- Nuclear RNase P
-
Nuclear RNase P 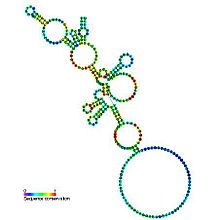
Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of RNaseP_nuc Identifiers Symbol RNaseP_nuc Rfam RF00009 Other data RNA type Gene; ribozyme Domain(s) Eukaryota; Bacteria; Archaea GO 0008033 0004526 0030677 SO 0000386 In molecular biology, nuclear ribonuclease P (RNase P) is a ubiquitous endoribonuclease, found in archaea, bacteria and eukarya as well as chloroplasts and mitochondria. Its best characterised enzyme activity is the generation of mature 5'-ends of tRNAs by cleaving the 5'-leader elements of precursor-tRNAs. Cellular RNase Ps are ribonucleoproteins. The RNA from bacterial RNase Ps retains its catalytic activity in the absence of the protein subunit, i.e. it is a ribozyme. Isolated eukaryotic and archaeal RNase P RNA has not been shown to retain its catalytic function, but is still essential for the catalytic activity of the holoenzyme. Although the archaeal and eukaryotic holoenzyme s have a much greater protein content than the bacterial ones, the RNA cores from all three lineages are homologous -- the helices corresponding to P1, P2, P3, P4, and P10/11 are common to all cellular RNase P RNAs. Yet there is considerable sequence variation, particularly among the eukaryotic RNAs.
References
- Frank, DN; Pace NR (1998). "Ribonuclease P: unity and diversity in a tRNA processing ribozyme". Annu Rev Biochem 67: 153–180. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.153. PMID 9759486.
- Brown, JW (1999). "The Ribonuclease P Database". Nucleic Acids Res 27 (1): 314–. doi:10.1093/nar/27.1.314. PMC 148169. PMID 9847214. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=148169.
- Frank, DN; Adamidi C, Ehringer MA, Pitulle C, Pace NR (2000). "Phylogenetic-comparative analysis of the eukaryal ribonuclease P RNA". RNA 6 (12): 1895–1904. doi:10.1017/S1355838200001461. PMC 1370057. PMID 11142387. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1370057.
- Xiao, S; Scott F, Fierke CA, Engelke DR (2002). "Eukaryotic Ribonuclease P: A Plurality of Ribonucleoprotein Enzymes". Annu Rev Biochem 71: 165–189. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135352. PMID 12045094.
- Marquez, SM; Harris JK, Kelley ST, Brown JW, Dawson SC, Roberts EC, Pace NR (2005). "Structural implications of novel diversity in eucaryal RNase P RNA". RNA. 11 (5): 739–751. doi:10.1261/rna.7211705. PMC 1370759. PMID 15811915. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1370759.
External links
Categories:- Molecular and cellular biology stubs
- Non-coding RNA
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
