- Exeter to Plymouth railway of the LSWR
-
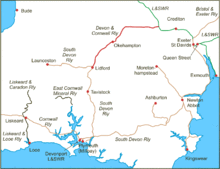
Exeter to Plymouth via Okehampton 
Meldon ViaductOverview Status Partly closed Locale Devon Termini Exeter Queen Street
Plymouth FriaryStations 24 Operation Opened 1851-1891 Closed 1968 (in part) Owner London and South Western Railway Technical No. of tracks 2 Track gauge 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) Standard gauge Exeter to Plymouth via Okehampton Legend

0.00 London Waterloo 




171.75 Exeter Central 

St David's Tunnel 


GWR to Plymouth 


172.50 Exeter St Davids 


Red Cow Crossing 


Cowley Bridge Jn GWR to London 


River Exe 


176.75 Newton St Cyres 


179.25 Crediton 


Crediton 


183.00 Yeoford 


Coleford Junction To Barnstaple 


187.75 Bow 


191.00 North Tawton 


193.75 Sampford Courtenay 

Fatherford Viaduct 


197.50 Okehampton 

Meldon Quarry 

Meldon Viaduct 


Meldon Junction To Bude 


Lake Viaduct 
To Rattlebrook Peat Works 


204.00 Bridestowe 


Lydford Viaduct 


GWR to Launceston 

207.25 Lydford 





208.75 Brentor 

GWR to Plymouth 


River Wallabrook Viaduct 


213.75 Tavistock North 


Tavistock Viaduct 


Shillamill Viaduct 

Shillamill Tunnel 

220.25 Bere Alston 


PDSJWR to Callington 


223.00 Bere Ferrers 


Tavy Viaduct 


Tamerton Foliot 


Tamerton Viaduct 


227.25 St Budeaux 


GWR to Penzance 


St Budeaux Jn 


GWR to Plymouth 


Weston Mill Halt 


Camels Head Halt 


Ford 


Ford Viaduct 


Ford Tunnel 


Albert Road Halt 


Devonport Park Tunnel 


229.50 Devonport 

To Stonehouse Pool 


Devonport Jn GWR to St Budeaux 




Plymouth Millbay 


Plymouth (North Road) 


