- DF-4
-
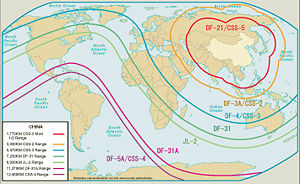
DF-4/CSS-3 Type ICBM Service history In service 1975-1976[1][2] Used by PRC Production history Manufacturer Factory 211 (Capital Astronautics Co.) Unit cost ? Specifications Weight 82,000 kg Length 28.05 m Diameter 2.24 m Warhead One,[1] or three (DF-4A)[6][7] Blast yield 3.3 Mt[1] Engine Liquid fueled Operational
range5,500 km[1]-7,000 km[3][4][5] Speed ? Guidance
systemInertial and celestial guidance The Dong Feng 4 (Chinese: 东风4) or DF-4 (also known as the CSS-3) is a two-stage Chinese Intercontinental ballistic missile[8] with liquid fuel (Nitric acid/UDMH). It was thought to be deployed in limited numbers in underground silos beginning in the 1970s and early 1980s. The Dong Feng 4 has a takeoff thrust of 1,224.00 kN, a takeoff weight of 82000 kg, a diameter of 2.25 m, a length of 28.05 m and a fin span of 2.74 m. The range of the Dong Feng 4, which is equipped with a 2,190 kg nuclear warhead with 3.3 Mt yield, with a nominal range of 5,500 km. The missile uses an inertial guidance system, resulting in a CEP of 1,500 meters.
Contents
History
The decision to develop the DF-4 was made in 1965[9] in response to the U.S. ballistic missile submarine patrols that began operating out of Guam. The missile's designer has been variously identified as Ren Xinmin or Tu Shou'e [屠守锷], and it was produced at Factory 211 (Capital Astronautics Co. [首都航天机械公司], also known as Capital Machine Shop [首都机械厂]).
In 1972 US intelligence estimated an IOC for this system as being expected in 1974 or 1975. Deployment actually began in 1975-76, but only four DF-4s were believed to be in place by 1984.[10]
There were two versions of the missile developed,[11] one version housed in caves or garages to be rolled out on launch and another silo based version.
The U.S. DoD estimates that the missile will continue to serve as a regional deterrence instrument until they can be replaced by the DF-31.[12]
Notes
- ^ a b c d The Federation of American Scientists & The Natural Resources Defense Council Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning p. 202 [1]
- ^ PRC Defense Policy and Armed Forces, National Intelligence Estimate 13-76, November 11, 1976, p. 47.
- ^ http://www.cdi.org/issues/nukef&f/database/chnukes.html#df4
- ^ http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/china/theater/df-4.htm
- ^ http://www.globalsecurity.org/wmd/world/china/df-4.htm
- ^ http://www.5school.com/wap.aspx?nid=12900&p=2&cid=100&sp=87
- ^ http://csatm.cn/f0309110006.html
- ^ 东风4型洲际导弹 (Dongfeng VI intercontinental ballistic missile)
- ^ U.S. Department of Defense, Office of the Secretary of Defense, The Military Power of the People’s Republic of China, 2005, 2005, p. 28
- ^ "DF-4 - China Nuclear Forces". Fas.org. http://www.fas.org/nuke/guide/china/theater/df-4.htm. Retrieved 2010-03-21.
- ^ U.S. Department of Defense, Office of the Secretary of Defense, The Military Power of the People’s Republic of China, 2000, 2000, p. 17.
- ^ U.S. Department of Defense, Office of the Secretary of Defense, Military Power of the People’s Republic of China, 2006, May 22, 2006, p. 50.
Operators
 China: The People's Liberation Army is the only operator of the Dong-Feng 4.
China: The People's Liberation Army is the only operator of the Dong-Feng 4.
External links
Preceded by
DF-3DF-4 Succeeded by
DF-5 Missiles of the People's Republic of China
Missiles of the People's Republic of ChinaSurface-to-
SurfaceBallistic MissilesAnti-ShipDF-21D[1]YJ-85 (C-805)[1] · YJ-12 · YJ-22 · YJ-7 (C-701) · C-703 · YJ-62 (C-602) · KD-88 · YJ-4 · KD-63 · YJ-63 (C-603) · YJ-2 · YJ-1 · C-611 · XW-41DH-2000 · HN-2000 · YJ-91 · YJ-83 (C-803) · FL-7 · HY-3 (C-301) · FL-2 (C-101) · CJ-1 · YJ-12 · YJ-22 · 3M-80MBE/E Moskit (SS-N-22) · 3M-54E/E1 Klub (SS-N-27) · C-302 · C-303 · YJ-2 · YJ-1YJ-82 (C-802) · YJ-8 (C-801) · C-704 · YJ-7 (C-701) · FL-10 · C-703 · YJ-62 (C-602) · TL-10 · FL-8 · TL-1 · TL-2 · TL-6 · FL-9 · SY-2 · SY-1 · HY-4 (C-401) · HY-2 (C-201) · HY-1 · C-611 · XW-41Air-to-
SurfaceYJ-2 · YJ-1 · C-611 · XW-41 · YJ-22 · YJ-12 · BA-7 · AKD-10 · AR-1 · YJ-85 (C-805)[1] · C-704KD · YJ-7 (C-701) · C-703 · YJ-62 (C-602) · KD-88 · KD-63 · YJ-63 (C-603) · Kh-59 · Kh-29 · YJ-4 · QW-1DH-2000 · HN-2000 · YJ-91 · YJ-83 (C-803) · FL-7 · HY-3 (C-301) · FL-2 (C-101) · CJ-1 · YJ-12 · YJ-22 · 3M-80MBE/E Moskit (SS-N-22) · 3M-54E/E1 Klub (SS-N-27) · C-302 · C-303 · YJ-2 · YJ-1YJ-82 (C-802) · YJ-8 (C-801) · C-704 · YJ-7 (C-701) · FL-10 · C-703 · YJ-62 (C-602) · TL-10 · FL-8 · TL-1 · TL-2 · TL-6 · FL-9 · SY-2 · SY-1 · HY-4 (C-401) · HY-2 (C-201) · HY-1 · C-611 · XW-41 · Kh-35GB-1 · LS series · LT series · FT series · YZ-100 series · YZ-102 series · YZ-200 series · KAB-1500Kr · KAB-500KrSurface-to-
AirFJ · KT-1 · KT-2 · KT-III · HQ-18 · S-300PMU-2 · HQ-15 · S-300PMU-1 (HQ-10) · HQ-9 · KS-2 · KS-1 · HQ-12HQ-19 · HQ-18 · S-300PMU-2 · HQ-15 · S-300PMU-1 (HQ-10) · HQ-9 · FD-2000 · S-300PMU · S-300FM · HQ-12 · KS-1 · KS-2Man Portable SAMsAir-to-Air Beyond Visual Range AAMsNotes: 1. Under Development
List of Chinese missiles · People's Liberation ArmyCategories:- Intercontinental ballistic missiles of the People's Republic of China
- People's Liberation Army guided missiles
- Nuclear program of the People's Republic of China
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.