- Conic constant
-
In geometry, the conic constant (or Schwarzschild constant[1], after Karl Schwarzschild) is a quantity describing conic sections, and is represented by the letter K. It is given by
where e is the eccentricity of the conic section.
The equation for a conic section with apex at the origin and tangent to the y axis is
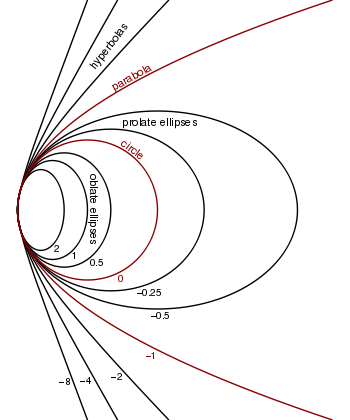
- y2 − 2Rx + (K + 1)x2 = 0
where K is the conic constant and R is the radius of curvature at x = 0.
This formulation is used in geometric optics to specify oblate elliptical (K > 0), spherical (K = 0), prolate elliptical (0 > K > −1), parabolic (K = −1), and hyperbolic (K < −1) lens and mirror surfaces. When the paraxial approximation is valid, the optical surface can be treated as a spherical surface with the same radius.
Some non-optical design references use the letter p as the conic constant. In these cases, p = K + 1.
References
- Smith, Warren J. (2008). Modern Optical Engineering, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 513–515. ISBN 978-0071476874.
- ^ Chan, L.; Tse, M.; Chim, M.; Wong, W.; Choi, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, M.; Sung, J. (May 2005). "The 100th birthday of the conic constant and Schwarzschild's revolutionary papers in optics". Proceedings of SPIE 5875: 587501. doi:10.1117/12.635041. ISSN 0277-786X.
Categories:- Mathematics stubs
- Mathematical constants
- Conic sections
- Geometrical optics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.