- Methylcholanthrene
-
3-Methylcholanthrene 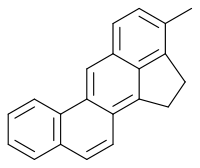
 Other names20–Methylcholanthrene
Other names20–MethylcholanthreneIdentifiers Abbreviations 3-MC
20-MCCAS number 56-49-5 
PubChem 299006 ChemSpider 264105 
ChEMBL CHEMBL40583 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c32cc1cccc5c1c(c2ccc4ccccc34)C(C)C5
Properties Molecular formula C21H16 Molar mass 268.35 g/mol Appearance Yellow solid Melting point 180 °C, 453 K, 356 °F
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Methylcholanthrene (MCA) is a highly carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon produced by burning organic compounds at very high temperatures[clarification needed]. It is a yellow solid with a melting point around 180 °C. Methylcholanthrene is used in laboratory studies of chemical carcinogenesis. It is an alkylated derivative of benz[a]anthracene and has a similar UV spectrum. The most common isomer is 3-methylcholanthrene, although the methyl group can occur in other places.
3-Methylcholanthrene, a known carcinogen which builds up in the prostate due to cholesterol breakdown, is implicated in prostate cancer.[citation needed] It "readily produces" primary sarcomas in mice.[1]
References
- ^ Donald C. Malins, Katie M. Anderson, Naomi K. Gilman, Virginia M. Green, Edward A. Barker and Karl Erik Hellström (2004). "Development of a Cancer DNA Phenotype Prior to Tumor Formation". PNAS 101 (29): 10721–10725. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403888101. JSTOR 3372726. PMC 490001. PMID 15249662. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=490001.
External links
Categories:- Carcinogens
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
