- Manifold (scuba)
-
In scuba diving a manifold is used to connect two diving cylinders (tanks) with breathing gas, providing a greater amount of gas for longer dive times and greater safety due to redundancy. Diving with two or more cylinders is associated with technical diving.
Contents
Function
Longer and deeper dives require a greater amount of breathing gas, in turn requiring either a larger cylinder or multiple cylinders. A large tank (up to 18 L) is very heavy and tends to raise the diver's center of mass, making them unbalanced in water. A simple multiple-tank configuration called separate doubles consists of two mechanically attached but otherwise unconnected tanks with two complete regulator sets (with a total of two first stage regulators and two second stage regulators).
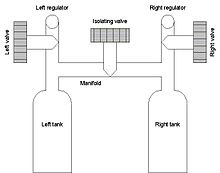
The function of a manifold is to connect the air supplies of two cylinders (called doubles or Twins), allowing the diver to breathe simultaneously from both. The manifold is a metal tube (usually made of aircraft grade brass[1]) with two cylinder connectors, two first-stage regulator connectors and three valves, as shown in the figure above. The left and the right valves allow to disconnect the corresponding first stage regulators, leaving the entire gas supply to be used through the remaining regulator. The central valve, called the isolating valve, separates the tanks into two independent systems, each with its own first-stage and second-stage regulators.
Common emergency procedures
This article is not a diving manual! See Wikipedia:Risk disclaimer. This section describes the standard procedures of addressing the out-of-air situation and the free-flow, an uncontrollable loss of breathing gas due to a mechanical malfunction of a regulator or a tank connection. The common technical diving configuration is assumed as defined by DIR.
Gas sharing
The diver breathes from the primary second-stage regulator connected to the right-shoulder cylinder by a long (2 meter/7-foot) hose. A secondary second-stage regulator is worn on his neck, connected to the left-shoulder cylinder by a short (0.5 meter/2-foot) hose. If a partner experiences an out-of-air emergency, diver hands him his primary regulator, which he knows for sure is functioning properly. The diver then switches to his secondary regulator. The entire gas supply is available to the two divers for the remainder of the dive.
Primary regulator free-flow malfunction
If the primary regulator malfunctions, the diver closes the right-shoulder cylinder valve and switches to the secondary regulator. The entire gas supply is available for the remainder of the dive.
Secondary second stage free-flow malfunction
If the secondary regulator malfunctions, the diver closes the left-shoulder cylinder valve, continuing to breathe through the primary regulator. The entire gas supply is available for the remainder of the dive.
Right cylinder connection free-flow malfunction
Cylinder to manifold connection malfunction, though rare, can result in an extremely violent gas loss. In case of the right shoulder connection free-flow, the diver closes the isolating valve and the right shoulder cylinder valve. He then switches to the secondary regulator. Closing the right shoulder valve does not conserve the remaining gas in the right cylinder, but rather reduces the distraction and loss of visibility due to bubble flow. A half of the remaining gas volume is available for the remainder of the dive.
Left cylinder connection free-flow malfunction
In case of the left shoulder connection free-flow, the diver closes the isolating valve and the left shoulder cylinder valve. He continues to breathe through the primary regulator. A half of the remaining gas volume is available for the remainder of the dive.
Advantages
Compared to the alternatives, the manifold offers the following advantages:
- Convenience - offers a better fit of cylinders than a single large tank, improving streamlining and comfort of the diver.
- Simplicity - the ability to breathe through an entire dive from a single regulator without the need to change second stages, except in an emergency.
- Ease of air sharing - a standard procedure exists for the situation when air sharing is needed. The long hose regulator is passed to the partner while the air donor switches to the short hose.
- Standard malfunction treatment - in case of a regulator or manifold malfunction a standard procedure can be used to minimize the gas loss. The diver can localize the malfunction and isolate it from the functioning system by closing the necessary valves.
Criticism
A manifold is a single point of failure for the gas supply, especially dangerous in overhead environments such as caves or wrecks.
Links
- DIR diving
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.