- Graham Taylor (footballer)
-
Graham Taylor Personal information Full name Graham Taylor Date of birth 15 September 1944 Place of birth Worksop, Nottinghamshire, England Senior career* Years Team Apps† (Gls)† 1962–1968 Grimsby Town 189 (2) 1968–1972 Lincoln City 150 (1) Teams managed 1972–1977 Lincoln City 1977–1987 Watford 1987–1990 Aston Villa 1990–1993 England 1994–1995 Wolverhampton Wanderers 1996–2001 Watford 2002–2003 Aston Villa * Senior club appearances and goals counted for the domestic league only.
† Appearances (Goals).Graham Taylor OBE (born 15 September 1944, Worksop, Nottinghamshire) is a football pundit, ex-football manager, and a former player. He is best known as the manager of the England national football team, as well as being manager of Watford, a club he took from the Fourth Division to the First in the space of five years, then from bottom of the second division to the Premier League in two seasons two decades later.
Taylor grew up in the industrial steel town of Scunthorpe, North Lincolnshire, a town with which he still has many connections and regards as his hometown.[1] The son of a sports journalist[2] with The Scunthorpe Evening Telegraph, Graham found his love of football in the stands of the "Old Show Ground" watching Scunthorpe United. He became a player, playing at full back for Grimsby Town and Lincoln City.
He retired as a player through injury in 1972. He became a manager and coach, winning success with Lincoln, Watford and Aston Villa. Taylor succeeded in rescuing and achieving promotion with all three clubs, leading Watford and Aston Villa to runners-up positions to Liverpool F.C in 1983 and 1990 respectively, while leading the former to an F.A Cup Final in 1984.
In 1990, he became the manager of the England team, but resigned in November 1993, after failing to qualify for the 1994 FIFA World Cup in the United States. Taylor was heavily criticised personally and professionally during his failed tenure. Taylor faced even more criticism, when a documentary which filmed the failed qualifying campaign, aired in 1994. Taylor was heard to utter the words "Do I not like that", when England conceded a goal to Poland, and it became a national catchphrase. He was also filmed berating the German linesman during the controversial and crippling defeat to the Netherlands in a World Cup qualifier.
Taylor returned to club management in March 1994, and achieved more success with Watford. The club was promoted to the Premier League in 1999, after slipping back down the leagues after Taylor's departure 12 years earlier. His most recent managerial role was manager of Aston Villa, who he returned to in 2002. He left at the end of the 2002–03 season. Taylor now works as a pundit for BBC Radio Five Live and is chairman of Watford F.C..
Contents
Early life
He moved to a council house in Scunthorpe in 1947, where his father Thomas was the sports reporter for the Scunthorpe Evening Telegraph. He went to the Henderson Avenue Junior School, then Scunthorpe Grammar School (now High Ridge School), where he met his wife, Rita, from Winteringham. He played for the England Grammar Schools football team, and joined the sixth-form after passing six-O-levels in 1961, but he left after one year to pursue a full-time career in football. This was highly unusual for a Grammar School pupil and his teachers disapproved of his actions. Taylor always preferred football to rugby at Grammar School. He joined Grimsby Town, and played his first competitive game for them in September 1963 against Newcastle United when they won 2–1. In early 1965 Graham Taylor married Rita Cowling. They had two daughters, Joanne and Karen, whilst Taylor was at Grimsby. They also lived in Cleethorpes. When he moved to Lincoln, he bought his first house in North Hykeham.
Playing career
His playing career began with Grimsby Town in 1962 for whom he went on to play 189 games at fullback, scoring twice. He was transferred to Lincoln City in the summer of 1968, he scored 1 goal in 150 appearances before being forced to retire from playing following a serious hip injury in 1972. He was dubbed to have said to be thinking of an early retirement shortly before this happened because of family matters, but this was never confirmed.