Mutley 


Mutley Tunnel 


Lipson Vale Halt 


GWR to Lydford and Exeter 


GWR to Yealmpton 


GWR to Sutton Harbour 


To Turnchapel and Cattewatter 


To Sutton Harbour 




Plymouth Friary The Exeter to Plymouth railway of the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) was the westernmost part of a route competing with that of the Great Western Railway (GWR) and its 'associated companies' from London to Exeter and Plymouth in Devon, England. Whereas the GWR route from Exeter followed the coast to Newton Abbot and then went around the southern edge of Dartmoor, the LSWR route followed the northern and western margins of Dartmoor, passing through the towns of Crediton, Okehampton,and Tavistock.
The route was constructed piecemeal by independent companies supported by the LSWR. Their trains first reached Plymouth in 1876 and the route took on its final form in 1891. The central part of the line closed in 1968 leaving just local services at either end.
Contents
History
Exeter and Crediton
The LSWR started out as the London and Southampton Railway, but the company soon expanded and changed its name to reflect greater ambitions. Extensions and branch lines were built around the core route, but westward extension into Devon and Cornwall was a strategic objective that took longer to achieve. This was supported by the government as it wished to have a continuous line of railway between its principal dockyards;[1] most were served by 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge railways such as the LSWR, but the GWR system that served the Devonport Dockyard near Plymouth used a broad gauge of 7 ft 0 1⁄4 in (2,140 mm).[2]
The Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) had reached St Davids station in Exeter in 1844 and was connected with the GWR at Bristol to form a continuous route from London. The South Devon Railway (SDR) continued the line westward from Exeter to reach Plymouth in 1848. The LSWR found itself in competition with these broad gauge 'associated companies' throughout its route from London to the West Country.[3]
The LSWR finally opened to Exeter on 19 July 1860 after considerable difficulty in gaining parliamentary approval and financial support. Its terminus was at Queen Street station (now Exeter Central),[1] but it soon continued further westward by leasing two local companies, the Exeter and Crediton Railway and the North Devon Railway. To reach them the LSWR built a new line from Queen Street (converting it to a though station) to St Davids, from where it was granted running powers northwards over the B&ER to Cowley Bridge Junction, where the Crediton line branched off westwards.[4]
The Exeter and Crediton had been authorised by Act of Parliament on 21 July 1845, and opened on 12 May 1851. It was a broad gauge line operated by the B&ER, which owned 40% of the company’s shares, but the LSWR owned the other 60% and leased it from 1 February 1862. LSWR trains began running from Queen Street to Crediton two days later, after which time the B&ER only operated freight trains on the line. A third rail was laid along the line between St Davids and Crediton to give a 'mixed gauge' on which trains of either gauge could run. The Exeter and Crediton company was sold to the LSWR in 1879.[4]
The route was continued north of Crediton by the North Devon Railway which had opened on 12 July 1854. This too was a broad gauge line but it was operated by Thomas Brassey, the engineer who built it. This line was leased to the LSWR from 1 August 1862 which then ran its trains right through to Barnstaple and Bideford. At first it had to use Brassey’s broad gauge stock, but the line was also mixed gauge from 2 March 1863. The North Devon was amalgamated into the LSWR on 1 January 1865.[4]
On to Plymouth
The Okehampton Railway, an independent company supported by the LSWR, was authorised on 17 July 1862 to build a line from Coleford Junction (north west of Crediton) to Okehampton. Before the line was built it had been leased to the LSWR and an extension authorised to Lidford. In 1864 it was renamed as the Devon and Cornwall Railway and construction finally started. It opened slowly in sections: from Coleford Junction to North Tawton on 1 November 1865; from there to Okehampton Road (later renamed Sampford Courtenay) on 8 January 1867; to Okehampton itself on 3 October 1871; and finally to Lidford on 12 October 1874.[4] (This was spelt Lydford from 3 June 1897.)[5] The Devon and Cornwall Company had been taken over by the LSWR in 1872, before its line was complete.[6]
Lidford was chosen as the terminus because from there a connection with the SDR's Tavistock branch line could give LSWR trains access to Plymouth via Tavistock. However it was only on 17 May 1876 that the connection was made and trains could run through to Plymouth. This was a broad gauge line so, as at Crediton, a third rail was added to create a mixed gauge route.[5]
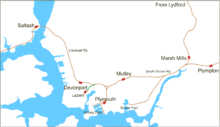
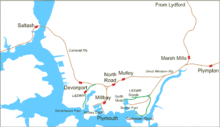
Running over the SDR line, the trains of the LSWR entered Plymouth from the east. Trains called at the cramped and inconvenient Mutley station, but on 28 March 1877 a new, more spacious, North Road station was opened a little further west. LSWR trains now used this as their principal Plymouth calling point, although some trains continued to call at Mutley. Both stations were shared with the broad gauge companies.[7] LSWR trains continued to the company's own Devonport and Stonehouse terminus.[8] At this time Devonport and Stonehouse, Plymouth were independent towns and the former, with its naval dockyards, was an important traffic source. To reach their station they used the 'Cornwall Loop', a newly built connection from the SDR to the Cornwall Railway which avoided a reversal at their Plymouth Millbay terminus.[9]
