- Digital room correction
-
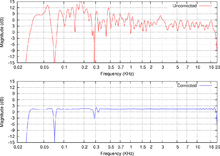
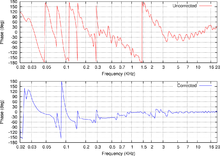
Digital room correction (or DRC) is a process in the field of acoustics where digital filters designed to ameliorate unfavorable effects of a room's acoustics are applied to the input of a sound reproduction system. Modern room correction systems produce substantial improvements in the time domain and frequency domain response of the sound reproduction system.
Contents
History
The use of analog filters, such as equalizers, to normalize the frequency response of a playback system has a long history; however, analog filters are very limited in their ability to correct the distortion found in many rooms. Although digital implementations of the equalizers have been available for some time, digital room correction is usually used to refer to the construction of filters which attempt to invert the impulse response of the room and playback system, at least in part. Digital correction systems are able to use acausal filters, and are able to operate with optimal time resolution, optimal frequency resolution, or any desired compromise along the Gabor limit. Digital room correction is a fairly new area of study which has only recently been made possible by the computational power of modern CPUs and DSPs.
Operation
The configuration of a digital room correction system begins with measuring the impulse response of the room at the listening location for each of the loudspeakers. Then, computer software is used to compute a FIR filter, which reverses the effects of the room and linear distortion in the loudspeakers. Finally, the calculated filter is loaded into a computer or other room correction device which applies the filter in real time. Because most room correction filters are acausal, there is some delay. Most DRC systems allow the operator to control the added delay through configurable parameters.
Challenges
DRC systems are not normally used to create a perfect inversion of the room's response because a perfect correction would only be valid at the location where it was measured: a few millimeters away the arrival times from various reflections will differ and the inversion will be imperfect. The imperfectly corrected signal may end up sounding worse than the uncorrected signal because the acausal filters used in digital room correction may cause pre-echo. Room correction filter calculation systems instead favor a robust approach, and employ sophisticated processing to attempt to produce an inverse filter which will work over a usably large area, and which avoid producing bad-sounding artifacts outside of that area, at the expense of peak accuracy at the measurement location.
See also
- Deconvolution
- Digital filter
- Filter (signal processing)
- Filter design
- LARES
- Minimum phase
- Stereophonic sound
- Surround sound
References
- Michael Gerzon's paper on Digital Room Equalization, on audiosignal.co.uk.
External links
Presentations
- Duff Room Correction, a wiki on digital room correction.
Papers
- On Room Correction and Equalization of Sound Systems, by Dr. Mathias Johansson
- Digital Room Equalization, by Michael Gerzon
Articles
- Room Correction: A Primer, by Nyal Mellor of Acoustic Frontiers
- Sound Correction in the Frequency and Time Domain, by Bernt Ronningsbak of Audiolense
- The Three Acoustical Issues a Room Correction Product Can't Actually Correct, by Nyal Mellor of Acoustic Frontiers
Categories:- Acoustics
- Sound technology
- Signal processing
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.