- Myoviridae
-
Myoviridae 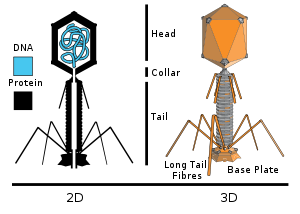
Structural overview of the T4 phage Virus classification Group: Group I (dsDNA) Order: Caudovirales Family: Myoviridae Genera I3-like viruses
Mu-like viruses
P1-like viruses
P2-like viruses
PhiH-like viruses
PhiKZ-like viruses
SPO1-like viruses
T4-like viruses
Vi01-like virusesThe Myoviridae is a family of bacteriophages. It has been divided into three subfamiles and a number of genera not yet assigned to a subfamily.[1] There are at least 130 species in this family.
Contents
Virology
These are non enveloped viruses and consist of a head and a tail separated by a neck.
The head has a diameter of 50 - 110 nm and has icosahedral symmetry (T = 13 Q = 21). It is composed of 152 capsomers which are hexagonal in outline.
The tubular tail has helical symmetry and is 16-20 nm in diameter. It consists of a central tube, a contractile sheath, a collar, a base plate, six tail pins and six long fibers. It is similar to Tectiviridae, but differs in the fact that a myovirus' tail is permanent.
Contractions of the tail require ATP. On contraction of the sheath, sheath subunits slide over each other and the tail shortens to 10-15 nm in length.
The genome is linear, double-stranded DNA between 33.6-170 kilobases in length. It has terminally redundant sequences. The guanine + cytosine content is ~35%. The genome encodes 200-300 proteins which are transcribed in operons.
5-hydroxy-methyl cytosine may be present in the genome (instead of thymidine).
Life cycle
On attaching to a host cell, the virus uses its contractile sheath like a syringe, piercing the cell wall with its central tube and injecting the genetic material into the host. The injected DNA takes over the host cell's mechanisms for transcription and translation and begins to manufacture new viruses. Lysis occurs once the host resources are exhausted and the new viruses escape from the dead host cell.
Although Myoviruses are in general lytic lacking the genes required to become lysogenic, a number of lysogenic species are known.
Subdivisions
The subfamily Teequatrovirinae is named after its type species Enterobacteria phage T4. Members of this subfamily are morphologically indistinguishable and have moderately elongated heads of about 110 nanometers (nm) in length, 114 nm long tails with a collar, base plates with short spikes and six long kinked tail fibers. The genera within this subfamily are divided on the basis of head morphology with the T4-like genus having a head length of 137 nm and those in the KVP40-like being 111 nm in length. Within the genera on the basis of protein homology the species have been divided into a number of groups.
The subfamily Peduovirinae have virions with heads of 60 nm in diameter and tails of 135 × 18 nm. These phages are easily identified because contracted sheaths tend to slide off the tail core. The P" phage is the type species.
The subfamily Spounavirinae are all virulent, broad-host range phages which infect members of the Firmicutes. They possess isometric heads of 87-94 nm in diameter and conspicuous capsomers, striated 140-219 nm long tails and a double base plate. At the tail tip are globular structures now know to be the base plate spikes and short kinked tail fibers with six-fold symmetry. Members of this group usually possess large (127–142 kb) nonpermuted genomes with 3.1–20 kb terminal redundancies. The name for this subfamily is derived from SPO plus una (latin for one).
Taxonomy
Subfamily Teequatrovirinae
- Genus T4-like viruses:
-
- Group T4 type:
- Species:
- Enterobacteria phage T2
- Enterobacteria phage T4
- Enterobacteria phage T6
- Escherichia coli phage RB69
- phage JS10
- phage JS98
- phage RB14
- phage RB32
- phage RB51
-
- Group 44RR-type:
- Species:
- Aeromonas phage 44RR2.8t
- phage 31
- phage 25
-
- Group RB43-type:
- Species:
- phage RB43
- phage RB16
-
- Group RB49-type:
- Species:
- phage RB49
- phage JSE
- phage phi1
- Genus KVP40-like viruses:
- Species:
- Vibrio parahaemolytius phage KVP40
- Vibrio natriegens phage nt-1
- Species:
-
- Other species:
- Acinetobacter phage 133
- Aeromonas phage 65
- Aeromonas phage Aeh1
- Enterobacteria phage SV14
- Escherichia coli phage RB43
- Escherichia coli phage RB49
- Pseudomonas phage 42
- Other species:
Subfamily Peduovirinae
- Genus P2-like viruses; type species: Enterobacteria phage P2
- Species:
- Enterobacteria phage 186
- Enterobacteria phage P2
- Species:
- Genus HP1-like viruses:
- Species:
- Aeromonas phage ΦO18P
- Haemophilus phage HP1
- Haemophilus phage HP2
- Species:
- Genus Unassigned
- Species
- Burkholderia cepacia phage KS5
- Burkholderia cepacia phage KS14
- Burkholderia cepacia phage KL3
- Species
- Genus SPO1-like viruses: type species: Bacillus phage SPO1
- Species:
- Bacillus phage SPO1
- Lactobacillus phage 222a
- Species:
- Genus Twort-like viruses:
- Species:
- Listeria phage A511
- Listeria phage P100
- Staphylococci aureus phage 812
- Staphylococci aureus phage G1
- Staphylococcus aureus phage ISP
- Staphylococci aureus phage K
- Staphylococci aureus phage MSA6
- Staphylococci aureus phage Twort
- Species:
Species unassigned to a genus in this subfamily:- Enterococcus faecalis phage phiEF24C
- Lactobacillus plantarum phage LP65
