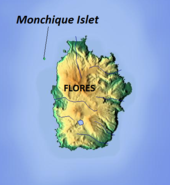
- Monchique Islet
-
Monchique Islet Islets (Ilhéus) Monchique IsletCountry  Portugal
PortugalAutonomous Region  Azores
AzoresIslands Eastern Group Location Azores Platform, Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Atlantic Ocean Archipelago Azores Highest point - elevation 110 m (361 ft) - coordinates 39°29′43″N 31°16′30″W / 39.49528°N 31.275°W Lowest point Sea level - location Atlantic Ocean - elevation 0 m (0 ft) Biome Marine (ocean) Geology Basalt Orogeny Volcanism Period Holocene The Monchique Islet or Ilhéu de Monchique is a small island, west of the village of Fajã Grande, Flores Island, in the western part of the Portuguese Azores. It lies just over a mile north-northwest of Ponta de Fenais and is considered the westernmost point of Europe. It functioned as an astronomical (celestial) navigational guide and reference mark for mariners, who calibrated their navigational equipment referencing the islet on long Atlantic crossings.[1][2][3][4]
The islet is protected for its rich biodiversity; ninety-six species of flora and fauna have been identified congregating on or in the waters of the islet, including the species of Dictyota dichotoma, Patella aspera ulyssiponensis, Megabalanus sp. Coris and julis. Approachable only by boat, the bay, which has water depth of about 43 metres, provides opportunities for scuba diving during the day in the summer.[5]
Contents
Geography
The islet is located more than a mile to the north-northwest of the island of Flores, in a bay between Ponta de Fenais (English: Point Fanaes or Fanais Port)[6] and Faja Grande. The islet is actually located on the North American plate between the two westernmost Azorean islands of Flores and Corvo. Historically, its unique geological formation attracted visitors travelling between Europe and America, intersecting here on their way to the ports of Lajes or Santa Cruz ports of Flores Island.
The islet is a solid monolith of black basaltic rock formation seen as vertical walls, remnants of a coastal volcanic cone, eroded by ocean forces, but extending steeply to a height of 110 feet (34 m) above sea level. It was formed from irregular lava flows that have produced many submarine cavities along the islet's relief. San and boulders are scattered all over the island. The islet is an elevated area that includes two rock outcroppings above the water's surface.[7][8] [9]
A deep channel separates the Monchique Islet from the shoreline, with only a rock outcrop called the Baxio Raza separating it from the shore. Since the channel is between 45 and 55 metres depth (43 metres has also been mentioned in other references), ships were able to anchor in the bay. Historically, the steep rock slopes of the islet and shoreline served as shelter from strong offshore gales. The deep channel, through which ships may navigate with care (while still avoiding some surface rocks) is considered safe for navigation. The Baxia Rasa rock formation extends over a length of 0.4 miles and its is a rough terrain situated to the west of Ponta de Fenais.[7]
Visits to Flores are considered ideal in spring (around June) or early summer (around July) when the weather is good and vegetation is green and flowers bloom.[10] The nearest airport to the islet is Flores Airport in Santa Cruz das Flores, located on the other side of the island. Locally, the islet is only accessible by boat.
Biome
The maximum depth of water in the coastal channel is40 metres (130 ft) and its water temperature varies in the range 17–23 °C (63–73 °F).[5][11] The islet is the centre of a region of great biodiversity, with 96 identified species, with a Margalef index of 11.0 biodiversity. The flora along its flanks are dominated by Dictyota dichotoma, an iridescent brown algae, while numerous faunal species of gastropods Patella ulyssiponensis (locally referred to as lapas or wild limpets) and Megabalanus (a species of barnacle), as well as Coris julis (Mediterranean rainbow wrasse). Shellfish species, including ulyssiponensis Patella aspera and Megabalanus sp. (Barnacles) are also found in the inner straits, in addition to plenty of kingfish.
