- Ophthalmic acid
-
Ophthalmic acid[1] 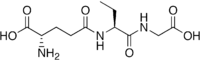
Identifiers CAS number 495-27-2 
PubChem 7018721 ChemSpider 5381695 
MeSH ophthalmic+acid Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC[C@H](NC(=O)CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)C(=O)NCC(O)=O
Properties Molecular formula C11H19N3O6 Molar mass 289.2851 g mol−1 Exact mass 289.127385355 g mol−1 Appearance Colorless crystals  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Ophthalmic acid, also known as ophthalmate (chemically L-Ύ-glutamyl-L-α-aminobutyrylglycine), is a tripeptide analogue of glutathione in which the cysteine group is replaced by L-2-aminobutyrate. It was first discovered and isolated from calf lens.[2]
Biosynthesis
Recent studies have shown that the ophthalmate can be biologically synthesized from 2-amino butyric acid through consecutive reactions with gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase. So the ophthalmic acid could be used as a biomarker in oxidative stress where the depletion of glutathione takes place.[3]
References
- ^ Ophthalmic acid
- ^ Waley SG; Biochem. J. 64, 715 (1956).
- ^ Tomoyoshi Soga, Richard Baran, Makoto Suematsu, Yuki Ueno, Satsuki Ikeda, Tadayuki Sakurakawa, Yuji Kakazu, Takamasa Ishikawa, Martin Robert, Takaaki Nishioka, and Masaru Tomita (June 2006). "Differential Metabolomics Reveals Ophthalmic Acid as an Oxidative Stress Biomarker Indicating Hepatic Glutathione Consumption". Journal of Biological Chemistry 281 (24): 16768–16776. doi:10.1074/jbc.+M601876200. PMID 16608839.
See also
Categories:- Peptides
- Amine stubs
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
