- Niijima
-
Niijima Native name: 新島 
Yunohama Onsen, Niijima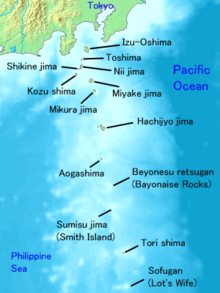
Geography Location Izu Islands Coordinates 34°22′N 139°16′E / 34.367°N 139.267°E Archipelago Izu Islands Area 23,870 m2 (256,930 sq ft) Length 11,000 m (36,000 ft) Width 3,000 m (10,000 ft) Highest elevation 432 m (1,417 ft) Country JapanDemographics Population 2700 (as of September 2009) Niijima (新島) is a volcanic Japanese island in the Philippine Sea, administered by Tokyo Metropolitan Government. It is one of the Izu Seven Islands group of the seven northern islands of the Izu archipelago, and is located approximately 163 kilometres (101 mi) south of Tōkyō and 36 kilometres (22 mi) south of Shimoda Shizuoka Prefecture. The island is the larger inhabited component of the village of Niijima Village, Ōshima Subprefecture of Tokyo Metropolis, which also contains the larger, neighboring island of Shikinejima and the smaller, uninhabited Jinai-tō. Niijima is also within the boundaries of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park.
On the southern tip of Niijima, was formerly a launch site for experimental and sounding rockets.
Contents
Geography
Niijima is unusual amongst the Izu Islands in that it has an elongated shape. Measuring approximately 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) long by 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) wide, it has a land area of 23.87 km². The island is made of eight rhyolitic lava domes in two groups at the northern and southern ends of the island, separated by a low, flat isthmus. The Mukaiyama (向山) complex in the southern portion of the island and the Achiyama lava dome at the northern end were formed during Niijima's only historical eruptions in the 9th century AD. The northern end also contains Miyatsukayama (宮塚山), the island’s highest point, at 432 metres (1,417 ft). Shikinejima and Jinnai-to are part of the same complex, and form separate islands to the southwest and west of Niijima. Rhyolite lava gives the island its famed white cliffs and white sandy beaches
Niijima is prone to earthquake swarms. According to the US Geological Survey map, the area around Niijima averages 10 – 20 earthquakes, with a magnitude of 5 or greater, each year. However, the often repeated legend that Niijima and Shikinejima were once a single island that was separated by huge tsunami caused by the 1703 Genroku earthquake has no basis in geology.
Access
Niijima is 2 hours and 20 minutes away by jet boat from Takeshiba Sanbashi Pier, in Tokyo, operated by Tōkai Kisen. Tōkai Kisen also operates a 9-hour over-night ferry. The ferry leaves Takeshiba Sanbashi at 22h00 (23h00 in the summer months) and arrives early morning in Izu Ōshima (approximately 6h00), before continuing on to Toshima (7h00), Niijima (8h00), Shikinejima (8h30), and Kōzushima (9h30). The ferry then returns following the same route, leaving Niijima at 12h00 and docking in Tokyo at 17h00. It is possible that in rough weather, the ferry is unable to dock in Niijima.
There are daily flights, weather permitting, from Chōfu Airport located in western Tokyo. The flight takes approximately 45 minutes.
Other ferries leave from Shimoda, Shizuoka Prefecture.
Niijima-mura also operates a high-speed ferry between Niijima and Shikinejima with 3 boats per day, and 4 per day in the summer months.
History
Niijima has been inhabited since prehistoric times, and archaeologists have found numerous remains from the Jōmon period, including stone and ceramic utensils. During the Edo period, as with Hachijōjima, Niijima was used as a place of exile for convicts. The practice was discontinued after the Meiji Restoration.
Industry
Main industries in Niijima include commercial and sports fishing, construction, koga rock mining, and tourism. There is also some small scale farming.
Koga stone, a silica-based volcanic rock called rhyolite in English, found on the island, is used to make transparent green glass art. It can also be used to make moyai art. The stone is indigenous only to Niijima and Lipari Island, Italy.
Tourism
Sites
Maehama Beach on the western side of Niijima sees many wind surfers. The triathlon and ocean water swims take place here. Mt. Fuji can often be seen from Maehama.
Habushi Beach, on the eastern side of the island, is a nationally protected reserve with its waves and white sand, and is a good location for surfing. The beach is approximately 6.5 km long and is overlooked by koga volcanic cliffs, the highest of which is 250 meters.