Club Managerial career
Records
Graham Taylor is the only manager to have twice led teams that amassed over 70 points in one Football League season under the League's original scoring system of two points for a win and one point for a draw which was introduced for the inaugural 1888–89 season and was retained for over 90 years until the reward for a win was increased to three points in 1981. He achieved this with Lincoln City (74 points – 1976) and Watford (71 points – 1978). To put this in perspective there were only two other occasions when this feat was accomplished, the other clubs concerned being Doncaster Rovers (72 points – 1947) and Rotherham United (71 points – 1951).
Lincoln City (1972–1977)
Taylor was the youngest person to become a FA coach, at the age of 27. Following his retirement from playing, Taylor became manager of Lincoln City, being the youngest manager in the league at the age of 28 in December 1972. Taylor led Lincoln to the Fourth Division title in 1976, during which the Imps set the league records for most wins (32), fewest defeats (4), and most points (74) (when 2 points were awarded for a win).
Watford (1977–1987)
In 1977, the 32-year-old Taylor was hired to manage Watford by new owner Elton John. He turned down an approach from First Division West Bromwich Albion in favour of a Fourth Division club, which caused a major surprise among many observers.
Taylor led Watford from the Football League Fourth Division to the First Division in only five years. In this first season in the Football League Fourth Division Watford won the title at his first attempt during the 1977–78 season, losing only five of 46 games and winning the league by 11 points. In the Football League Third Division Taylor led Watford to another promotion, finishing second, and losing out on the title by one point in the 1978–1979 season.
Taylor's third season in the Football League Second Division was less successful. Indicating the tougher competition, Watford managed only a 18th finish, out of 22 teams, avoiding relegation by eight points and winning only 12 of their 42 games in the 1979–1980 season. In the next season, the 1980–1981 season, Taylor improved Watford's performance, ending it with 16 wins and a 9th place finish. In the 81–82 season Watford achieved promotion, ending the season in 2nd place, and gaining 23 wins and 11 draws in 46 games.
In the First Division with Taylor as manager, Watford gained its highest-ever victory (8–0 against Sunderland, with Luther Blissett scoring four) as well as the "double" over Arsenal, an away win at Tottenham Hotspur, and home victories over Everton and Liverpool; this resulted in Watford finishing runners-up in the entire Football League. He then took the side to the third round of the UEFA Cup, having finished second in 1982–83 (the club's first season as a top division club). Taylor also led Watford to the 1984 FA Cup Final, which Watford lost to Everton 2–0. In his final season, 1986–87, Watford finished ninth in the league and reached the FA Cup semi-finals, missing out on another Wembley appearance when they lost to Tottenham, their chances hardly helped by the fact that both of their first team goalkeepers were injured.
Aston Villa (1987–1990)
In June 1987, Taylor left Watford for a new challenge at Aston Villa, who had just been relegated from the First Division. It was a terrible setback for the Midlanders, who had won the European Cup just five years earlier and had been league champions six years earlier.
Taylor managed to take Aston Villa back to the top flight with his first attempt, securing their top flight safety in 1988–89 with a win on the final day of the league season. During his third season at the club Villa finished runners-up in the first division, having led the league table at several stages of the season before being overhauled in the final weeks by Liverpool. Following this success, Taylor accepted an offer to take over the England national football team from Bobby Robson, who left the job after England's world cup semi-final defeat to Germany.