Genera not yet assigned to a subfamily
- Genus Bcep781-like viruses
- Species:
- Burkholderia cepacia phage Bcep 1
- Burkholderia cepacia phage Bcep 43
- Burkholderia cepacia phage Bcep 781
- Burkholderia cepacia phage Bcep NY3
- Xanthomonas phage OP2
- Species:
- Genus BcepMu-like viruses:
- Species
- Burkholderia cenocepacia phage BcepMu
- Burkholderia thailandensis phage E255
- Species
- Genus Felix O1-like viruses:
- Species
- Enterobacteria phage wV8
- Erwinia amylovora phage Ea21-4
- Salmonella phage Felix O1
- Species
- Genus HAP1-like viruses:
- Species
- Halomonas aquamarina phage HAP-1
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus phage VP882
- Species
- Genus I3-like viruses; type species: Mycobacterium phage I3
- Species:
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage Bxz1
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage Cali
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage Catera
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage I3
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage Myrna
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage Rizal
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage ScottMcG
- Mycobacterium smegmatis phage Spud
- Species:
- Genus Mu-like viruses; type species: Enterobacteria phage Mu
- Species:
- Enterobacteria phage D108
- Enterobacteria phage Mu
- Escherichia blattae prophage MuEb
- Haemophilus influenzae Rd prophage Hin-Mu
- Rhodobacter capsulatus phage RcapMu
- Shewanella oneidensis prophage MuSo2
- Species:
- Genus P1-like viruses; type species: Enterobacteria phage P1
- Species:
- Aeromonas phage 43
- Enterobacteria phage P1
- Species:
- Genus PB1-like viruses:
- Species
- Pseudomonas phage PB1
- Pseudomonas phage F8
- Burkholderia cepacia phage BcepF1
- Pseudomonas phage 14-1
- Pseudomonas phage LBL3
- Pseudomonas phage LMA2
- Pseudomonas phage SN
- Species
- Genus phiCD119-like viruses
- Species:
- Clostridium difficile phage ΦCD27
- Clostridium difficile phage phiC2
- Clostridium difficile phage ΦCD119
- Species:
- Genus PhiH-like viruses; type species: Halobacterium phage phiH
- Species
- Halobacterium salinarium phage phiH
- Species
- Genus PhiKZ-like viruses; type species: Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage phiKZ
- Species:
- Pseudomonas phage 2012-1
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage Lin21
- Pseudomonas phage Lin68
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage NN
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage phiKZ
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage PTB80
- Species:
- Genus Vi01-like viruses; type species: Salmonella typhi phage Vi01
- Species
- Salmonella typhi phage Vi01
- Salmonella typhimurium phage PhiSH19
- Shigella phage SboM-AG3
- Species
Unassigned species
- Genus Unassigned
- Species:
- Acinetobacter phage E4
- Acinetobacter phage E5
- Aeromonas phage 1
- Aeromonas phage 25
- Acinetobacter calcoaceticus phage E14
- Aeromonas salomicida phage 31
- Aggregatibacter phage Aaphi23
- Bacillus phage G
- Bacillus phage PBS1
- Bacillus cereus phage Bace-11
- Bacillus megaterium phage MP13
- Bacillus subtilis killer virus defect particle
- Bacillus thuringiensis phage 03058-36
- Clostridium phage c-st
- Cronobacter sakazakii phage ES2
- Cronobacter sakazakii phage ESP2949-1
- Escherichia phage phiEcoM-GJ1
- Escherichia phage rV5
- Gluconobacter virus Wer
- Microcystis aeruginosa phage Ma-LMM01
- Natrialba magadii virus psiCh1
- Pseudomonas phage EL
- Ralstonia solanacearum phage RSL1
- Ralstonia solanacearum phage RSA1
- Rhodothermus phage RM378
- Streptococcus phage EJ-1
- Thermus phage YS40
- phage P-SSM2
- phage P-SSM4
- phage S-PM2
- phage Syn9
- Species:
References
- ^ Lavigne R, Darius P, Summer EJ, Seto D, Mahadevan P, Nilsson AS, Ackermann HW, Kropinski AM (2009) Classification of Myoviridae bacteriophages using protein sequence similarity. BMC Microbiol 9:224.
External links
Baltimore (virus classification) DNA I: dsDNA viruses HerpesviralesUnassignedNLCDV: Asfarviridae · Iridoviridae · Marseilleviridae · Megaviridae · Mimiviridae · Phycodnaviridae · Poxviridae
nonenveloped: Adenoviridae · Papillomaviridae · Papovaviridae (obsolete) · Polyomaviridae
Ascoviridae · Baculoviridae · Corticoviridae · Fuselloviridae · Guttaviridae · Lipothrixviridae · Nimaviridae · Plasmaviridae · Rudiviridae · TectiviridaeII: ssDNA viruses non-enveloped: Parvoviridae (Parvovirus B19)
ungrouped: Circoviridae · Geminiviridae · Inoviridae · Microviridae · NanoviridaeRNA III: dsRNA viruses Birnaviridae · Chrysoviridae · Cystoviridae · Hypoviridae · Partitiviridae · Reoviridae (Rotavirus) · TotiviridaeIV: (+)ssRNA viruses (primarily icosahedral) PicornaviralesDicistroviridae · Iflaviridae · Marnaviridae · Picornaviridae (Enterovirus, Rhinovirus) · SecoviridaeTymoviralesUnassignedAstroviridae · Barnaviridae · Bromoviridae · Caliciviridae · Closteroviridae · Comoviridae · Flaviviridae · Flexiviridae · Leviviridae · Luteoviridae · Narnaviridae · Nodaviridae · Potyviridae · Sequiviridae · Tetraviridae · Togaviridae (Rubella virus) · TombusviridaeV: (-)ssRNA viruses (primarily helical) RT VI: ssRNA-RT viruses VII: dsDNA-RT viruses Categories:- Caudovirales
- Bacteriophages
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
