- Osteoid osteoma
-
Osteoid osteoma Classification and external resources 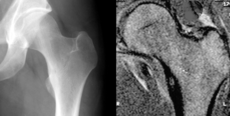
Osteoid osteoma of the trochanter minor: X-ray and MRI with marked sclerosis around the nidus.ICD-O: 9191/0 DiseasesDB 31488 eMedicine article/392850 MeSH D010017 An osteoid osteoma is a benign bone tumor which arises from osteoblasts and originally thought to be a smaller version of an osteoblastoma. Osteoid osteomas tend to be less than 1.5 cm in size. The tumor can be in any bone in the body but are most common in long bones, such as the femur and tibia. They account for 10 to 12 percent of all benign bone tumors. "Osteoid osteomas may occur at any age, and are most common in patients between the ages of 4 and 25 years old. Males are affected approximately three times more commonly than females." [1]
Contents
Presentation
Characterized by less than 1.5 cm in diameter, osteoid osteomas most frequently occur in young men (Male:Female ratio 3:1) and may occur in any bone of the body, most frequently around the knee but often also seen in the vertebrae, in the long bones and less commonly in the mandible or other craniofacial bones.
Severe pain typically occurs at night.[2] Radiographs in osteoid osteoma typically show a round lucency, containing a dense sclerotic central nidus (the characteristic lesion in this kind of cancer), surrounded by sclerotic bone. The nidus is seldom larger than 1.5 cm.
The chief complaint may only be of dull pain which is non radiating and persistent throughout 24 hours but increases significantly at night. The lesion can easily be detected on CT scan. Plain radiographs are not always diagnostic. MRI adds little to the CT findings which are useful for localisation. Radionuclide scanning shows intense uptake which is useful for localisation at surgery using a hand held detector, and for confirmation that the entire lesion has been removed. [3]
Histological Findings
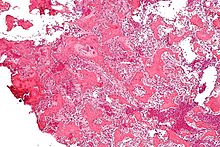 Micrograph of an osteoid osteoma showing the characteristic anastomosing bony trabeculae and osteoblastic rimming. H&E stain.
Micrograph of an osteoid osteoma showing the characteristic anastomosing bony trabeculae and osteoblastic rimming. H&E stain.
On histological examination osteoid osteoma consists of a small (< 1.52 cm), yellowish to red nidus of osteoid and woven bone with interconnected trabeculae, and a background and rim of highly vascularized, fibrous connective tissue. Varying degrees of sclerotic bone reaction may surround the lesion. Benign osteoblastoma is virtually indistinguishable from osteoid osteoma. The usual appearance included a fibrovascular stroma with numerous osteoblasts, osteoid tissue, well-formed woven bone, and giant cells. The osteoblasts were generally small and regular in shape. "http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/465365_2"
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of an Osteoid Osteoma are:
- dull pain that escalates to severe at night
- limping
- muscle atrophy
- bowing deformity
- swelling
- increased or decreased bone growth
[4] [5] The most common symptom is pain that can be relieved with over the counter pain medication in the beginning. After the benign tumor develops further the pain can not be alleviated with medication and minor to severe swelling starts to occur. The tumor is often found through x-ray imaging. "Conventional radiographs reveal a well-demarcated lytic lesion (nidus) surrounded by a distinct zone of sclerosis" that allow doctors to identify the tumor. [6]
Treatment
Pain may be relieved by aspirin or other nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.
Osteoid osteoma will resolve spontaneously in approximately 33 months, the reason for this is unknown. The type of treatment may also vary based on the health of the individual with the tumor. If an individual is healthy and is willing to endure the pain, pain relievers are given until the tumor resolves. If the patient does not want to endure the pain or to be treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatories, surgical or percutaneous ablation may be considered. [7] If surgery is preferred, the individual may be referred to an orthopedic surgeon to perform the ablation. Post-surgery therapy and strengthening may be needed, depending on the tumor location and health of the individual. Recently, percutaneous radiofrequency ablation is the preferred treatment option. "This is a minimally invasive procedure in which radio frequencies are passed beneath the skin through a needle to kill the tumor cells by heating them to a high temperature."[8] This technique is performed by a radiologist and is preferred because it is done under general anesthesia and does not weaken the bone as much a surgery does. The recovery time is also shorter for this treatment.
Ablation is performed in some cases.[9][10]
References
- ^ http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00507
- ^ Mungo DV, Zhang X, O'Keefe RJ, Rosier RN, Puzas JE, Schwarz EM (January 2002). "COX-1 and COX-2 expression in osteoid osteomas". J. Orthop. Res. 20 (1): 159–62. doi:10.1016/S0736-0266(01)00065-1. PMID 11853083.
- ^ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/392850-overview
- ^ "Osteoid Osteoma". Knol. http://knol.google.com/k/osteoid-osteoma#Symptoms%7Cpublisher=Knol.
- ^ "Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors: Benign Tumors". Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. http://www.dana-farber.org/pat/pediatric-care/pediatric-programs/bone-and-soft-tissue-tumors/osteoma.html#faq_3.
- ^ Singh, Arun Pal. "Osteoid Osteoma-Diagnosis And Treatment". http://boneandspine.com/musculoskeletal-tumours/osteoid-osteomadiagnosis-treatment/.
- ^ http://www.bonetumor.org/tumors-bone/osteoid-osteoma
- ^ "Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors: Benign Tumors". http://www.dana-farber.org/pat/pediatric-care/pediatric-programs/bone-and-soft-tissue-tumors/osteoma.html.
- ^ Lindner NJ, Ozaki T, Roedl R, Gosheger G, Winkelmann W, Wörtler K (April 2001). "Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in osteoid osteoma". J Bone Joint Surg Br 83 (3): 391–6. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.83B3.11679. PMID 11341426. http://www.jbjs.org.uk/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11341426.
- ^ Donkol RH, Al-Nammi A, Moghazi K (February 2008). "Efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in children". Pediatr Radiol 38 (2): 180–5. doi:10.1007/s00247-007-0690-z. PMID 18040677.
Connective tissue neoplasm: Osseous and Chondromatous tumors (ICD-O 9180–9269) (C40–C41/D16, 170/213) Diaphysis Metaphysis Chondroma/ecchondroma/enchondroma (Enchondromatosis, Extraskeletal chondroma) · Chondrosarcoma (Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, Myxoid chondrosarcoma)Epiphysis Other/ungrouped External links
Categories:- Anatomical pathology
- Osseous and chondromatous neoplasia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
