- Cosmopolitanism
-
Cosmopolitanism is the ideology that all human ethnic groups belong to a single community based on a shared morality. This is contrasted with communitarian and particularistic theories, especially the ideas of patriotism and nationalism.[citation needed] Cosmopolitanism may entail some sort of world government or it may simply refer to more inclusive moral, economic, and/or political relationships between nations or individuals of different nations. A person who adheres to the idea of cosmopolitanism in any of its forms is called cosmopolite.
The cosmopolitan community might be based on an inclusive morality, a shared economic relationship, or a political structure that encompasses different nations. In its more positive versions, the cosmopolitan community is one in which individuals from different places (e.g. nation-states) form relationships of mutual respect. As an example, Kwame Anthony Appiah suggests the possibility of a cosmopolitan community in which individuals from varying locations (physical, economic, etc.) enter relationships of mutual respect despite their differing beliefs (religious, political, etc.).
The word derives from Greek cosmos Κόσμος (the Universe) and polis Πόλις (city).
Contents
Philosophical cosmopolitanism
Further information: Global justice, Moral universalismPhilosophical roots
Cosmopolitanism can be traced back to Diogenes of Sinope (c. 412 B.C.), the founding father of the Cynic movement in Ancient Greece. Of Diogenes it is said: "Asked where he came from, he answered: 'I am a citizen of the world (kosmopolitês)'".[1] This was a ground-breaking concept, because the broadest basis of social identity in Greece at that time was either the individual city-state or the Greeks (Hellenes) as a group. The Stoics, who later took Diogenes' idea and developed it into a full blown concept, typically stressed that each human being "dwells […] in two communities – the local community of our birth, and the community of human argument and aspiration".[2] A common way to understand Stoic cosmopolitanism is through Hierocles' circle model of identity that states that we should regard ourselves as concentric circles, the first one around the self, next immediate family, extended family, local group, citizens, countrymen, humanity. The task of world citizens becomes then to "draw the circles somehow towards the centre, making all human beings more like our fellow city dwellers, and so forth."[3]
Modern cosmopolitan thinkers
 Immanuel Kant argued for a ius cosmopoliticum.
Immanuel Kant argued for a ius cosmopoliticum.
In his 1795 essay Perpetual Peace, Immanuel Kant stages a ius cosmopoliticum (cosmopolitan law/right) as a guiding principle to protect people from war, and morally grounds this cosmopolitan right by the principle of universal hospitality. Kant there claimed that the expansion of hospitality with regard to "use of the right to the earth's surface which belongs to the human race in common" (see common heritage of humanity) would "finally bring the human race ever closer to a cosmopolitan constitution".[4]
The philosophical concepts of Emmanuel Levinas, on ethics, and Jacques Derrida, on hospitality, provide a theoretical framework for the relationships between people in their everyday lives and apart from any form of written laws or codes. For Levinas, the foundation of ethics consists in the obligation to respond to the Other. In Being for the Other, he writes that there is no "universal moral law," only the sense of responsibility (goodness, mercy, charity) that the Other, in a state of vulnerability, calls forth. The proximity of the Other is an important part of Levinas's concept: the face of the Other is what compels the response.
For Derrida, the foundation of ethics is hospitality, the readiness and the inclination to welcome the Other into one's home. Ethics, he claims, is hospitality. Pure, unconditional hospitality is a desire that underscores the conditional hospitality necessary in our relationships with others. Levinas's and Derrida's theories of ethics and hospitality hold out the possibility of an acceptance of the Other as different but of equal standing. Isolation is not a feasible alternative in the world, therefore, it is important to consider how best to approach these interactions, and to determine what is at stake for ourselves and the others: what conditions of hospitality to impose, and whether or not we have responded to the call of the Other. Further, both theories reveal the importance of considering how best to interact with the Other and others, and what is at stake.
