- Coloborhynchus
-
Coloborhynchus
Temporal range: Early Cretaceous, 98 MaSkeletal cast of the possible species C. spielbergi Scientific classification 
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: †Pterosauria Suborder: †Pterodactyloidea Family: †Ornithocheiridae Genus: †Coloborhynchus
Owen, 1874Type species Ornithocheirus clavirostris
Owen, 1874Species C. capito?
(Seeley 1869 [originally Ptenodactylus])
C. clavirostris
(Owen, 1874 [originally Ornithocheirus])
C. sedgwicki?
(Owen 1874 [originally Pterodactylus])
C. araripensis?
(Wellnhofer 1985 [originally Santanadactylus])
C. robustus?
(Wellnhofer 1987 [originally Tropeognathus])
C. ligabuei?
(Dalla Vecchia 1993 [originally Cearadactylus])
C. piscator?
(Kellner & Tomida, 2000 [originally Anhanguera])
C. spielbergi?
Veldmeijer, 2003Synonyms Ptenodactylus Seeley, 1869 (preoccupied)
Amblydectes Hooley, 1914
Santanadactylus? Wellnhofer 1985 Siroccopteryx? Mader & Kellner, 1999
Uktenadactylus? Rodrigues & Kellner, 2008Coloborhynchus is a genus in the pterosaur family Ornithocheiridae, and is known from the Lower Cretaceous of England (Albian age, 98 million years ago), and possibly the Aptian age (112-99 million years ago) of Brazil and Texas, depending on which species are included.
Contents
Description
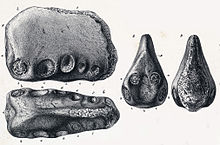
The type specimen of Coloborhynchus is known only from a partial upper jaw. Therefore, according to Rodrigues and Kellner's 2008 re-evaluation on Coloborhynchus clavirostris, it can only be differentiated from its relatives based on its unique combination of tooth socket positions. In Coloborhynchus, the two front teeth pointed forward and were higher on the jaw than the other teeth, while the next three pairs of teeth pointed to the sides. The final two (preserved) pairs of teeth pointed downward. Finally, a unique oval depression was located below the first pair of teeth.[1]
Like the related Anhanguera and Uktenadactylus, the tip of the snout flared out into a wider rosette, in contrast to the narrow posterior jaws. Also like its close relatives, Coloborhynchus had a keel-shaped crest on the front of its jaws, though it was broad and thinned from base to top, rather than the uniformly thin crests of its relatives. This kind of thickened crest is also seen in Siroccopteryx moroccensis, which may be its closest relative or a member of the same genus. It also had a straight, rather than curved, front margin, unlike its relatives, and begins at the tip of the snout, rather than further back as in other species.[1]
A second specimen showing all of these same unique features was reported to Brazilian paleontologist Alexander Kellner by Darren Naish in 2007, and likely represents a second specimen of C. clavirostris, though it has not yet been described.[1]
The possible species Coloborhynchus capito represents the largest known ornithocheirid, and indeed the largest toothed pterosaur known. A referred specimen from the Cambridge Greensand of England described in 2011 consists of a very large upper jaw tip which displays the tooth characteristics that distinguish C. capito from other species. The jaw tip is nearly 10 cm tall and 5.6 cm wide, with teeth up to 1.3 cm in base diameter. If the proportions of this specimen were consistent with other known species of Coloborhycnhus, the total skull length could have been up to 75 cm, leading to an estimated wingspan of 7 metres (23 ft).[2]
Classification and species
Like many ornithocheiroid pterosaurs named during the 19th century, Coloborhynchus has a highly convoluted history of classification. Over the years numerous species have been assigned to it, and often, species have been shuffled between Coloborhynchus and related genera by various researchers.
In 1874 Richard Owen, rejecting the creation by Harry Govier Seeley of the genus Ornithocheirus, named a species Coloborhynchus clavirostris based on holotype BMNH 1822, a partial snout from the Hastings Beds of the Wealden Group of East Sussex, England. The genus name means "maimed beak", a reference to the damaged and eroded condition of the fossil; the specific name means "key snout", referring to its form in cross-section. Owen also reclassified Ornithocheirus cuvieri and O. sedgwickii as species within the genus Coloborhycnhus, though he did not designate any of these three as the type species. Owen considered the defining trait of the genus to be the location of the front tooth pairs high on the side of the upper jaws. However, in 1913 Reginald Walter Hooley concluded that this location was an artefact of the erosion and that the genus was indistinguishable from Criorhynchus simus, the second genus and species Owen erected in 1874. Hooley also ignored Owen's re-assignment of the two former Ornithocheirus species, leaving them in that genus. In 1967, Kuhn agreed with Hooley that Coloborhynchus clavirostris was a synonym of Criorhynchus simus. Furthermore, Kuhn was the first to formally designate C. clavirostris as the type species of the genus, rather than one of the Ornithocheirus species. Most later researchers followed these opinions, regarding Coloborhynchus as invalid relative to Criorhynchus.[1]