International management: England (1990–1993)
Appointment
When Graham Taylor took over the highest managerial job in English Football many complained that he was doing so without ever having won a major trophy – even though he had taken teams to second place in the league twice and an FA Cup final once. It was also pointed out Taylor had never played in 'top flight' football let alone international level and that winning the respect of the players would be difficult. His critics also noted although he had ditched the long-ball game at Aston Villa there was still tactical worries about his intentions when English clubs were looking to dispense with "route one" football in favour of a more "picturesque route to goal".[3]
1992 European Championship
Despite the unease at his appointment, England lost just once in Taylor's first 23 matches ( a 0–1 defeat to Germany at Wembley Stadium in September 1991).[4] However, England struggled to qualify for Euro '92. In a group containing Turkey, Ireland, and Poland England were held to 1–1 twice by the Irish and managed just 1–0 wins home and away against Turkey. It was only a last ditch goal from Gary Lineker against Poland that saw England qualify at the expense of the Irish. England's qualification for the Euro 92 finals proved to be the high point of Taylor's tenure.[5]
The number of players that Taylor was using in the run up to the championship was also questioned, and the gentlemen of the press viewed this as evidence Taylor did not not know his best team. He used 59 players in total, as he struggled to find a 'new spine' after the retirement of Peter Shilton, Terry Butcher and Bryan Robson.[6] He also faced accusations he could not cope with 'stars', after he dropped Paul Gascoigne for Gordon Cowans for a qualifying game against Ireland,[7] fearing he might "lose his head" in what would a "bruising" encounter.[8]
Matters were not helped by Taylor's reluctance to use creative players who did not have high work rates, such as Chris Waddle and Peter Beardsley. He also suffered several injuries, notably to Gary Stevens, Lee Dixon, John Barnes and Paul Gascoigne, leaving the squad in make-shift mode going into the finals. The loss of Mark Wright led to Taylor trying to call up Tony Adams, but UEFA refused, citing that it was too late.
England was drawn to face France, Denmark and hosts Sweden. In the opening game England started brightly and missed several chances to take a healthy lead. Platt was guilty of particularly glaring miss. Thereafter, the Danes began to dominate the match, and nearly won the game with minutes left as John Jensen struck a post. The game ended 0–0.[9] In the match against France, Platt nearly scored with a diving header which went inches wide of the post, and Stuart Pearce hit the bar with a free-kick. The game ended 0–0.[10]
England needed to beat hosts Sweden to advance to the semi-finals. Lineker crossed for Platt to open the scoring on four minutes, with a miss-kicked volley. However, England wasted several chanced to extend their lead. Platt made a pass to Tony Daley who wasted a chance to pass to Lineker in the open. England held a slender 1–0 lead at half-time.[11][12] After half-time, the Swedes changed their personnel and formation, and dominated the second half, scoring twice to win 2–1. England was eliminated.[13]
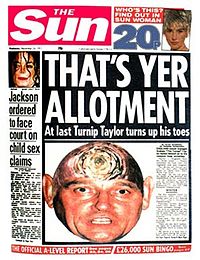
During the game, after 60 minutes and with the score at 1–1, Taylor substituted Gary Lineker in his final game for England. By doing this, he prevented Lineker from having the chance of equalling, or possibly even breaking, Bobby Charlton's record of 49 goals for England. Many were dismayed to see Taylor substitute England's top striker when his side needed a goal. This led to the media's vilification of Taylor, including the "turnip" campaign by The Sun, which began the morning after the game under the headline: "Swedes 2 Turnips 1". During that campaign the newspaper's back page featured an image of Taylor's face superimposed onto a turnip.[14]
1994 World Cup Qualification
Stuttering start
Taylor's relationship with the press was partially restored when he admitted his mistakes a few weeks after the finals.[15] However, this did not last long. England's first game after Euro 92 ended in a 1–0 defeat to Spain in a friendly, The Sun depicted Taylor as a "Spanish onion".[16]
England were drawn in Qualification Group 2 for the 1994 FIFA World Cup in the United States. The group contained Norway, The Netherlands, Poland, Turkey and San Marino. England were expected to qualify along with the Dutch.
England began with a disappointing 1–1 draw with Norway. Norway were the early pace setters, with victories over San Marino, the Netherlands and Turkey. Gascoigne returned, but the Norwegians were confident.[17] Despite dominating the game, England could muster only half chances. Platt gave England the lead in the 55th minute after a cross from Stuart Pearce. Norway rarely threatened, but equalised in the 77th minute, when Kjetil Rekdal scored from 20 yards. The draw flattered the Norwegians, but put them clear in the group.
