- Perfluoroisobutene
-
Perfluoroisobutene 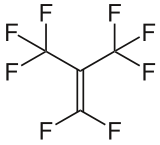 1,1,3,3,3-pentafluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)prop-1-eneOther namesPerfluoroisobutene, Perfluoroisobutylene, Octafluoroisobutylene, Octafluoro-sec-butene, PFIB
1,1,3,3,3-pentafluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)prop-1-eneOther namesPerfluoroisobutene, Perfluoroisobutylene, Octafluoroisobutylene, Octafluoro-sec-butene, PFIBIdentifiers CAS number 382-21-8 PubChem 61109 RTECS number UD1800000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C(=C(F)F)(C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F
- InChI=1/C4F8/c5-2(6)1(3(7,8)9)4(10,11)12
Properties Molecular formula C4F8 Molar mass 200.030 g/mol Density 8.2 g/l Boiling point 7.0 °C (280 K)
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Perfluoroisobutene (PFIB), also known as 1,1,3,3,3-pentafluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)prop-1-ene, is a fluorocarbon alkene. It is a hydrophobic reactive gas with boiling point at 7 °C. It is a strong electrophile.
PFIB is about 10 times as toxic as phosgene. Its inhalation can lead to pulmonary edema, which may be fatal. Onset of symptoms can take 1-4 hours after inhalation. Treatment is based on management of the pulmonary edema (usually with high-dose corticoids and other medication/measures) and associated disorders (e.g. heart failure, hypocalcemia etc.). Many cases resolve within 72 hours without major long-term effects.
In contact with water PFIB undergoes rapid hydrolysis, producing various reactive compounds and fluorophosgene.
PFIB is a product of pyrolysis of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), one of the substances causing polymer fume fever.
It is a Schedule 2 substance of the Chemical Weapons Convention.
External links
Categories:- Perfluorinated compounds
- Alkenes
- Pulmonary agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