Moyai Hill, overlooking Yunohama and Maehama beaches, contains more than 100 large stone carvings. In the local dialect, moyai means 'to work together in effort', and these statues make evident this effort. On the western side of JR Shibuya in Tokyo proper is a giant moyai statue, a gift from the people of Niijima.
Yunohama Onsen hot spring, on Yunohama Beach, is a large outdoor bath built in the style of pseudo-Greek ruins that provides stunning panoramic views of the setting sun and the Pacific Ocean. The bath itself accommodates up to 100 bathers. Water used in the bath is drawn from the ocean below.
Jūsansha Jinja, is a Shinto shrine at the base of the cliffs of Mt. Miyatsuka in the north-western corner of the main village on the island. This shrine, built in the Edo period, is recognized as caretakers of intangible cultural assets by the Tokyo government for the kagura music and sacred dancing, known as shishi-kiyari that are held every December 8.
Nearby Jūsansha is Chōei-ji, Chōei Temple, a temple dedicated to Nichiren Buddhism. Beside the temple lies the Exiles' Cemetery. The cemetery, covered with the local white sand, is dominated by the gravestones of the 118 exiles, banished to Niijima by the Tokugawa Shogunate during the Edo era for non-political crimes.
A short walk from Chōei Temple is the Exile Execution Ground. Eleven exiles who committed crimes on the island were executed here. Komori Yasu, from the kabuki story 'Yowa Nasake Ukinano Yokoguchi' is buried here.
Niijima Glass Art Center is a world-renowned site which hosts the Niijima International Glass Art Festival every autumn. At the center, visitors are able to create their own glass work to take home. Next to the museum is the Niijima Glass Art Museum which houses works from guest artists at the festival.
Niijima-mura Museum, houses artifacts from the island’s pre-history up to its modern-day surfing culture. Included is a replica fishing vessel and house from the Edo period. Details of the criminal exiles are given. A collaborative effort between the education board and the English department at Niijima High School ensured that the museum is completely bilingual: Japanese-English.
Events
Niijima hosts the Tokyo Islands Triathlon in Niijima (1.5 km swim, 35 km bicycle ride, and a 10 km run) every May and the Niijima Open Water Swimming (1.5, 3, and 4.5 km open water swims). In the summer months, a number of surfing competitions take place at Habushi Beach. Sport fishing and scuba diving are also popular with both residents and tourists.
Every autumn, the Niijima International Glass Art Festival takes place. The festival has taken place since 1988. The festival draws leading glass artists who lead workshops and demonstrations in glass art. Artists who have participated in the festival in the past include: Dale Chihuly, William Morris, and Lucio Bubaco. Work by the above artists, and many more, are on display in the museum.
Other attractions
Other attractions on Niijima include: Ebine (Calanthe discolor), a pinkish-purplish orchid, can be found throughout the island, especially in Ebine Park, which opens from early spring.
Souvenirs from Niijima include the island specialty kusaya - a dried fish, usually mackerel scad (Decapterus macarellus), that has been soaked in a special brine. Kusaya, which means smells bad in Japanese, has an odor that is indeed 'quite' distinct. The village museum has a video on the making of kusaya. If you can get past the smell, you will be rewarded with a rich, delicious meal. Other souvenirs are milk senbei, the ashitaba plant, Niijima glass art, and a local Shōchū called Shima Jiman, island pride.
Popular Youtuber from Japan, Chris Gen, featured a trip to Niijima and some of his favorite spots of interest in his video.
Further points of interest
- LORAN-C transmitter Niijima
See also
References
External links
- Entry at Oceandots.com
- Japan Travel Guide: Niijima, in English with Japanese Subtitles
- Village of Niijima (Administering Niijima and Shikinejima), in Japanese
- Encyclopedia Astronautica - Niijima
- Niijima Glass Art Center, in English
- Niijima-mura Museum, in Japanese
- Metropolis, Travel, Niijima, in English
- Tokyo Niijima Island Sports Series, in Japanese
- Tokai Kisen Ferry, in Japanese
- Central Air, Chōfu, Tokyo, in Japanese
Categories:- Islands of Tokyo
- Izu-Bonin volcanic arc
- Active volcanoes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.










