- Chemotaxis assay
-
Chemotaxis assays are experimental tools for evaluation of chemotactic ability of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells. A wide variety of techniques are known and applied for such reason. Some of them qualitative and investigator can determine whether the cells prefer or not the tested chemical, others are quantitative and we can get information about the intensity of the responses in a more detailed way.
Contents
Quality control
In general, the most important requisite to calibrate the incubation time of the assay both to the model cell and the ligand to be evaluated. Too short incubation time results no cells in the sample, while too long time perturbs the concentration gradients and measures more chemokinetic than chemotactic responses.
The most commonly used techniques are grouped into two main groups:
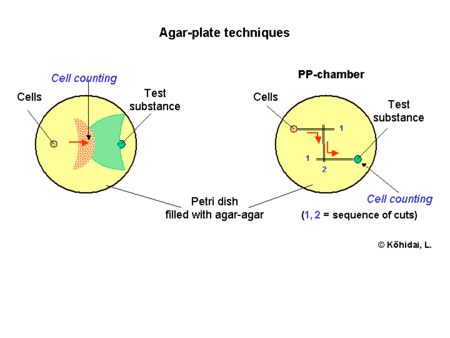
Agar-plate techniques
This way of evaluation deals with agar-agar or gelatine containing semi-solid layers made prior to the experiment. Small wells are cut into the layer and filled with cells and the test substance. Cells can migrate towards the chemical gradient in the semi solid layer or under the layer as well. Some variations of the technique deal also with wells and parallel channels connected by a cut at the start of the experiment (PP-technique). Radial arrangement of PP-technique (3 or more channels) provides the possibility to compare chemotactic activity of different cell populations or study preference between ligands.[1]
Counting of cells: positive responder cells could be counted from the front of migrating cells, after staining or in native conditions in light microscope.
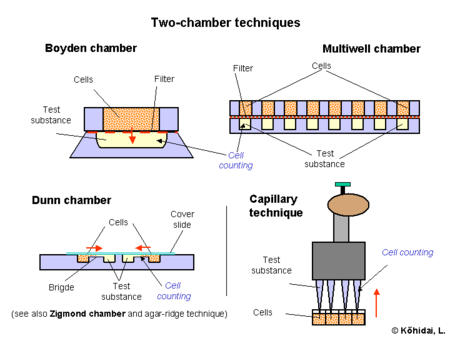
Two-chamber techniques
Chambers isolated by filters are proper tools for accurate determination of chemotactic behaviour. The pioneer type of these chambers was constructed by Boyden.[2] The motile cells are placed into the upper chamber, while the test substance containing fluid is filled into the lower one. The size of the motile cells to be investigated determines the pore size of the filter; it is essential to choose a diameter which allows active transmigration. For modelling in vivo conditions, several protocols prefer coverage of filter with molecules of extracellular matrix (collagen, elastin etc.) Efficiency of the measurements was increased by development of multiwell chambers (e.g. NeuroProbe), where 24, 96, 384 samples are evaluated in parallel. Advantage of this variant is that several parallels are assayed in identical conditions.
In another setting the chambers are connected side by side horizontally (e.g. Zigmond chamber)[3] or as concentric rings on a slide (e.g. Dunn chamber)[4] Concentration gradient develops on a narrow connecting bridge between the chambers and the number of migrating cells is also counted on the surface of the bridge by light microscope. In some cases the bridge between the two chambers is filled with agar and cells have to "glide[disambiguation needed
 ]" in this semisolid layer.
]" in this semisolid layer.Some capillary techniques provide also a chamber like arrangement, however, there is no filter between the cells and the test substance.[5] Quantitative results are gained by the multiwell type of this probe using 4-8-12-channel pipettes. Accuracy of the pipette and increased number of the parallel running samples is the great advantage of this test.[6]
Counting of cells: positive responder cells are count from the lower chamber (long incubation time) or from the filter (short incubation time). For detection of cells general staining techniques (e.g. trypan blue) or special probes (e.g. mt-dehydrogenase detection with MTT assay) are used. Labelled (e.g. fluorochromes) cells are also used, in some assays cells get labelled during transmigration the filter.