A further state of cosmopolitanism occurred after the Second World War. As a reaction to the Holocaust and the other massacres, the concept of crimes against humanity became a generally-accepted category in international law. This clearly shows the appearance and acceptance of a notion of individual responsibility that is considered to exist toward all of humankind.[5]
Philosophical cosmopolitans are moral universalists: they believe that all humans, and not merely compatriots or fellow-citizens, come under the same moral standards. The boundaries between nations, states, cultures or societies are therefore morally irrelevant. A widely cited example of a contemporary cosmopolitan is Kwame Anthony Appiah.[6]
Some philosophers and scholars argue that the objective and subjective conditions arising in today's unique historical moment, an emerging planetary phase of civilization, creates a latent potential for the emergence of a cosmopolitan identity as global citizens and possible formation of a global citizens movement.[7] These emerging objective and subjective conditions in the planetary phase include improved and affordable telecommunications; space travel and the first images of our fragile planet floating in the vastness of space; the theory of global warming and other ecological threats to our collective existence; new global institutions such as the United Nations, World Trade Organization, or International Criminal Court; the rise of transnational corporations and integration of markets often termed economic globalization; the emergence of global NGOs and transnational social movements, such as the World Social Forum; and so on. Globalization, a more common term, typically refers more narrowly to the economic and trade relations and misses the broader cultural, social, political, environmental, demographic, values and knowledge transitions taking place.
Contemporary cosmopolitan thinkers
A number of contemporary theorists propose, directly and indirectly, various ways of becoming or being a cosmopolitan individual.
Thich Nhat Hanh discusses what he calls "Interbeing" as a way of living one's life in relation to others; "Interbeing" might easily be compared to cosmopolitanism. Nhat Hanh's philosophical beliefs are grounded in the precepts of Buddhist teachings, which involve compassion and understanding to protect and live in harmony with all people, animals, plants, and minerals (88). He further describes what he calls "Mindfulness Training of the Order of Interbeing" as being aware of sufferings created by, but not limited to, the following causes: fanaticism and intolerances that disrupt compassion and living in harmony with others; indoctrination of narrow-minded beliefs; imposition of views; anger; and miscommunication (89-95).[8] Understanding and compassion for others seems to be achieved by the understanding of others' suffering and the root causes of suffering. Therefore, to be responsible is to recognize and understand suffering, which then leads to compassion. It is through this process that others can be recognized as people.
Other theorists, philosophers, and activists contend that recognizing suffering is necessary to end violence. In Scared Sacred, Velcrow Ripper takes a journey to different sites of great suffering that ultimately leads him toward developing compassion.[9] In "The Planet", Paul Gilroy explores how the construction and naturalization of race and the hierarchies produced by difference shape the hatred of others. It is the deconstruction of these ideologies that can lead to the compassion and humanization of others. Thus individual responsibility is being aware of what Judith Butler calls the precariousness of life in self and other; being a cosmopolitan seems to be, above all, a social, ethical enterprise.
In Cosmopolitanism: Ethics in a World of Strangers, Kwame Anthony Appiah notices something important about how social ethics seem to operate: Whatever obligation I might have to another, especially a foreign other, that obligation does not supersede the obligations I have to those people most familiar to me. However, as Judith Butler questions, "at what cost do I establish the familiar as the criterion" for valuing others? (Precarious Life 38).[10] If I value the familiar more than the foreign, what are the consequences? Paul Gilroy offers a possible alternative to this emphasis on familiarity arguing that "methodical cultivation of a degree of estrangement from one's own culture and history ... might qualify as essential to a cosmopolitan commitment" (The Planet 67). This estrangement entails a "process of exposure to otherness" in order to foster "the irreducible value of diversity within sameness" (67).[11] Estrangement, therefore, could lead to de-emphasising the familiar in ethics by integrating otherness.
For Gilroy, being cosmopolitan seems to involve both a social, ethical enterprise and a cultural enterprise. In "The Planet", Gilroy describes the cases of Tom Hurndall (80) and Rachel Corrie (81); each seems to exemplify what might be considered Gilroy's figure of the cosmopolitan. Both Hurndall and Corrie removed themselves (geographically) from their home cultures, presumably both physically and mentally estranging themselves from their own cultures and histories. Interestingly, though, Hurndall and Corrie were both killed in 2003 (in separate incidents) and their stories might serve as affirmations of familiarity, rather than models of estrangement. Gilroy’s model of estrangement might actually undermine itself through its examples; this might be construed as a failure of Gilroy’s theory to address the practical difficulties of estranging oneself from the familiar.[12]
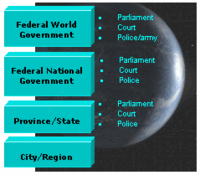 Cosmopolitanism is a broader concept than world government
Cosmopolitanism is a broader concept than world government
Some forms of cosmopolitanism also fail to address the potential for economic colonization by powerful countries over less powerful ones. Frantz Fanon, in “The Wretched of the Earth”, observes that when nations achieved independence from European colonizers, frequently there was no system in place to secure their economic future, and they became "manager[s] for Western enterprise...in practise set[ting] up its country as the brothel of Europe" (154).[13] When "third world" nations are drawn into economic partnerships with global capital, ostensibly to improve their national quality of life, often the only ones benefitting from this partnership are well-placed individuals and not the nation itself.