Measures to conserve the islet along with the Flores island have been initiated.[5] It currently falls under the Plano do Ordenamento da Orla Costeira (POOC) Flores, which identifies the islet as part of an area of conservation and preservation both for ecological and tourist requirements. The islet itself is identified as vulnerable and designated as areas for terrestrial and marine species protection, limiting the use and access to the islet and surrounding waters.[12][13]
Tourism
The water around the coast is suitable for scuba diving as the underwater visibility is good in the warm, clear and clean waters of the ocean. There is an advisory which states diving in these waters should be done only during day time as taking precautionary measure to avoid any surprises from the currents in the sea flows.[3][14] Kayakers can travel to Monchique Islet from Flores Island.[5][15]
References
- ^ "Europe Map". Maps of World. http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:K-eVVz3RDhwJ:www.mapsofworld.com/europe/+Monchique+Islet&cd=7&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=in&client=firefox-a. Retrieved December 2, 2010.
- ^ "Island of natural wonders...". Destinazores Azores Tourist Guide. http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:2R_npxEaIgAJ:www.destinazores.com/en/index.php%3Fregion_id%3D9+Monchique+Islet&cd=8&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=in&client=firefox-a. Retrieved December 2, 2010.
- ^ a b "Spot de Mergulho: Ilhéu de Monchique, Ilha das Flores, Portugal". Skaphandrus.com. http://www.skaphandrus.com/locais_mergulho/spot/Portugal/Ilha_das_Flores/Ilh%C3%A9u_de_Monchique. Retrieved December 3, 2010.
- ^ "Reserva de la Biosfera por la UNESCO". Guia dos Acores-Ilha das Flores. http://www.guiacores-flores.com/1050es.html. Retrieved December 3, 2010.
- ^ a b c d "Ilhéu de Monchique". Scubazores. http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:Q670CbXS72UJ:www.horta.uac.pt/scubazores/Flores/Monchique.htm+Ilh%C3%A9u+de+Monchique&cd=6&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=in&client=firefox-a. Retrieved December 4, 2010.
- ^ Purdy, John (1845). Alex G. Findlay. ed. Memoir, descriptive and explanatory, to accompany the general chart of the Northern ocean, Davis' strait and Baffin's bay (9 ed.). London: R.H. Laurie. p. 382. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=wPYHAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA382&dq=Monchique+Islet&hl=en&ei=ljL5TPvSM8mDhQf1s-CECQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0CEgQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=Monchique%20Islet&f=false.
- ^ a b The Atlantic navigator (4 ed.). London: James Imray and Son. 1854. pp. 215, 219. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=HxQEAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA215. Retrieved December 2, 2010.
- ^ Atlantic Navigator. BoD – Books on Demand,. 2010. pp. 215–216. ISBN 3861951703. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=FkvX4xxsWj4C&pg=PA215. Retrieved December 4, 2010.
- ^ National Geospatial-intelligence Agency (2005). Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 West Coast of Europe & Northwest Africa Enroute. ProStar Publications. p. 146. ISBN 1577856600. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=y-AeYaLGY1MC&pg=PA146. Retrieved December 4, 2010.
- ^ "History". Amazing Tours. http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:QConWtSFG1wJ:www.amazingtours.se/uk/history.htm+Monchique+Islet&cd=11&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=in&client=firefox-a. Retrieved December 2, 2010.
- ^ "Ilhéu de Monchique". Enciclopédia Açores XXI. http://acores.wikia.com/wiki/Ilh%C3%A9u_de_Monchique. Retrieved December 3, 2010.
- ^ DROTRH, ed (2009). "POOC Flores".
- ^ (in Portuguese) Plano de Ordanemento da Orla Costeira da ilha das Flores (Decreto No.24/2008A) (1 ed.). Diário da República. 26 November 2008. http://sig.sram.azores.gov.pt/sig/Regulamentos/POOC%20das%20Flores.pdf.
- ^ "Scuba Dive Site: Ilhéu de Monchique, Flores Island, Portugal". Skaphndrus.com. http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:x0_PhJ3r3rMJ:www.skaphandrus.com/dive_locations/site/Portugal/Flores_Island/Ilh%C3%A9u_de_Monchique+Ilh%C3%A9u+de+Monchique,+Flores+-+Portugal&cd=1&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=in&client=firefox-a. Retrieved December 3, 2010.
- ^ "Why Travel to Flores and Corvo?". Flores and Corvo Travel Guide. http://www.addictedtotravel.com/travel-guides/places-to-visit/flores--corvo_azores-travel-guide. Retrieved 4 December 2010.
Categories:- Islands of the Azores
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.