Three wins and a Dutch draw
The campaign seemed to get back on track with two wins against Turkey (4–0 at home and 2–0 away) and a 6–0 home victory over San Marino. In April 1993 England faced the Netherlands at Wembley Stadium. England went 2–0 up in 24 minutes through John Barnes and David Platt. However Taylor's luck had started to take a turn for the worse, as Paul Gascoigne was injured by Jan Wouters' elbow, but the Dutchman was not sent off. Dennis Bergkamp scored a goal for the Netherlands towards the end of the first half, against the run of play, but England continued to control the game, and looked to be heading for a win which would have ended Dutch hopes of qualification, following the side's defeat in Norway, and a draw at home to the Poles. But four minutes from full-time Marc Overmars outpaced Des Walker, prompting Walker to foul him inside the penalty area. The penalty was converted by Peter Van Vossen and the game ended 2–2. Suddenly England's "World Cup life" looked in danger.[16]
Draw in Poland, defeat in Norway
England's next chance of reviving their flagging fortunes came in May, requiring at least a win and draw away against Poland and Norway which were to be played just three days apart. England were poor against Poland and were largely outplayed.[18] Dariusz Adamczuk of Poland scored in the 36th minute, although the team missed several chances to extend their lead. Ian Wright salvaged a vital point through forcing an equaliser in the 85th minute, for a final score of 1–1.[18] Taylor was again vilified for his team's poor performance. England's next opponents were Norway.
The Norwegians had arrived from obscurity and had taken the group by storm with a series of early victories which had left England, Poland, and The Netherlands scrapping for second place.[18] Taylor made wholesale changes of personnel and tactics, which again drew criticism, his actions considered risky in what was now a crucial game. Lee Sharpe and Lee Dixon came on as wing-backs, while Carlton Palmer and Platt occupied midfield berths. Gascoigne supported Teddy Sheringham and Les Ferdinand up-front. Des Walker, Tony Adams and Gary Pallister formed a back three.[18]
England lost 2–0, with few attempts on goal. Lars Bohinen and Øyvind Leonhardsen scored the goals in the 42nd and 47th minutes. The first was caused by a Des Walker error, while Walker was beaten for pace by a Norwegian counter-attack for Bohinen to score[19]
Subsequently Taylor said "We made a complete mess of it. I'm here to be shot at and take the rap. I have no defence for our performance",[20] although his honesty did not spare him a roasting from the press, who were now calling for his head.[20] The press came up with headlines such as "NORSE MANURE" and "OSLO RANS".[21]
The US Cup
With their World Cup hopes hanging by a thread, Taylor's England were to play a four-team Tournament in the U.S (1993 U.S. Cup), which was expected to be a precursor to the following summer's tournament. Taylor stated before the game against the USA:
In football, you're only as good as your last game, and at the moment we're poor. You can always lose any game, to anyone. It's how you lose that matters. That was the thing that shocked us all in Norway. We would have been looking for a win here anyhow, but if we'd won last week it wouldn't have been considered essential. Now it is. Whether we like it or not, people expect us to beat America, and there is definitely more intensity about this game because of our performance in the last one.[22]
For Taylor the US Cup began with a humiliating 2–0 defeat in Boston to the USA which was reported by the tabloid press in Britain as "YANKS 2 PLANKS 0!".[23][24] Some pride was restored with a credible 1–1 draw with Brazil and a narrow 2–1 defeat to Germany. Taylor was now living on borrowed time.[25]
The Holland game
The 1993–94 season began with a much improved performance, with a 3–0 win over Poland raising the nation's hopes going into what was now the crucial match against the Dutch in Rotterdam.[26]
In October England were to play the Netherlands in Rotterdam. With Norway having won the group the encounter would effectively decide the second and last qualifier of the group. The game was played at a furious pace, with the Dutch putting the English under pressure early on. However England hit back with a string of counter attacks, with Platt heading just wide and Tony Adams having a shot cleared off the line by Erwin Koeman, while Tony Dorigo hit a post with a 35-yard free-kick after 25 minutes.[26][27] Two minutes before half-time England were fortunate to have a Frank Rijkaard goal ruled out for offside, even though replays showed the goal was legitimate.[26] However later in the second half with the game locked at 0–0 David Platt was fouled by Ronald Koeman as he raced in on goal. The German referee failed to apply the rule of sending him off for a professional foul. The Dutch charged down Dorigo's free-kick, with Dutch players clearly encroaching.[28] Just minutes later the Dutchman took an identical free kick outside England's penalty area. His first shot was blocked, but it was ordered to be retaken because of encroachment.[26] Koeman scored at the second attempt. Paul Merson hit a post with a free-kick moments later, while Dennis Bergkamp scored just moments later, despite using his arm to control the ball, for 2–0 win.[26] In the meantime Taylor was in an apoplectic mood on the touchline, berating the officials and referee as the significance of the result sank in.[26]
San Marino and resignation
England still had a chance to qualify if the Netherlands lost in Poland on the same night England were hoping they could run up a big score against part-time minnows San Marino. But it was in the final game that Taylor was to suffer the ultimate humiliation. After just 8.3 seconds of play David Gualtieri, a computer salesman, scored the fastest World Cup goal (as of 2009 it remains the fastest World Cup goal). England took another twenty minutes to find an equaliser and eventually won 7–1, but the Dutch had won in Poland and England had failed to qualify.