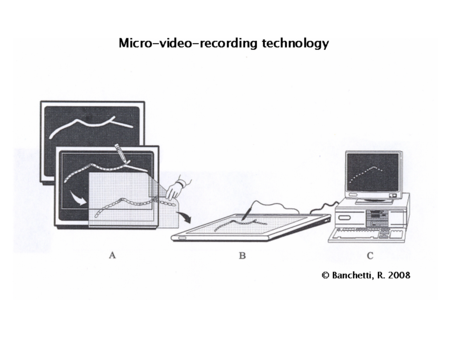
Micro-video-recording technology
The ethograms of Tetrahymena, Euplotes, Oxytricha and other ciliates contain rightward and leftward arcs, which are combined with straight segments and several types of directional change to locomotory patterns that lead walking specimens in a random manner over an area.[7][8] Within the diversity of all behavioural traits the arcs, considered as segments of circles, constitute the basic elements. The reason is that each limitation of behavioural capacity leads to circular walking. Behaviour registration is performed by real-time digitized dark-field tracks of walking cells, with a time resolution of around 80 μm. Registration is complemented by light-field videotracking (at different magnifications) of freely running specimens where movements of the whole cell and (part of) their cirri could be analyzed. All tracks are representative for at least 20, mostly 50 specimens.
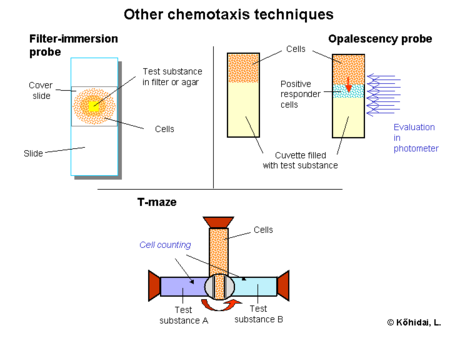
Other techniques
Besides the above mentioned two, most commonly used family of techniques a wide range of protocols were developed to measure chemotactic activity. Some of them are only qualitative, like aggregation tests, where small pieces of agar or filters are placed onto a slide and accumulation of cells around is measured.
In another semiquantitative technique cells are overlayed the test substance and changes in opalescence of the originally cell-free compartment is recorded during the incubation time.[9]
The third very frequently used, however, qualitative technique is the T-maze and its adaptations for microplates. In the original version a container drilled in a peg is filled with cells. Then the peg is twisted and the cells get contact with two other containers filled with different substances. The incubation is stopped with resetting the peg, the cell number is counted from the containers.[10]
References
- ^ Kőhidai L. (1995). "Method for determination of chemoattraction in Tetrahymena pyriformis.". Curr Microbiol 30 (4): 251–3. doi:10.1007/BF00293642. PMID 7765899.
- ^ Boyden, S.V. (1962). "The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes.". J Exp Med 115 (3): 453. doi:10.1084/jem.115.3.453. PMC 2137509. PMID 13872176. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2137509.
- ^ Zigmond S.H. (1988). "Orientation chamber in chemotaxis.". Methods Enzymol 162: 65–72. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(88)62064-7. PMID 3067054.
- ^ Zicha D., Dunn G.A., Brown A.F. (1991). "A new direct-viewing chemotaxis chamber.". J Cell Sci 99: 769–75. PMID 1770004.
- ^ Leick V.and Helle J. (1983). "A quantitative assay for ciliate chemotaxis.". Anal Biochem 135 (2): 466–9. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(83)90713-3. PMID 6660520.
- ^ Kőhidai, L., Lemberkovits, É. and Csaba, G. (1995). "Molecule dependent chemotactic responses of Tetrahymena pyriformis elicited by volatile oils.". Acta Protozool 34: 181–5.
- ^ Ricci, N. (1990). "The behaviour of ciliated protozoa.". Anim Behav 40 (6): 1048. doi:10.1016/S0003-3472(05)80172-1.
- ^ Ricci, N., Luverà, G., Cacciatori, M., Banchetti, R., Lueken, W. (1997). "The effects of 2 µM Hg++ on the ethogram of Euplotes vannus (Ciliata, Hypotrichida)". Europ J Protistol 33: 63.
- ^ Koppelhus U., Hellung-Larsen P. and Leick V. (1994). "An improved quantitative assay for chemokinesis in Tetrahymena.". Biol Bull (Marine Biological Laboratory) 187 (1): 8–15. doi:10.2307/1542160. JSTOR 1542160. PMID 7918798.
- ^ Van Houten J., Martel E. and Kasch T. (1982). "Kinetic analysis of chemokinesis of Paramecium.". J Protozool 29 (2): 226–30. PMID 7097615.
External links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.