Further, Mahmood Mamdani in Good Muslim, Bad Muslim suggests that the imposition of Western cultural norms, democracy and Christianity to name only two, has historically resulted in nationalist violence;[14] however, Appiah has implied that democracy is a pre-requisite for cosmopolitan intervention in developing nations (Kindness to Strangers 169).[15] Cosmopolitanism, in these instances, appears to be a new form of colonization: the powerful exploit the weak and the weak eventually fight back.
Much of the political thinking of the last two centuries has taken nationalism and the framework of the sovereign nation-state for granted. Now, with the advance of globalization and the increased facility of travel and communication, some thinkers consider that the political system based on the nation-state has become obsolete and that it is time to design a better and more efficient alternative. Jesús Mosterín analyzes how the world political system should be organized in order to maximize individual freedom and individual opportunity. Rejecting as muddled the metaphysical notion of free will, he focuses on political freedom, the absence of coercion or interference by others in personal decisions. Because of the tendencies to violence and aggression that lurk in human nature, some constraint on freedom is necessary for peaceful and fruitful social interaction, but the more freedom we enjoy, the better.[16]
Especially, there is no rational ground for curtailing the cultural freedoms (of language, religion and customs) in the name of the nation, the church or the party. From this point of view, Internet provides a much more attractive model than the nation-state. Neither is there any just reason for restraining the free circulation of people, ideas or goods. Mosterín thinks that the nation-state is incompatible with the full development of freedom, whose blossoming requires the reorganization of the world political system along cosmopolitan lines. He proposes a world without sovereign nation-states, territorially organized in small autonomous but not-sovereign cantonal polities, complemented by strong world organizations.[17] He emphasizes the difference between international institutions, led by representatives of the national governments, and world or universal institutions, with clearly defined aims served by directors selected by their personal qualifications, independently of any national bias or proportion.
Political and sociological cosmopolitanism
Ulrich Beck (b. May 15, 1944) is a sociologist who has posed the new concept of cosmopolitan critical theory in direct opposition to traditional nation-state politics. Nation-state theory sees power relations only among different state actors, and excludes a global economy, or subjugates it to the nation-state model. Cosmopolitanism sees global capital as a possible threat to the nation state and places it within a meta-power game in which global capital, states and civil society are its players.
It is important to mark a distinction between Beck's cosmopolitanism and the idea of a world state. For Beck, imposing a single world order is considered hegemonic at best and ethnocentric at worst. Rather, political and sociological cosmopolitanism rests upon these fundamental foundations:
- "Acknowledging the otherness of those who are culturally different"
- "Acknowledging the otherness of the future"
- "Acknowledging the otherness of nature"
- "Acknowledging the otherness of the object"
- "Acknowledging the otherness of other rationalities"
 Emmanuel Levinas argued for cosmopolitanism in terms of moral choices in conscience supporting the "Other".
Emmanuel Levinas argued for cosmopolitanism in terms of moral choices in conscience supporting the "Other".
A number of philosophers, including Emmanuel Levinas, have introduced the concept of the "Other". For Levinas, the Other is given context in ethics and responsibility; we should think of the Other as anyone and everyone outside ourselves. According to Levinas, our initial interactions with the Other occur before we form a will—the ability to make choices. The Other addresses us and we respond: even the absence of response is a response. We are thus conditioned by the Other's address and begin to form culture and identity. After the formation of the will, we choose whether to identify with the addresses by others and, as a result, continue the process of forming identity.[18]
During this process, it is possible to recognize ourselves in our interactions with Others. Even in situations where we engage in the most minimal interaction, we ascribe identities to others and simultaneously to ourselves. Our dependence on the Other for the continuous formation of language, culture, and identity means that we are responsible to others and that they are responsible to us. Also once we've formed a will, it becomes possible to recognize this social interdependence. When we have gained the capacity for recognition, the imperative is to perform that recognition and thereby become ethically responsible to the Other in conscience.[19]
Cosmopolitanism shares some aspects of universalism--namely the globally acceptable notion of human dignity that must be protected and enshrined in international law. However, the theory deviates in recognising the differences between world cultures. Thus, a "cosmopolitan declaration of human rights" would be defined in terms of negatives that no one could disagree over.
