- Cyropolis
-
Cyropolis (Latin form of Gr. "Kuroúpolis" from Ir. *Kuru(š)-kaθa-), (literally "The City of Cyrus") was an ancient city founded by Cyrus the Great in northern Tajikistan in 544 BCE to mark the northeastern border of his Persian empire.
Location
There appear to be a number of alternative locations for this city:
- One alternative reports that: Today the city is named Kurkath or Kurkad, short for Kurosh Kadeh or Kurus Katha.
- The article on the river Syr Darya, states that Cyropolis is the same place as Alexandria Eschate, and that the present day location of both is the modern day city of Khujand.
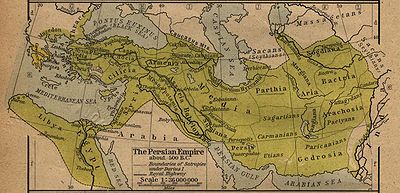
- The accompanying 1923 map gives the location of the city as approximately 40°N 69°E / 40°N 69°E. This is the location of the present day city of Istarawshan, a place of human settlement of great antiquity. The degree of confidence which can be placed in the map can be judged from the position it gives for the city of Bactra (approximately 37°N 67°E / 37°N 67°E), which corresponds very closely with the actual location of Bactra (or Balkh).
History
Cyropolis was the largest of seven towns in the region that Alexander the Great targeted for conquest in 329 B.C. His goal was the conquest of Sogdiana. Alexander first sent Craterus to Cyropolis, the largest of the towns holding Sogdiana against Alexander's forces. Craterus' instructions were to "take up a position close to the town, surround it with a ditch and stockade, and then assemble such siege engines as might suit his purpose...." The idea was to keep the inhabitants focused on their own defenses and to prevent them from sending assistance out to the other towns. Starting from Gazza, Alexander went on to conquer the other surrounding towns. Five of the seven towns were taken in two days. Many of the inhabitants were killed. Alexander then arrived at Cyropolis, which was the best fortified of the towns and had the largest population. It also had reputedly the best fighters of the region. Alexander battered Cyropolis' defenses with the siege engines. While the bombardment went on, Alexander ordered certain of his troops to sneak through a dried-up water course that went under the town's wall. Alexander also joined on this mission and once inside his troops opened the town's gate to admit his attacking force. Once the natives saw that the town was taken, they fell violently upon the attackers. Alexander received a violent blow from a stone that landed upon his head and neck. Craterus was wounded by an arrow. But the defenders were driven off. Arrian puts the defender's force at about 15,000 fighting men and claims that 8,000 of them were killed in the first phase of the operation. The rest apparently sought refuge inside the town's central fortress, but surrendered after one day for lack of water. Arrian (1971). The Campaigns of Alexander. London: Penguin Books. p. 204. ISBN 0140442537.
Accounts of how the battle went down differ among authors. Arrian cites Ptolemy as saying Cyropolis surrendered from the start, and Arrian also states that according to Aristobulus the place was stormed and everyone was massacred. Arrian (1971). The Campaigns of Alexander. London: Penguin Books. p. 204. ISBN 0140442537.
Categories:- Tajikistan stubs
- Iran stubs
- Achaemenid cities
- Former populated places in Tajikistan
- Cyrus the Great
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.