- Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine
-
Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine 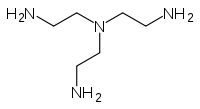 Tris(2-aminoethyl)amineOther names2,2',2-Nitrilotriethylamine
Tris(2-aminoethyl)amineOther names2,2',2-Nitrilotriethylamine
2,2',2-Triaminotriethylamine
TAEA
4-(2-aminoethyl)diethylenetriamine
nitrilotris(ethylamine)
tris(aminoethyl)amine
tris(beta-aminoethyl)amine
TrenIdentifiers CAS number 4097-89-6 
PubChem 77731 RTECS number KH8587082 Properties Molecular formula (NH2CH2CH2)3N Molar mass 146.236 g/mol Appearance colourless Density 0.977 g/cm3 Melting point −16 °C
Boiling point 265 °C
Solubility in water miscible Solubility polar organic solvents Hazards MSDS Fisher Scientifc MSDS R-phrases 22-24-34 S-phrases 26-36/37/39-45 Main hazards Corrosive  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine is the organic compound with the formula N(CH2CH2NH2)3. This colourless liquid is soluble in water and is highly basic, consisting of a tertiary amine center and three pendant primary amine groups. Abbreviated "tren," it is the archetypal tripodal ligand of interest in coordination chemistry.
Contents
Coordination chemistry
Tren is a tripodal, tetradentate chelating ligand that forms stable complexes with transition metals, especially those in the 2+ and 3+ oxidation states. Tren complexes exist with relatively few isomers, reflecting the constrained connectivity of this tetramine. Thus, only a single achiral stereoisomer exists for [Co(tren)X2]+, where X is halide or pseudohalide.[1] In contrast, for [Co(trien)X2]+ five diastereoiomers are possible, four of which are chiral. In a few cases, tren serves as a tridentate ligand with one of the primary amine groups non-coordinated.
Related tripodal ligands
The permethylated derivative of tren is also well known. With the formula N(CH2CH2NMe2)3, "Me6tren," forms a variety of complexes but, unlike tren, does not stabilize Co(III). Related amino-triphosphines are also well developed, such as N(CH2CH2PPh2)3 (m.p. 101-102 °C). This species is prepared from the nitrogen mustard N(CH2CH2Cl)3.[2]
The tripodal ligand of greatest commercial significance is nitrilotriacetate, N(CH2CO2-)3.
Organic chemistry
Tren is a common impurity in the more common triethylenetetramine ("trien"). As a trifunctional amine, tren forms a triisocyanate when derivatized with COCl2.[3]
Safety considerations
(NH2CH2CH2)3N, like other polyamines, is corrosive.[4]
References
- ^ Donald A. House “Ammonia & N-donor Ligands” in Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry John Wiley & Sons, 2006. doi:10.1002/0470862106.ia009.
- ^ R. Morassi, L. Sacconi "Tetradentate Tripod Ligands Containing Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Arsenic as Donor Atoms" Inorganic Syntheses, 1976, vol. 16 p. 174-180. doi:10.1002/9780470132470.ch47
- ^ Pressure Chemical
- ^ The Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory Oxford University MSDS
Categories:- Amines
- Polyamines
- Tripodal ligands
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