In addition, cosmopolitanism calls for equal protection of the environment and against the negative side effects of technological development. Human dignity, however, is convoluted because it is necessary to first distinguish who has the right to be respected and second to consider what rights are protectable. Under cosmopolitanism, all humans have rights; however, history shows that recognition of these rights is not guaranteed.
As an example, Judith Butler discusses a Western discourse of "human" in Precarious Life: The Powers of Mourning and Violence. Butler works through the idea of "human" and notes that "human" has been "naturalized in its 'Western' mold by the contemporary workings of humanism" (32). Thus, there is the idea that not all "human" lives will be supported in the same way, indeed, that some human lives are worth more protection than others.
This idea is reiterated in Sunera Thobani's "Nationality in the Age of Global Terror," where she discusses a discourse in which Muslim people fall into a good/bad dichotomy: a "good Muslim" is one who has been Westernized and a "bad Muslim" is one who visibly rejects Western cultural influences. Thobani notes that it is through media representations that these ideas become naturalized. Individuals who embrace Western ideals are considered fully "human" and are more likely to be afforded dignity and protection than those who defend their non-Westernized cultural identities.
According to those who follow Beck's reasoning, a cosmopolitan world would consist of a plurality of states, which would use global and regional consensus to gain greater bargaining power against opponents. States would also utilise the power of civil society actors such as Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and consumers to strengthen their legitimacy and enlist the help of investors to pursue a cosmopolitan agenda.
Other authors imagine a cosmopolitan world moving beyond today's conception of nation-states. These scholars argue that a truly cosmopolitan identity of Global Citizen will take hold, diminishing the importance of national identities. The formation of a global citizens movement would lead to the establishment of democratic global institutions, creating the space for global political discourse and decisions, would in turn reinforce the notion of citizenship at a global level. Nested structures of governance balancing the principles of irreducibility (i.e., the notion that certain problems can only be addressed at the global level, such as global warming) and subsidiarity (i.e., the notion that decisions should be made at as local a level possible) would thus form the basis for a cosmopolitan political order.[20]
Daniele Archibugi proposes a renewed model for global citizenship:[21] institutional cosmopolitanism. It advocates some reforms in global governance to allow world citizens to take more directly a part into political life. A number of proposals have been made in order to make this possible. Cosmopolitan democracy, for example, suggests strengthening the United Nations and other international organizations by creating a World Parliamentary Assembly.[22]
See also
- Anti-nationalism
- Anti-patriotism
- Cosmopolitan (disambiguation)
- Cross-culturalism
- Democratic globalization
- Diogenes of Sinope
- Europeanism
- Existential migration
- Global Citizens Movement
- Global justice
- Globalization
- Interculturalism
- Internationalism (politics)
- Liberalism
- Multiculturalism
- Polyculturalism
- Rootless cosmopolitan
- Transnationalism
- World citizen
Notes
- ^ Diogenes Laertius, "The Lives of Eminent Philosophers", Chapter VI, line 63.
- ^ Nussbaum, Martha C. (1997). Kant and Stoic Cosmopolitanism, in The Journal of Political Philosophy, Volume 5, Nr 1, pp. 1-25
- ^ Ibid: p. 9
- ^ Immanuel Kant. 'Toward Perpetual Peace' in Practical Philosophy-Cambridge Edition of the Works of Immanuel Kant. Gregor MJ (trans.). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. 1999. p329 (8:358).
- ^ Beck, Ulrich (2006). The Cosmopolitan Vision, Cambridge: Polity Press, p. 45
- ^ Appiah, Kwame Anthony (2006), Cosmopolitanism. Ethics in a World of Strangers, London: Penguin Books
- ^ GTI Paper Series see Dawn of the Cosmopolitan: The Hope of a Global Citizens Movement, paper #15, and Global Politics and Institutions, paper #3
- ^ Thich Nhat Hanh, Being Peace. (1987) Berkeley: Parallax, 1996.
- ^ Ripper, Velcrow. Scared Sacred. National Filmboard of Canada. 2004
- ^ Butler, Judith. Precarious Life: The Powers of Mourning and Violence. New York: Verso, 2004
- ^ Gilroy, Paul. After Empire: Multiculture or Postcolonial Melancholia. New York: Columbia UP, 2005.