Taylor resigned on 24 November 1993. He went 'with great sadness', saying: 'No one can gauge the depth of my personal disappointment at not qualifying for the World Cup.' There had been no question of him wanting to stay on, in any capacity. 'This is the appropriate course of action in the circumstances,' he said. 'If we didn't qualify, it was always my intention to offer my resignation.'[29]
Taylor had also agreed to be filmed during the qualifying campaign for Cutting Edge, a Channel 4 fly-on-the-wall documentary series, in which his portrayal further undermined his authority. During the film, Taylor was heard to use foul language, and what became his personal catchphrase: "Do I not like that", uttered just before England conceded a goal to Poland.
Return to club management
Wolverhampton Wanderers (1994–1995)
Sir Jack Hayward appointed Taylor as manager of Wolves in March 1994, replacing Graham Turner. Taylor had been a generally unpopular figure in English football since his unsuccessful reign as national coach, and few people seemed willing to forgive him for his first managerial failure – one that mattered most to so many people up and down the country.
But he took the Midlands club to fourth in Division One to qualify for the playoffs – their highest league finish since their last top division season 11 years earlier – where they lost out to Bolton Wanderers. They also reached the quarter finals of the FA Cup after a memorable replay penalty shootout victory over Sheffield Wednesday, in which they were 3–0 down on penalties, only to win the shootout 4–3, in which Chris Bart-Williams had two penalties saved over the two matches.
Taylor spent heavily on players while at Wolves, paying large sums for the likes of Steve Sedgley, Tony Daley and Don Goodman.[30]
However, the 1994–95 season proved to be his only full season at Molineux, as, after a poor start to the following campaign, winning just 4 from the 16 opening league games, he resigned in November 1995 due to overwhelming supporter pressure. During his tenure, he attempted to perform a citizen's arrest on a fan who had spat at him, prompting calls for closer crowd controls in the English game.[31]
Return to Watford (1996–2001)
In February 1996 Elton John, who had recently bought Watford for a second time, appointed Taylor as General Manager at Vicarage Road. Just over a year later Taylor had appointed himself as the club's manager succeeding Kenny Jackett, who was relegated to a coaching capacity at the club. He won the Division Two championship at his first attempt in 1998, despite having a life-threatening abscess that blocked his windpipe and almost killed him.[32]
The following season Taylor won the Division One Play-off Final, beating Bolton Wanderers 2–0 at Wembley, and with it promotion to the Premier league, where Watford were relegated after one season. Despite starting the following season well – unbeaten through the first fifteen league games and heading the table – Watford slumped to finish 9th in Division One with Taylor publicly stating he had lost his powers of motivation. At this point Taylor decided to retire. During this final season Taylor had become only the third manager to manage 1,000 league games in England, after Brian Clough and Jim Smith.
Return to Aston Villa (2002–2003)
Taylor came out of retirement in February 2002 to return to his old job at Aston Villa, but retired for a second time after Villa finished the 2002–03 season in 16th place in the Premiership.[33] He subsequently cited tensions in his relationship with the club's chairman Doug Ellis and argued for an overhaul of the club's upper management to allow the club to be more competitive.
