- Coumestrol
-
Coumestrol 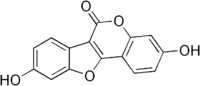 3,9-Dihydroxy-6-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromenone
3,9-Dihydroxy-6-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromenoneIdentifiers CAS number 479-13-0 PubChem 5281707 ChemSpider 4445024 
UNII V7NW98OB34 
KEGG C10205 
ChEMBL CHEMBL30707 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C1=CC2=C(C=C1O)OC3=C2C(=O)OC4=C3C=CC(=C4)O
O=C3Oc4cc(O)ccc4c2oc1c(ccc(O)c1)c23
Properties Molecular formula C15H8O5 Molar mass 268.22102 Melting point 385 °C (decomp)[1]
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Coumestrol is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as coumestans. It has garnered research interest because of its estrogenic activity and its prevalence in some foods, such as soybeans.
Coumestrol was first identified by E. M. Bickoff in alfalfa in 1957.[2] It has since be found in a variety of legumes, soybeans, brussels sprouts, and spinach. Clover and soybeans have the highest concentrations.[3]
Coumestrol is a phytoestrogen, mimicking the biological activity of estrogens. The chemical shape of coumestrol orients its two hydroxy groups in the same position as the two hydroxy groups in estradiol, allowing it to inhibit the activity of aromatase and hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.[4] These enzymes are involved in the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, and inhibition of these enzymes results in the modulation of hormone production.[3]
References
- ^ Bickoff, E. M.; Livingston, A. L.; Witt, S. C.; Knuckles, B. E.; Guggolz, Jack; Spencer, R. R. (1964). "Isolation of coumestrol and other phenolics from alfalfa by countercurrent distribution". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 53 (12): 1496–9. doi:10.1002/jps.2600531213. PMID 14255129.
- ^ E. M. Bickoff, A. N. Booth, R. L. Lyman, A. L. Livingston, C. R. Thompson, and F. Deeds (1957). "Coumestrol, a New Estrogen Isolated from Forage Crops". Science 126 (3280): 969–970. doi:10.1126/science.126.3280.969-a. PMID 13486041.
- ^ a b Amr Amin and Michael Buratovich (2007). "The Anti-Cancer Charm of Flavonoids: A Cup-of-Tea Will Do!". Recent Patents on Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery 2 (2): 109–117. doi:10.2174/157489207780832414. PMID 18221056.
- ^ Blomquist CH, Lima PH, Hotchkiss JR (2005). "Inhibition of 3a-hydroxysteoid dehydogenase (3a-HSD) activity of human lung microsomes by genistein, daidzein, coumestrol and C18-, C19- and C21 hydroxysteroids and ketosteroids". Steroids 70 (8): 507–514. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2005.01.004. PMID 15894034.
Categories:- Coumestans
- C1=CC2=C(C=C1O)OC3=C2C(=O)OC4=C3C=CC(=C4)O
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