- ^ Gilroy, Paul. After Empire: Multiculture or Postcolonial Melancholia. New York: Columbia UP, 2005.
- ^ Fanon, Frantz. “The Pitfalls of National Consciousness" in The Wretched of the Earth.
- ^ Mamdani, Mahmood. Good Muslim, Bad Muslim: America, the Cold War, and the Roots of Terror. New York: Pantheon Books, 2004.
- ^ Appiah, Anthony Kwame. “Moral Disagreement” and “Kindness to Strangers” in Cosmopolitanism: Ethics in a World of Strangers. New York: W. W. Norton and Co., 2006. Pp.45-68, 155-174.
- ^ Mosterín, Jesús (2008). La cultura de la libertad. Madrid: Espasa-Calpe. 304 pp. ISBN 978-84670-2697-9.
- ^ Mosterín, Jesús (2005). “A World without Nation States”. Acta Institutionis Philosophiae et Aestheticae (Tokyo), vol. 23 (2005), pp. 55-77.
- ^ Emmanuel Levinas. Totality and Infinity. An Essay on Exteriority. Lingis A (trans) Duquesne University Press, Pittsburgh, PA 1998. pp84, 100-101
- ^ Emmanuel Levinas. Totality and Infinity. An Essay on Exteriority. Lingis A (trans) Duquesne University Press, Pittsburgh, PA 1998. pp84, 100-101
- ^ GTI Paper Series see Global Politics and Institutions, paper #3
- ^ Daniele Archibugi, The Global Commonwealth of Citizens: Toward a Cosmopolitan Democracy, Princeton University Press, 2009.
- ^ Daniele Archibugi, Debating Cosmopolitics, London: Verso, 2003.
Resources
- Amanda Anderson. 1998. Cosmopolitanism, Universalism, and the Divided Legacies of Modernity. In Cosmopolitics: Thinking and Feeling beyond the Nation, edited by P. Cheah and B. Robbins. Minneapolis and London: University of Minnesota Press.
- Ankerl, Guy (2000). Global communication without universal civilization. INU societal research. Vol.1: Coexisting contemporary civilizations : Arabo-Muslim, Bharati, Chinese, and Western. Geneva: INU Press. ISBN 2-88155-004-5.
- Daniele Archibugi and David Held. editors, 1995. Cosmopolitan Democracy. An Agenda for a New World Order. Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Kwame Anthony Appiah, 2006. Cosmopolitanism: Ethics in a world of strangers. New York: W. W. Norton and Co.
- Simon Caney, 'Cosmopolitanism' in Duncan Bell (ed.), Ethics and World Politics (Oxford University Press, 2010)
- Luke Martell. 2008. Beck's Cosmopolitan Politics Contemporary Politics 2008.
- Bruce Robbins. 1998. Comparative Cosmopolitanisms. In Cosmopolitics: Thinking and Feeling beyond the Nation, edited by P. Cheah and B. Robbins. Minneapolis and London: University of Minnesota Press.
- 2005. The Political Philosophy of Cosmopolitanism, edited by Gillian Brock and Harry Brighouse. Cambridge University Press.
- 2005. Power in the Global Age, by Ulrich Beck. Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Kleingeld, Pauline; Brown, Eric. Edward N. Zalta. ed. Cosmopolitanism (Fall 2002 ed.). The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. http://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2002/entries/cosmopolitanism/.
- ref 1: GTI Paper Series see Dawn of the Cosmopolitan: The Hope of a Global Citizens Movement, paper #15, and Global Politics and Institutions, paper #3
Global governance and identity Proposals Theories Cosmopolitanism · Democratic globalization · Global governance · Transnational governance · Global citizenship · Globalism · Internationalism · World citizen · World currency · world taxation systemOrganisations External links
- "Expatacular - Global expat community bridging cultures"
- "InterNations - the Community for Expatriates and Global Minds"
- Cosmopolitanism entry by Pauline Kleingeld and Eric Brown in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- Living in the World Risk Society by Ulrich Beck at the London School of Economics
- "Global Community of United Earth"
- "Linkexpats - Social networking website for expatriates"
Categories:- Human migration
- Political theories
- Politics and race
- Political philosophy
- Social philosophy
- Philosophical movements
- Social movements
- Cultural geography
- World government
- Philosophical schools and traditions
- Interculturalism
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