Post managerial career (Since 2003)
In 2003, Taylor became vice-president at League One club Scunthorpe United, his hometown club. Since 2004, he has worked as a pundit on BBC Radio Five Live, and has managed a team of celebrities for Sky One's annual series, The Match.
His time at Scunthorpe has seen a turnaround in the club's fortunes. In his first season on the board, they narrowly avoided relegation to the Conference. The following season, they were promoted to League One. Two years after that, they were promoted to the Football League Championship as League One champions.
Taylor returned to Watford on 23 January 2009, being appointed to the new board as a non-executive director and was appointed interim chairman on 16 December 2009.[34]
Other work
Graham Taylor is a supporter of Sense-National Deafblind and Rubella Association and is a Patron of DebRa (www.debra.org.uk). He is a Celebrity Ambassador for the Sense Enterprise Board in Birmingham, and has worked to raise both funds and awareness, including running the London Marathon in 2004. He regularly hosts moderated "online coaching seminars" on the DALnet channel irc://irc.dal.net/digi . He also supports the Royal British Legion and cycled from London to Paris in 2010 to raise funds for the RBL's Poppy appeal.
Honours
As a player
- Lincolnshire Senior Cup winner: 1967–68
- Lincolnshire Senior Cup winner: 1968–69, 1969–70
As a manager
- Lincolnshire Senior Cup winner: 1974–75
- Football League Fourth Division champions: 1975–76
- Football League Fourth Division champions: 1977–78
- Football League Third Division runners up: 1978–79
- Football League Second Division runners up: 1981–82
- Football League First Division runners up: 1982–83
- FA Cup runner-up: 1984
- Football League Division Two champions: 1997–98
- Football League Division One play-off winner: 1998–99
- Football League Second Division runners up: 1987–88
- Football League First Division runners up: 1989–90
Managerial statistics
All teams managed by Graham Taylor have been English.
Team From To Record G W D L Win % Lincoln City Dec 1972 Jun 1977 211 97 61 53 45.97 Watford Jun 1977 May 1987 466 210 114 142 45.06 Aston Villa May 1987 Jul 1990 142 65 35 42 45.77 England 1990 1993 38 18 13 7 47.37 Wolverhampton Wanderers Mar 1994 Nov 1995 87 36 27 24 41.38 Watford Feb 1996 Jun 2001 275 104 80 91 37.82 Aston Villa Feb 2002 May 2003 60 19 14 27 31.67 References
- England: The Official F.A History, Niall Edworthy, Virgin Publishers, 1997, ISBN 1-85227-699-1.
- Gary Lineker: Strikingly Different, Colin Malam, Stanley Paul Publications, London, 1993 ISBN 0-09-175424-0
- Do I not Like That – The Final Chapter, Chrysalis Sport, Distributed by Polygram Record Operations, 1994.
- ^ Taylor, Graham (2005-02-19). "Taylor on Saturday". Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/sport/main.jhtml?xml=/sport/2005/02/19/sfntay19.xml. Retrieved 2008-03-16.
- ^ Edworthy, p. 156
- ^ Edworthy, pp. 14–147
- ^ Edworthy, p. 148
- ^ Edworthy 1997, p. 148.
- ^ Edworthy 1997, p. 156.
- ^ Edworthy 1997, p. 149.
- ^ Edworthy 1997, p. 1150.
- ^ Granville, Brian England's Managers: The Toughest Job in Football 2007, ISBN 978-0755316519 p. 176.
- ^ http://www.englandfootballonline.com/MatchRsl/SumsGiller1990-96.html England v France 14 June 1992.
- ^ http://www.englandfootballonline.com/Seas1990-00/1991-92/M0688Swe1992.html England National Football Team Match No. 688, 17 June 1992
- ^ Granville, Brian England's Managers: The Toughest Job in Football 2007, ISBN 978-0755316519 p. 177.