Having obtained a foothold in both Plymouth and Devonport, the LSWR now set about improving its facilities in the area so that it could reduce its dependency on the broad gauge companies. On 1 February 1878 it opened its own goods station at Friary on the east side of Plymouth. This used a connection over the SDR's Sutton Harbour branch, which made an east-facing connection with the main line at Laira Junction that allowed LSWR goods trains to run directly from the Lidford line to Friary. The LSWR opened a short extension from Friary to the wharves at nearby Sutton Harbour on 22 October 1879.[7]
In 1880 it made another line from near Friary to the Plymouth and Dartmoor Railway's old 4 ft 6 in (1,372 mm) gauge route to Cattewater, which gave it access to more quays. Meanwhile on the other side of Plymouth, the Stonehouse Pool Improvement Company had been formed to create a quay that large vessels could use at all states of the tide. It proposed to build a railway connection to Devonport station which the LSWR agreed to rent, and this opened for freight traffic on 1 March 1886.[7] From 1904 to 1910 transatlantic passengers joined fast London boat trains at the quay.[10]
Independent route
Access to Plymouth was inconvenient as LSWR trains had to run over the GWR's lines from Lidford to Plymouth and Devonport, most of which was just a single-track where GWR trains were given precedence. In 1882 an Act of Parliament was passed to allow the construction of independent lines alongside the GWR route from Lydford to a new station in the centre of Plymouth. This scheme was replaced the following year by that of another independent company supported by the LSWR, the Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway (PD&SWJR). This obtained its Act on 25 August 1883 for a new railway from Lidford which would pass to the west of Tavistock then down the valley of the River Tamar to reach Plymouth. In 1889 the idea of a central station in Plymouth was abandoned in favour of running to Devonport and converting Friary to a passenger terminus.[11]
The PD&SWJR line opened on 2 June 1890 and this changed Devonport into a through station. The new west-facing connection to Friary was brought into use on 1 April 1891. Trains to London now started from Friary, ran through Plymouth from east to west, called at North Road, and continued westwards through Devonport before heading north alongside the Tamar.[11] They might have passed a GWR train for London running in the other direction through Plymouth; at Exeter this anomaly was repeated when they ran southwards from Cowley Bridge to St Davids, where GWR trains to London ran northwards.
In 1897 a branch was opened from Friary to Turnchapel. Competition from tramways in Plymouth and Devonport in the first decade of the twentieth century spurred the company into constructing several new stations in the towns and running an intensive suburban railmotor service.[8]
The GWR had amalgamated with the B&ER, SDR and Cornwall Railway during the 1870s and 1880s, and converted their lines to standard gauge in 1892. In the weeks before the conversion some of the new rolling stock required was worked over the LSWR to reach the Plymouth area, and during the two days that the line was closed they also sent the important London mail trains by this route.[3]
After the LSWR
Unlike the other companies supported by the LSWR, the PD&SWJR remained an independent company until, in 1923, it and the LSWR became a part of the new, larger Southern Railway. This in turn became the Southern Region of British Railways in 1948, at the same time as the GWR became the Western Region of British Railways. During the 1950s and 1960s there were many boundary changes between the two regions, but eventually all the former LSWR lines in Devon and Cornwall became part of the Western Region. Traffic was now concentrated on the former GWR routes. The last timetabled through service, from Brighton to Plymouth, used the route in March 1967.[11] Friary station had been closed to passengers on 15 September 1958 but was retained as the city's principal goods depot; passenger trains then used North Road as their terminus.[8] Devonport station closed on 7 September 1964 and trains were diverted to the former GWR route between Plymouth and St Budeaux. Here they regained the LSWR route by a connection that had been opened on 2 March 1941 as a precaution against damage on either line during World War II.[12] The line onwards to Bere Alston was retained as access to the Gunnislake branch, which is nowadays marketed as the Tamar Valley Line.[13]
Trains between Exeter and Plymouth via Okehampton were withdrawn from 6 May 1968. The 20 miles (32 km) section between Meldon Quarry and Bere Alston was lifted, and between Meldon and Okehampton the line was only retained for freight trains. Okehampton to Exeter passenger services were withdrawn on 5 June 1972. This left just Barnstaple line services between Exeter and Yeoford (the Tarka Line)[14] however since 1997 a limited service has run between Okehampton and Exeter on Sundays during the summer.[8] The heritage trains of the Dartmoor Railway also operate between Meldon Quarry, Okehampton and Sampford Courtenay at other times.[15] A cycle path follows the route over Meldon, Lake, Wallabrook and Tavistock viaducts. The other two viaducts, at Lydford and Shillamill, remain intact.[citation needed]
There are proposals to reopen the line from Tavistock to Bere Alston for a through service to Plymouth.[16] Devon and Cornwall Railways are planning to reintroduce a weekday service between Okehampton and Exeter.[17]
Geography
Engineering features
