- Dinosaur Cove
-
Not to be confused with the children's book series of the same name.
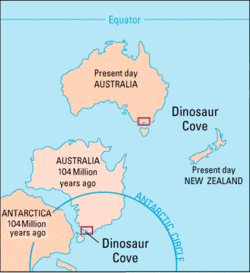
Dinosaur Cove in Victoria, Australia is a fossil bearing site in south-east of the continent where the Otway Ranges meet the sea to the west of Cape Otway, adjacent to Great Otway National Park (map).[1] The inaccessible ocean-front cliffs include fossil-bearing strata that date back to about 106 million years ago (MYA) and has provided discoveries important in research of natural history of dinosaurs in Australia and southern hemisphere as a whole.
Contents
Geological time-line
During the Early Cretaceous the location was a flood plain within a great rift valley that formed as Australia started to separate northward from Antarctica. Sand, mud and silt deposits covered and sometimes preserved the remains of dead animals and plants. As the rift valley sank, the deposits were overlaid by sediment, which turned to rock under pressure. In the last 30 million years the sediments have been uplifted to form the Otway Ranges and Strzelecki Ranges, bringing them near the surface again.
The richest find of petrified dinosaur bones is confined to narrow thin (up to 0.3 m) layers, most likely ancient stream beds serving as repositories of the bones of smaller animals.[2]
History of discovery
In 1903, geologist William Hamilton Ferguson was mapping the rocky coastal outcrops a few kilometres west of Inverloch and uncovered the first dinosaur fossil ever discovered in Australia.[3]
75 years later, the exploration and excavation of the Dinosaur Cove site was conducted by teams of volunteers overseen by Thomas H. Rich and Patricia Rich. The dinosaur taxa, Leaellynasaura amicagraphica and Timimus hermani, are named for the children of the Riches', Tim and Leaellyn. Heavy mining equipment and dynamite was used to blast away overlying strata to uncover the fossiliferous rock layers in the cliff face. [3]
In the 1980s and 90s Dinosaur Cove yielded hypsilophodontid-like dinosaurs as Leaellynasaura amicagraphica and Atlascopcosaurus loadsi, and a Coelurosaur, as well as fragments of what may be a caenagnathid (relatives of the Oviraptors). One fossil from this diverse taxa, collectively called the "polar dinosaurs of Australia", has been interpreted as showing possible adaptations to vision in low light conditions and possibly were warm-blooded; this has been suggested as an explanation for how some of these dinosaurs foraged for food during the polar winter months. It is worth noting that although these dinosaurs lived at polar latitudes, the Cretaceous climate was significantly milder than today, so temperatures within the Antarctic and Arctic Circles were vastly different to the climate at these latitudes today, because the lopsided arrangements of the continents made sea currents and monsoon winds blow across the polar areas and not round and round them, and so stopped cold pools from developing around the poles.
An astragalus bone of an ancient relative of Allosaurus was discovered at the site, making it the first discovery in the southern hemisphere. [4]
See also
- Dinosaur Dreaming
- List of fossil sites (with link directory)
References
- ^ "Dinosaur Cove", Victorian Resources Online (Department of Primary Industries), 31 December 2009, http://www.dse.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/coranregn.nsf/pages/corangamite_landform_dinosaur_cove, retrieved 2011-02-21
- ^ "Dinosaur Cove – mine of polar dinosaurs by Wondermondo". http://www.wondermondo.com/Countries/Au/AU/Victoria/DinosaurCove.htm. Retrieved 29 March 2010.
- ^ a b Rich, Thomas H.. "The Discovery of Dinosaur Cove". Museum Victoria. http://museumvictoria.com.au/history/dinosaur.html. Retrieved January 2010.
- ^ Piper, Kylie. "T-Rex Relative Turns Up Down Under". Australian Geographic. //www.australiangeographic.com.au/journal/trex-relative-turns-up-down-under.htm. Retrieved 26 March 2010.
Coordinates: 38°46′54″S 143°24′53″E / 38.78167°S 143.41472°E
Categories:- Geology of Victoria (Australia)
- Bays of Victoria (Australia)
- Otway Ranges
- Cretaceous paleontological sites of Australia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.