- ^ http://www.englandfootballonline.com/MatchRsl/SumsGiller1990-96.html England v Sweden 17 June 1992
- ^ Edworthy, p. 149
- ^ Malam, pp. 120–121
- ^ a b Edworthy, p. 151
- ^ http://www.independent.co.uk/sport/football-england-turn-to-gascoigne-for-dream-start-1557388.html England turn to Gascoigne for dream start
- ^ a b c d Edworthy, p. 152
- ^ Lovejoy, Joe (3 June 1993). "Norway destroy Taylor's England: Calamity in Oslo as a revamped team collapses in the face of Scandinavian skill". The Independent (London). http://www.independent.co.uk/sport/football--world-cup-norway-destroy-taylors-england-calamity-in-oslo-as-a-revamped-team-collapses-in-the-face-of-scandinavian-skill-1489441.html.
- ^ a b Edworthy, p. 153
- ^ Do I Not Like That -The Final Chapter
- ^ Lovejoy, Joe (9 June 1993). "Football: Batty given the safety-pin role for belt-and-braces England: Walker and Sheringham dropped in wake of Norway humiliation as US Cup opener against United States becomes of vital importance to Taylor's tenure". The Independent (London). http://www.independent.co.uk/sport/football-batty-given-the-safetypin-role-for-beltandbraces-england-walker-and-sheringham-dropped-in-wake-of-norway-humiliation-as-us-cup-opener-against-united-states-becomes-of-vital-importance-to-taylors-tenure-1490608.html. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
- ^ http://www.independent.co.uk/sport/football-the-painful-failure-of-a-proud-man-trevor-haylett-on-the-highs-and-lows-in-graham-taylors-career-1506464.html Football: The painful failure of a proud man: Trevor Haylett on the highs and lows in Graham Taylor's career
- ^ Joe Lovejoy (10 June 1993). "England's new low as US pile on the misery". The Independent. http://www.independent.co.uk/sport/football-englands-new-low-as-us-pile-on-the-misery-dooley-and-lalas-add-a-further-chapter-to-taylors-tale-of-woe-as-the-americans-go-one-better-than-their-forebears-in-belo-horizonte-1490806.html. Retrieved 23 June 2010.
- ^ Edworthy, p. 154
- ^ a b c d e f Edworthy, p. 154
- ^ http://www.mirrorfootball.co.uk/incoming/article109937.ece/BINARY/Holland+2-0+England Rotter: Holland 2 England 0, October 1993.
- ^ Glanville, Brian. England Managers: The Toughest Job in Football, p. 185.
- ^ http://www.independent.co.uk/sport/football-howe-set-to-become-england-caretaker-taylor-accepts-the-inevitable-and-tenders-resignation-as-fa-considers-its-options-with-chief-executive-favouring-twotier-administration-1506463.html Football: Howe set to become England caretaker: Taylor accepts the inevitable and tenders resignation as FA considers its options with chief executive favouring two-tier administration.
- ^ [1]
- ^ Duxbury, Nick (25 April 1995). "FOOTBALL Tait's 'prank' finishes with an FA charge". The Independent (London). http://www.independent.co.uk/sport/football--------------------------taits-prank-finishes-with-an-fa-charge-1617082.html. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
- ^ http://www.independent.co.uk/arts-entertainment/profile-graham-taylor--the-turnip-strikes-back-1111071.html The Turnip Strikes Back
- ^ "Taylor quits Villa". BBC Sport. 2003-05-14. http://news.bbc.co.uk/sport1/hi/football/teams/a/aston_villa/3027817.stm. Retrieved 2007-12-08.
