- Square root of 3
-
List of numbers – Irrational and suspected irrational numbers
γ – ζ(3) – √2 – √3 – √5 – φ – ρ – δS – α – e – π – δBinary 1.1011101101100111101... Decimal 1.7320508075688772935... Hexadecimal 1.BB67AE8584CAA73B... Continued fraction 
The square root of 3 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number 3. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 3, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. It is denoted by
The first sixty significant digits of its decimal expansion are:
- 1.73205 08075 68877 29352 74463 41505 87236 69428 05253 81038 06280 5580... (sequence A002194 in OEIS)
The rounded value of 1.732 is correct to within 0.01% of the actual value. A close fraction is
 (1.7321 42857...).
(1.7321 42857...).The square root of 3 is an irrational number. It is also known as Theodorus' constant, named after Theodorus of Cyrene.
It can be expressed as the continued fraction [1; 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, ...] (sequence A040001 in OEIS), expanded on the right.
It can also be expressed by generalized continued fractions such as
which is [1;1, 2,1, 2,1, 2,1, ...] evaluated at every second term.
Contents
Proof of irrationality
Suppose that √3 is rational, and express it in lowest possible terms (i.e., as a fully reduced fraction) as
 for natural numbers m and n. Then √3 can be expressed in lower terms as
for natural numbers m and n. Then √3 can be expressed in lower terms as  , which is a contradiction.[1]
, which is a contradiction.[1]Geometry
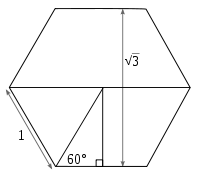
If an equilateral triangle (equilateral polygon with three sides) with sides of length 1 is cut into two equal halves, by bisecting an internal angle across to make a right angle with one side, the right angle triangle's hypotenuse is length one and the sides are of length 1/2 and
 From this the trigonometric function tangent of 60 degrees equals
From this the trigonometric function tangent of 60 degrees equals 
It is the distance between parallel sides of a regular hexagon with sides of length 1.
It is the length of the space diagonal of a unit cube.
The shape Vesica piscis has a major axis: minor axis ratio equal to the square root of three, this can be shown by constructing two equilateral triangles within it.
Other uses
Power engineering
In power engineering, the voltage between two phases equals
 times the line to neutral voltage.
times the line to neutral voltage.See also
References
- ^ Grant, M.; Perella, M. (July 1999). "Descending to the irrational". Mathematical Gazette 83 (497): 263–267. doi:10.2307/3619054.
S., D.; Jones, M. F. (1968). "22900D approximations to the square roots of the primes less than 100". Mathematics of Computation 22 (101): 234–235. JSTOR 2004806.
Uhler, H. S. (1951). "Approximations exceeding 1300 decimals for
 ,
,  ,
,  and distribution of digits in them". Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 37: 443–447. PMC 1063398. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1063398.
and distribution of digits in them". Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 37: 443–447. PMC 1063398. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1063398.Wells, D. (1997). The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Numbers (Revised ed.). London: Penguin Group. p. 23.
External links
Categories:- Algebraic numbers
- Mathematical constants
- Irrational numbers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

![[2; -4, -4, -4, ...] = 2 - \cfrac{1}{4 - \cfrac{1}{4 - \cfrac{1}{4 - \ddots}}}](3/6e38eb120969229bccfe8f7e70bd52a1.png)