- Buprestidae
-
Buprestidae 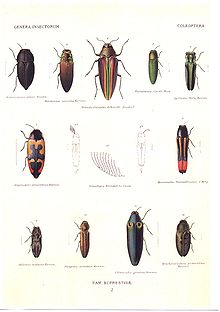
Agrilinae (bottom row), Chrysochroinae (top row, left 3), and Buprestinae (others) from Genera Insectorum Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Infraclass: Neoptera Superorder: Endopterygota Order: Coleoptera Suborder: Polyphaga Infraorder: Elateriformia Superfamily: Buprestoidea Family: Buprestidae
Leach, 1815Subfamilies Agrilinae
Buprestinae
Chrysochroinae
Galbellinae
Julodinae
†Parathyreinae
Polycestinae
(but see text)Buprestidae is a family of beetles, known as jewel beetles or metallic wood-boring beetles because of their glossy iridescent colors. The family is among the largest of the beetles, with some 15,000 species known in 450 genera. In addition, almost 100 fossil species have been described.[1]
The larger and more spectacularly colored jewel beetles are highly prized by insect collectors. The elytrae of some Buprestidae species have been traditionally used in beetlewing jewellery and decoration in certain countries in Asia, like India, Thailand and Japan.
Contents
Description and ecology
Shape is generally cylindrical or elongate to ovoid, with lengths ranging from 3 mm to an impressive 100 mm, although most species are under 20 mm. A variety of bright colors are known, often in complicated patterns. The iridescence common to these beetles is not due to pigments in the exoskeleton, but instead physical iridescence in which microscopic texture in their cuticle selectively reflects specific frequencies of light in particular directions. This is the same effect that makes a compact disc reflect multiple colors.
The larvae bore through roots, logs, stems, and leaves of various types of plants, ranging from trees to grasses. The wood boring types generally favor dying or dead branches on otherwise-healthy trees, while a few types attack green wood; some of these are serious pests capable of killing trees and causing major economic damage. Some species are attracted to recently-burned forests to lay their eggs. They can sense pine wood smoke from up to 50 miles away, and can see infrared light, helping them to zero in as they get closer to a forest fire[citation needed]. They will bite if they feel threatened, and can aggregate to swarms of biting beetles in recently burned areas.
-
Buprestinae (center right and lower left), Julodinae (center) and Polycestinae (others) from Charles Kerremans' Monographie des Buprestides
-
Fossil jewel beetle from the Eocene, found in the Messel Pit (Germany)
Systematics
Jewel beetle classification is not yet robustly established, although there appear to be five or six main lineages, which may be considered subfamilies, possibly with one or two being raised to families in their own right. Some other systems define up to 14 subfamilies.
The commonly-accepted subfamilies, with some representative genera and species, are:
Agrilinae – cosmopolitan, with most taxa occurring in the Northern Hemisphere
- Agrilus
- Anodontodora Obenberger, 1931
- Asymades Kerremans, 1893
- Brachys
- Chalcophlocteis Obenberger, 1924
- Discoderoides Théry, 1936
- Entomogaster Saunders, 1871
- Ethiopoeus Bellamy, 2008
- Madecorformica Bellamy, 2008
- Meliboeus
- Pachyschelus
- Paracylindromorphus
- Paradorella Obenberger, 1923
- Pseudokerremansia
- Strandietta Obenberger, 1931
Buprestinae – cosmopolitan
- Agrilozodes
- Anthaxia
- Bubastoides
- Buprestis
- Calodema – found only in Australia and New Guinea; usually in rain forests
- Castiarina – about 500 species, found only in Australia and New Guinea, previously considered a subgenus of Stigmodera
- Chrysobothris
- Colobogaster
- Conognatha
- Eurythyrea
- Hiperantha
- Metaxymorpha – found only in Australia, New Guinea, and Indonesia; usually in rain forests
- Stigmodera – 7 species remain here
- Temognatha – About 83-85 species, found only in Australia and New Guinea, previously considered a subgenus of Stigmodera
- Capnodis
- Chalcophora
- Chalcophora japonica – Flat-headed Wood-borer, ubatamamushi (Japanese)
- Chrysochroa
- Chrysodema Laporte & Gory, 1835 (= Cyalithoides)
- Halecia
- Lampetis Dejean, 1833 – sometimes included in the tribe Psilopterini, but actually not very close to Psiloptera (tentatively placed here)
- Lampropepla
- Perotis
- Psiloptera (tentatively placed here)
Galbellinae
- Galbella
Julodinae
- Aaata
- Amblysterna
- Julodella
- Julodis
- Neojulodis
- Sternocera
Polycestinae
- Acmaeodera
References
- Bellamy, C.L. & Nelson, G.H. (2002): Buprestidae. In: Arnett, Ross H. Jr. & Thomas, Michael C.: American Beetles (Volume 2). CRC Press.
- Akiyama, K. and S. Ohmomo. 2000. The Buprestid Beetles of the World. Iconographic Series of Insects 4. ISBN 4-943955-04-5. A 341 page work with 120 colour plates.
External links
- Julodini
- Jewel beetle site, with extensive lists of species and many photos
- Flickr Images
- ZinRus Impressive photos.
- The World of Jewel Beetles (Buprestidae Home Page)
- Jewel beetles of Prague, with pictures
- Jewel beetles depicted on postage stamps
- Jewel beetles can hear fires, short summary of a JEB-Paper
- Bibliography
- Taiwanese Site Images Binomial Names
- Images of types at NHM(London)
- Hampshire Museum - Beetles in jewelry
Categories:- Buprestoidea
- Buprestidae
- Woodboring beetles
- Insect pests of tropical forests
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.