- ^ http://www.watfordfc.com/page/NewsDetail/0,,10400~1529215,00.html
External links
Links to related articles Lincoln City F.C. – managers Martin (1896–97) · West (1897–1900) · Calderhead (1900–07) · Strawson (1907–14) · Fraser (1919–21) · Calderhead, Jr. (1921–24) · Henshall (1924–27) · Parkes (1927–36) · McClelland (1936–46) · Anderson (1946–65) · Moulson (1965) · Chapman (1965–66) · Gray (1966–70) · Loxley (1970–71) · Herd (1971–72) · Taylor (1972–77) · Kerr (1977) · Bell (1977–78) · Murphy (1978–85) · Pickering (1985) · Kerr (1985–87) · Daniel (1987) · Murphy (1987–90) · Clarke (1990) · Thompson (1990–93) · Alexander (1993–94) · Ellis (1994–95) · Wicks (1995) · Beck (1995–98) · Westley (1998) · Reames (1998–2000) · Stant (2000–01) · Buckley (2001–02) · Alexander (2002–06) · Schofield (2006–07) · Brown & Onuora (2007) · Jackson (2007–09) · Clark (2009) · Sutton (2009–10) · Lindsey (2010) · Tilson (2010–11) · Brown (2011) · Holdsworth (2011–)
Watford F.C. – managers Goodall (1903–10) · Kent (1910–26) · Pagnam (1926–29) · McBain (1929–37) · Findlay (1938–47) · Bray (1947–48) · Hapgood (1948–50) · Gray (1950–51) · Green (1951–52) · Goulden (1952–55) · Paton (1955–56) · Goulden (1956) · McBain (1956–59) · Burgess (1959–63) · McGarry (1963–64) · Furphy (1964–71) · Kirby (1971–73) · Keen (1973–77) · Taylor (1977–87) · Bassett (1987–88) · Harrison (1988–90) · Lee (1990) · Perryman (1990–93) · Roeder (1993–96) · Taylor (1996) · Jackett (1996–97) · Taylor (1997–2001) · Vialli (2001–02) · Lewington (2002–05) · Boothroyd (2005–08) · Mackay (2008) · Rodgers (2008–09) · Mackay (2009–11) · Dyche (2011–)
Aston Villa F.C. – managers Ramsay (1884–1926) · Smith (1926–34) · McMullan (1934–35) · Hogan (1936–39) · Massie (1945–50) · Martin (1950–53) · Houghton (1953–58) · Mercer (1958–64) · D. Taylor (1964–67) · Cummings (1967–68) · Docherty (1968–70) · Crowe (1970–74) · Saunders (1974–82) · Barton (1982–84) · Turner (1984–86) · McNeill (1986–87) · G. Taylor (1987–90) · Venglos (1990–91) · Atkinson (1991–94) · Little (1994–98) · Gregory (1998–2002) · G. Taylor (2002–03) · O'Leary (2003–06) · O'Neill (2006–10) · Houllier (2010–11) · McLeish (2011–)
England national football team – managers Winterbottom (1946–1962) · Ramsey (1963–1974) · Mercer (caretaker) (1974) · Revie (1974–1977) · Greenwood (1977–1982) · Robson (1982–1990) · G. Taylor (1990–1993) · Venables (1993–1996) · Hoddle (1996–1999) · Keegan (1999–2000) · Wilkinson (caretaker) (2000) · P. Taylor (caretaker) (2000–2001) · Eriksson (2001–2006) · McClaren (2006–2007) · Capello (2008–)
England squad – UEFA Euro 1992 
Wolverhampton Wanderers F.C. – managers Worrall (1877–85) · Addenbrooke (1885–1922) · Jobey (1922–24) · Hoskins (1924–26) · Scotchbrook (1926–27) · Buckley (1927–44) · Vizard (1944–48) · Cullis (1948–64) · Beattie (1964–65) · Allen (1965–68) · McGarry (1968–76) · Chung (1976–78) · Barnwell (1978–82) · Greaves (1982) · Hawkins (1982–84) · Docherty (1984–85) · McGarry (1985) · Chapman (1985–86) · Turner (1986–94) · Taylor (1994–95) · McGhee (1995–98) · Lee (1998–2000) · Jones (2001–04) · Hoddle (2004–06) · McCarthy (2006–)
Categories:- UEFA Euro 1992 managers
- England national football team managers
- English football managers
- Premier League managers
- Aston Villa F.C. managers
- Lincoln City F.C. managers
- Watford F.C. managers
- Watford F.C. directors
- English footballers
- Grimsby Town F.C. players
- Wolverhampton Wanderers F.C. managers
- Lincoln City F.C. players
- People from Worksop
- Officers of the Order of the British Empire
- 1944 births
- Living people
- People from Scunthorpe
- The Football League players
- English Football Hall of Fame inductees
- British association football commentators
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.