- 4-Deoxypyridoxine
-
4-Deoxypyridoxine 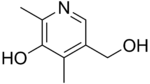 5-(Hydroxymethyl)-2,4-dimethylpyridin-3-ol
5-(Hydroxymethyl)-2,4-dimethylpyridin-3-olIdentifiers CAS number 148-51-6 PubChem 6094 ChemSpider 5869 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- CC1=C(C(=NC=C1CO)C)O
Oc1c(c(cnc1C)CO)C
Properties Molecular formula C8H11NO2 Molar mass 153.18 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references 4-Deoxypyridoxine is a vitamin B6 antagonist.[1] It may be toxic to developing embryos since it can have negative effects on collagen and elastin during development.[2] The presence of this compound can produce vitamin B6 deficiency, which suppresses the immune system.[3] This immunosuppression can be beneficial in animal models of Trichinella spiralis infections.[4]
References
- ^ Coburn SP, Mahuren JD, Schaltenbrand WE, Wostmann BS, Madsen D (1 February 1981). "Effects of vitamin B-6 deficiency and 4'- deoxypyridoxine on pyridoxal phosphate concentrations, pyridoxine kinase and other aspects of metabolism in the rat". J. Nutr. 111 (2): 391–8. PMID 6257871. http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=6257871.
- ^ Bird TA, Levene CI (1983). "The effect of a vitamin B-6 antagonist, 4-deoxypyridoxine, on the cross-linking of collagen in the developing chick embryo". Biochem. J. 210 (3): 633–8. PMC 1154271. PMID 6135414. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1154271.
- ^ Trakatellis A, Dimitriadou A, Exindari M, et al. (1992). "Effect of pyridoxine deficiency on immunological phenomena". Postgrad Med J 68 Suppl 1: S70–7. PMID 1409221.
- ^ Frydas S, Papaioanou N, Vlemmas I, et al. (1999). "Vitamin B6-deficient diet plus 4-deoxypyridoxine (4-DPD) reduces the inflammatory response induced by T. spiralis in diaphragm, masseter and heart muscle tissue of mice". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 197 (1–2): 79–85. doi:10.1023/A:1006958310081. PMID 10485327.
Categories:- Immunosuppressants
- Pyridines
- CC1=C(C(=NC=C1CO)C)O
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