As the line leaves Exeter Central it drops at 1 in 37 and passes through a tunnel to reach St Davids station, where the line is only just above the level of the River Exe. It follows this and crosses it shortly after leaving the GWR route at Cowley Bridge Junction. From here to Yeoford it follows river valleys,[4] but the next stage of the route, through Okehampton and Lydford, takes it around the northern edge of Dartmoor. Meldon Summit to the west of Meldon Junction was the highest point on the line. Indeed, it was the highest point on the whole of the Southern Railway, at 950 feet (290 m) above sea level.[11]
The GWR route from Lydford to Plymouth crossed many valleys on timber viaducts.[5] The PD&SWJR route into Plymouth followed the valley of the River Tamar but still involved much heavy engineering with gradients as steep as 1 in 73. Between Tavistock and the Tamar the line passes through the 605-yard (553 m) Shillamill Tunnel. Two wide tributaries join the Tamar which are crossed by the long iron Tavy Viaduct and Tamerton Viaduct. After passing twice beneath the GWR Cornish Main Line there and two tunnels of 363 yards (332 m) and 534 yards (488 m) at Ford and Devonport Park.[11] On the GWR section the line crossed the viaduct which carries the Cornwall Loop near North Road station, and dives through Mutley Tunnel.[18]
Stations
Dates of opening and closure refer to passenger services unless otherwise stated.[8]
- Exeter Queen Street – opened 19 July 1860
- Exeter St Davids – LSWR services from 3 February 1862
- Newton St Cyres – LSWR services from 3 February 1862
- Crediton – LSWR services from 3 February 1862
- Yeoford – LSWR services from 1 August 1862
- Bow – opened 1 November 1865, closed 5 June 1972
- North Tawton – opened 1 November 1865, closed 5 June 1972
- Sampford Courtenay – opened 8 January 1867, closed 5 June 1972, reopened 23 May 2004
- Okehampton – opened 3 October 1871, closed 5 June 1972, reopened 24 May 1997
- Meldon Quarry - Staff Halt opened c.1925, closed 6 May 1968. New station opened in 2000
- Bridestowe – opened 12 October 1874, closed 6 May 1968
- Lydford – LSWR services from 12 October 1874, closed 6 May 1968
- Mary Tavy and Blackdown Halt – LSWR services from 17 May 1876 to 31 May 1890
- Tavistock GWR – LSWR services from 17 May 1876 to 31 May 1890
- Horrabridge – LSWR services from 17 May 1876 to 31 May 1890
- Yelverton – opened 1 May 1885, LSWR services to 31 May 1890
- Bickleigh – LSWR services from 17 May 1876 to 31 May 1890
- Marsh Mills – LSWR services from 17 May 1876 to 31 May 1890
- Brentor – opened 1 June 1890, closed 6 May 1968
- Tavistock – opened 1 June 1890, closed 6 May 1968
- Bere Alston – opened 1 June 1890
- Bere Ferrers – opened 1 June 1890
- Tamerton Foliot – opened 22 December 1897, closed 10 September 1962
- St Budeaux – opened 1 June 1890
- Weston Mill Halt – opened 1 November 1906, closed 27 June 1921
- Camels Head Halt – opened 1 November 1906, closed 4 May 1942
- Ford – opened 1 June 1890, closed 7 September 1964
- Albert Road Halt – opened 1 October 1906, closed 13 January 1947
- Devonport – opened 17 May 1876, closed 7 September 1964 (goods traffic to 7 March 1971)
- Plymouth North Road – opened 28 March 1877
- Mutley – LSWR services from 17 May 1876, closed 3 July 1939
- Lipson Vale Halt – SR services from 8 July 1930,[19] closed 22 March 1942
- Plymouth Friary – opened 1 July 1891, closed 15 September 1958 (goods traffic 1878 to 1963)
See also
References
- ^ a b Phillips, Derek; Pryer, George (1997). The Salisbury to Exeter Line. Sparkford: Oxford Publishing Company. ISBN 0-86093-525-6.
- ^ Burkhalter, Paul (1996). Devonport Dockyard Railway. Truro: Twelveheads Press. ISBN 0-90629-437-1.
- ^ a b MacDermot, E T (1931). History of the Great Western Railway. 2 (1863-1921) (1 ed.). London: Great Western Railway.
- ^ a b c d e Nicholas, John (1992). The North Devon Line. Sparkford: Oxford Publishing Company. ISBN 0-86093-461-6.
- ^ a b c Anthony, GH; Jenkins, SC (1997). The Launceston Branch. Headington: Oakwood Press. ISBN 0-853614-91-3.
- ^ St John Thomas, David (1973). West Country Railway History. Newton Abbot: David and Charles. p. 102. ISBN 0-715363-63-8.
- ^ a b c Williams, R A (1973). The London and South Western Railway. 2. Newton Abbot: David and Charles. ISBN 0-7153-5940-1.
- ^ a b c d e Oakley, Mike (2007). Devon Railway Stations. Wimbourne: The Dovecote Press. ISBN 1-904349-55-6.
- ^ Gregory, R H (1982). The South Devon Railway. Salisbury: Oakwood Press. ISBN 0-853612-86-2.
- ^ Kitteridge, Alan (1993). Plymouth: Ocean Liner Port-of-Call. Truro: Twelveheads Press. ISBN 0-906294-30-4.
- ^ a b c d e Cheeseman, AJ (1967). The Plymouth, Devonport & South Western Junction Railway. Blandford Forum: Oakwood Press.
- ^ Crozier, Larry (2000). Mechanical Signalling in Plymouth. Wallasey: Signalling Record Society. ISBN 1-873228-18-X.
- ^ "The Tamar Valley Line". Car Free days Out. Devon and Cornwall Rail Partnership. http://www.carfreedaysout.com/tamar.html. Retrieved 2010-08-03.
- ^ "The Tamar Valley Line". Car Free days Out. Devon and Cornwall Rail Partnership. http://www.carfreedaysout.com/tarka.html. Retrieved 2010-08-03.
- ^ "Timetables and fares". Dartmoor Railway. Dartmoor Railway. http://www.dartmoor-railway.co.uk/timetables.html. Retrieved 2010-08-03.
- ^ Harris, Nigel (2008). "Taking trains back to Tavistock". Rail (Bauer) (590): 40–45.
- ^ "Okehampton daily service proposed". Modern Railways (Ian Allan) 67 (740): 6. May 2010. ISSN 9926-8356.
- ^ Jacobs, Gerald (2005). Railway Track Diagrams Book 3: Western. Bradford-on-Avon: Trackmaps. ISBN 0-954986-61-X.
- ^ St John Thomas, David (1973). West Country Railway History. Newton Abbot: David and Charles. p. 249. ISBN 0-715363-63-8.
Categories:- Rail transport in Devon
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.