- ENTH domain
Pfam_box
Symbol = ENTH
Name =
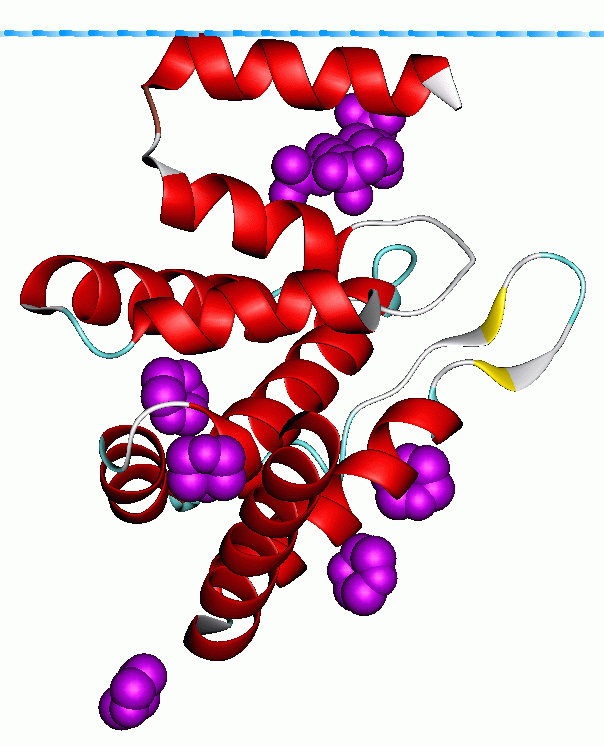
width =200
caption = ENTH domain of Epsin-1
Pfam= PF01417
InterPro= IPR001026
SMART=
PROSITE = PDOC50942
SCOP = 1edu
TCDB =
OPM family= 39
OPM protein= 1h0a
PDB=PDB3|1eyhA:17-140 PDB3|1h0aA:17-140 PDB3|1eduA:17-140PDB3|1inzA:17-140 PDB3|1xgwA:21-145 The ENTH (Epsin N-terminal homology) domain astructural domain that was found in proteins involved inendocytosis andcytoskeletal machinery.tructure
This domain is approximately 150 amino acids in length and is always found located at the N-termini of proteins. The domain forms a compact globular structure, composed of 9 alpha-helices connected by loops ofvarying length. The general topology is determined by three helical hairpins that are stacked consecutively with a right hand twist.cite journal |author=Chen H, Bateman A, de Camilli P, Hyman J, Panepucci E, Brunger AT |title=The ENTH domain |journal=FEBS Lett. |volume=513 |issue=1 |pages=11–18 |year=2002 |pmid=11911874 |doi=10.1016/S0014-5793(01)03306-3] . An N-terminal helix folds back, forming a deep basic groove that forms the binding pocket for the Ins(1,4,5)P3 ligandcite journal |author=Evans PR, McMahon HT, Ford MG, Mills IG, Peter BJ, Vallis Y, Praefcke GJ |title=Curvature of clathrin-coated pits driven by epsin |journal=Nature |volume=419 |issue=6905 |pages=361–366 |year=2002 |pmid=12353027 |doi=10.1038/nature01020] . The lipid ligand is coordinated by residues from surrounding alpha-helices and all three phosphates are multiply coordinated.
Interactions with the lipid bilayer
Proteins containing this domain have been found to bind
PtdIns(4,5)P2 and PtdIns(1,4,5)P3 suggesting that the domain is a membrane interacting module. The main function of proteins containing this domain appears to be to act as accessoryclathrin adaptors in endocytosis, Epsin is able to recruit and promote clathrin polymerisation on a lipid monolayer, butmay have additional roles in signalling and actin regulationcite journal |author=Kay BK, Yamabhai M, Wendland B, Emr SD |title=Identification of a novel domain shared by putative components of the endocytic and cytoskeletal machinery |journal=Protein Sci. |volume=8 |issue=2 |pages=435–438 |year=1999 |pmid=10048338] . Epsin causes a strong degree of membrane curvature and tubulation, even fragmentation of membranes with a highPtdIns(4,5)P2 content. Epsin binding to membranes facilitates their deformation by insertion of the N-terminal helix into the outer leaflet ofthe bilayer, pushing the head groups apart. This would reduce the energy needed to curve the membrane into a vesicle, making it easier for the clathrin cage to fix and stabilise the curved membrane. This points to a pioneering role for epsin in vesicle budding as it provides both a driving force and a link between membrane invagination and clathrin polymerisation.In particular, Epsin-1 shows specificity for the membrane glycophospholipid phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, however not all ENTH domains bind to this molecule. Binding causes tubulation of
liposome s and "in vivo" this membrane-binding function is normally coordinated withclathrin polymerisation.The N-terminal alpha-helix of this domain is hydrophobic and inserts into the membrane like a wedge and helps to drive membrane curvature.
Human proteins containing this domain
CLINT1 ;ENTHD1 ;EPN2 ;EPN3 ;External links
* [http://www.endocytosis.org/epsin/epsin.htm Endocytosis.org entry on epsin]
* [http://www.expasy.org/cgi-bin/nicedoc.pl?PDOC50942 ENTH domain] inPROSITE References
Further reading
Ford, M.G.J., Mills, I.G., Peter, B.J., Vallis, Y., Praefcke, G.J.K., Evans, P.R. and McMahon, H.T. (2002) Curvature of clathrin-coated pits driven by epsin. Nature 419, 361-366. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=12353027&query_hl=11&itool=pubmed_docsum pubmed]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