This changed in 1994 when Yuong-Nam Lee named Coloborhynchus wadleighi for a snout found in 1992 in the Albian age Paw Paw formation Texas. The revival of the genus meant that of several related species, then assigned to other genera, had to be re-evaluated to determine whether or not they actually belonged to Coloborhynchus. In 2008, Taissa Rodrigues and Alexander Kellner re-formulated the key features of Coloborhynchus, again based mainly on the unique positions of the tooth sockets. Rodrigues and Kellner argued that Lee's C. wadleighi, which possessed some differences in the skull and teeth from C. clavirostris, and from an earlier time period, belonged in its own genus, which they named Uktenadactylus.[1]
A partial lower jaw originally named Tropeognathus robustus from the Romualdo Member of the Santana Formation in Brazil was assigned to Coloborhycnhus in 2001 by Fastnacht, as Coloborhynchus robustus. In 2002, David Unwin supported this position, and also synonymized the more well-known species Anhanguera piscator with C. robustus. Rodrigues and Kellner disagreed with this classification, however, noting that both did not possess the unique straightened crest beginning at the snout tip, or sideways pointed teeth, of C. clavirostris. Instead, Rodrigues and Kellner regarded both Anhanguera robustus and Anhanguera piscator as valid species of Anhanguera.[1]
Another Brazilian species from the Romualdo Member was named Coloborhynchus speilbergi by Veldmeijer in 2003. It shares one or two characters in common with C. clavirostris (such as a flattened upper surface of the snout), though Rodrigues and Kellner regarded them as dubious, and noted that they are also present in related species and so are not unique to Coloborhynchus. Rodrigues and Kellner also noted that C. speilbergi didn't have as high a tooth row (exposing the palate) as the type species. Its crest is also very thin, similar to Anhanguera, to which genus Kellner assigned it in 2006. Similarly, Kellner excluded C. araripensis (formerly assigned to the genus Santanadactylus from the genus, based on lack of comparable diagnostic features. Unwin, in 2001, assigned the species Siroccopteryx moroccensis to Coloborhycnhus, based on its similarity to C. wadleighi (aka Uktenadactylus). Kellner, who regarded Uktenadactylus as a distinct genus in 2008, also regarded Siroccopteryx as distinct, and noted that like the other species assigned to Coloborhynchus, lacked its unique characteristics of the tooth row, a position also supported by Fastnacht in 2001.[1]
Finally, Unwin (in 2001) also re-assigned the two other species from the Cambridge Greensand to Coloborhycnhus: C. capito and C. sedgwickii, the second of which being one of the original members of the genus according to Richard Owen in 1874. According to Kellner, C. capito is too incomplete to fully compare to C. claviraostris, and its precise classification is open to debate. He noted that C. sedgwicki does not possess the unique features of C. clavirostris (in fact it lacks a crest altogether), and may instead belong to the same genus as "Ornithocheirus" compressirostris (=Lonchodectes).[1]
List of species and synonyms
Species which have been assigned to Coloborhynchus by various scientists since 2000 include:
- ?C. capito (Seeley 1869) = Pterodactylus capito Sauvage 1882 = Ornithocheirus capito Seeley 1870 = Ptenodactylus capito Seeley 1869
- C. clavirostris Owen, 1874, the type species
- ?C. sedgwicki (Owen 1874) = Ornithocheirus sedgwicki (Newton 1888) = Pterodactylus sedgwickii Owen 1859 [also classified as Ornithocheirus]
- ?C. araripensis[3] (Wellnhofer 1985) = Santanadactylus araripensis Wellnhofer 1985 [also classified as Anhanguera]
- ?C. robustus (Wellnhofer 1987) = Tropeognathus robustus Wellnhofer 1987 [also classified as Anhanguera]
- ?C. ligabuei (Dalla Vecchia 1993) = Cearadactylus ligabuei Dalla Vecchia 1993 [also classified as Anhanguera or Cearadactylus]
- ?C. wadleighi Lee 1994 [also classified as Uktenadactylus]
- ?C. moroccensis (Mader & Kellner 1999) = Siroccopteryx moroccensis Mader & Kellner 1999
- ?C. piscator[3] (Kellner & Tomida 2000) = Anhanguera piscator Kellner & Tomida 2000 [also classified as Anhanguera or C. robustus]
- ?C. spielbergi[3] Veldmeijer 2003 [also classified as Anhanguera]
Species assigned to Coloborhynchus in the past include:
- C. cuvieri (Owen 1874) = Ornithocheirus sedgwicki (Newton 1888) = Pterodactylus cuvieri Bowerbank 1851 [now classified as either Ornithocheirus or Anhanguera]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h Rodrigues, T. and Kellner, A.W.A. (2008). "Review of the pterodactyloid pterosaur Colobrohynchus." Pp. 219–228 in: Hone, D.W.E. and Buffetaut, E. (eds), Flugsaurier: pterosaur papers in honour of Peter Wellnhofer. Zitteliana B, 28.
- ^ Martill, D.M. and Unwin, D.M. (2011). "The world's largest toothed pterosaur, NHMUK R481, an incomplete rostrum of Coloborhynchus capito (Seeley 1870) from the Cambridge Greensand of England." Cretaceous Research, (advance online publication). doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2011.09.003
- ^ a b c Veldmeijer, A.J. (2003). "Description of Coloborhynchus spielbergi sp. nov. (Pterodactyloidea) from the Albian (Lower Cretaceous) of Brazil." Scripta Geologica, 125: 35-139.
Categories:- Ornithocheiroids
- Cretaceous pterosaurs
- Prehistoric reptiles of Europe
- Prehistoric reptiles of North America
- Prehistoric reptiles of South America
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.