar (hPa) A weak depression existed on June 17 before it made landfall near Berhampur. The depression was monitored by the IMD, not the JTWC.
Deep Depression BOB 03
Deep depression (IMD) 
Duration July 27 – July 28 Intensity 55 km/h (35 mph) (3-min), 990 mbar (hPa) A depression formed on July 27, strengthened slightly before moving inland into the Orissa state on July 28. The depression was monitored by the IMD, not the JTWC.
Depression BOB 04
Depression (IMD) 
Duration August 6 – August 9 Intensity 45 km/h (30 mph) (3-min), 992 mbar (hPa) A depression formed in the northern Bay of Bengal on August 6 and moved inland into the Orissa state the next day. It was dissipated by August 8. The depression was monitored by the IMD, not the JTWC.
Very Severe Cyclonic Storm BOB 05 (04B)
Very severe cyclonic storm (IMD) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
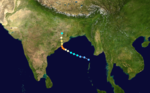
Duration October 15 – October 19 Intensity 165 km/h (105 mph) (3-min), 968 mbar (hPa) On October 15, a developing area of low pressure, located 220 nm northwest of the Andaman Islands began to intensify. By 1730Z a TCFA was issued and the first advisory on Tropical Storm 04B was issued at 2100Z. 04B was moving to the west-northwest at 8-12 knots as it continued to intensify. On October 17, the storm began to turn to a more northerly direction as it intensified to a cyclone. 04B underwent explosive intensification the same day and reached its peak of 140 mph at 0000Z. The storm held this intensity as it made landfall on the Orissa coastline. The storm began to weaken due to the interaction with land and dissipated on October 19.
04B was responsible for at least 80 fatalities and hundreds of houses and huts in low lying areas were destroyed by flooding.[6] Several thousand others were injured by the storm and hundreds were left homeless. The Prime Minister of India requested that relief supplies be distributed to the affected region immediately.[7]
Super Cyclonic Storm BOB 06 (05B)
Super cyclonic storm (IMD) Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
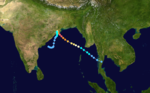
Duration October 25 – November 3 Intensity 260 km/h (160 mph) (3-min), 912 mbar (hPa) Main article: 1999 Orissa cycloneOn October 23, a TCFA was issued for an area of low pressure in the South China Sea. The low did not develop further and the TCFA was cancelled. On October 25, the low crossed the Malay Peninsula. Later that day, the low reorganized and another TCFA was issued at 1930Z. The low was upgraded to Tropical Storm 05B the next day ay 0300Z. The storm tracked to the northwest and continued to intensify quickly. 05B began to intensify faster than the climatological rate and peaked as a 160 mph category five on October 28 at 1800Z. 11 hours after peaking, 05B weakened slightly to 155 mph and made landfall near the same area that 04B did only 11 days earlier. The storm slowly weakened as it stalled just onshore in Orissa, India while dumping torrential rains. The storm reentered the Bay of Bengal on October 31 as a 45 mph tropical storm. 05B slowly weakened as it drifted southward. 05B weakened to a tropical depression on November 2 and dissipated the next day.
Damage from the cyclone was tremendous. Flooding from the storms rain was described as the worst in 100 years as well as the worst in India's history. The storm claimed the lives of at least 15,000 people[8] and 406,000 livestock. Damages from the storm totaled to $4.5 billion (1999 USD).[9]
Depression BOB 07
Depression (IMD) 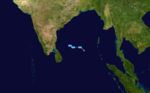
Duration December 8 – December 10 Intensity 45 km/h (30 mph) (3-min), 998 mbar (hPa) A Tropical Depression formed in the Bay of Bengal on December 8. The depression was monitored by the IMD, not the JTWC. The depression remained out over open waters before dissipating on December 10.[10]
See also
- List of North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons
- 1999 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1999 Pacific hurricane season
- 1999 Pacific typhoon season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1998–99, 1999–00
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 1998–99, 1999–00
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 1998–99, 1999–00
References
- ^ http://www.imd.gov.in/services/cyclone/impact.htm Archived 19 October 2008 at WebCite
- ^ "IMD Cyclone Warning Services: Tropical Cyclones". Archived from the original on May 29, 2009. http://web.archive.org/web/20090529004113/http://www.imd.ernet.in/services/cyclone/tropical-cyclone.htm.
- ^ http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1999atcr/pdf/01b.pdf[dead link]
- ^ http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1999atcr/pdf/02a.pdf[dead link]
- ^ http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1999atcr/pdf/03b.pdf[dead link]
- ^ http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1999atcr/pdf/04b.pdf[dead link]
- ^ Staff Writer (October 20, 1999). "Cyclone kills 79". The Birmingham Post. http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-60485385.html. Retrieved July 30, 2009.
- ^ "Natural catastrophes and man-made disasters in 2008: North America and Asia suffer heavy losses". Swiss Reinsurance Company Ltd. 21 January 2009. p. 38. http://swissre.com/resources/dd6346004d4e9669ac76eecedd316cf3-sigma2_2009_e.pdf. Retrieved 18 January 2010.[dead link]
- ^ http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/1999atcr/pdf/05b.pdf[dead link]
- ^ Northern Hemisphere 1999 Tropical Cyclone Season Review
External links
1990–99 North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
