- Cumulus cloud
-
Cumulus Cloud 
Abbreviation Cu Genus Cumulus (heap) Altitude Base usually below 2,000 m (below 6,500 ft)
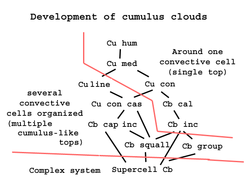
but may be higher (mid-level altitude) during conditions of very low relative humidity. (tops vary)Classification moderate vertical (family D1) or towering vertical (family D2). Appearance puffy Precipitation cloud? Depends. Cumulus humilis and mediocris, most likely no, but congestus and castellanus sometimes yes. Cumulonimbus, yes, but may be virga. Cumulus clouds are a type of cloud with noticeable vertical development and clearly defined edges. Cumulus means "heap" or "pile" in Latin. They are often described as "puffy" or "cotton-like" in appearance. Cumulus clouds may appear alone, in lines, or in clusters. Cumulus clouds are often precursors of other types of clouds, such as cumulonimbus, when influenced by weather factors such as instability, moisture, and temperature gradient. Cumulus clouds are part of the larger category of cumuliform clouds, which include cumulus, cumulus congestus, and cumulonimbus clouds, among others.[1] The most intense cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds may be associated with severe weather phenomena such as hail, waterspouts and tornadoes.
Contents
Formation
Cumulus clouds typically form when warm air rises and reaches a level of cool air, where the moisture in the air condenses. This usually happens through convection, where a parcel of air is warmer than the surrounding air.[2] As it rises, the air cools at the dry adiabatic lapse rate (approximately 3°C per 1000 ft or 1°C per 100 m), while the dewpoint of the air falls by 0.5°C per 1000 ft.[3] When the temperature of the air reaches the dewpoint, some water condenses out of the air to form the cloud. The size of the cloud depends on the temperature profile of the atmosphere and the presence of any inversion. If the top of the cumulus cloud reaches above the altitude where the temperature is at or below the freezing level, then precipitation from the cloud is possible.[4] The temperature of the air at ground level will determine if this falls as rain or snow.
In windy conditions, the clouds can form lines (cloud streets) parallel with the wind.[5] In mountainous areas, they may also form lines at an angle to the wind, due to the presence of lee waves above the clouds.[6] They form around 0 feet in the air.
Over the sea cumulus clouds may be found in regularly spaced lines or patterns.[7] The best examples of these lines are found in the trade winds, where they may extend for many miles[vague]. Such lines create a pattern in the vertical movement of air, causing it to roll horizontally. Between the lines of cloud are stronger, more gusty, and slightly veering winds, but beneath the lines of cloud, somewhat lighter and more backing winds prevail.
The height at which the cloud starts to form (cloud base) depends on the amount of moisture in the air parcel that forms the cloud. Humid air will generally result in a lower cloud base.[8] In temperate areas, the base of the cumulus clouds is usually up to 8,000 ft (2,400 m) in altitude. In arid and mountainous areas, the cloudbase can be in excess of 20,000 ft (6,000 m).
Glider pilots often pay close attention to cumulus clouds, as they can be indicators of rising air drafts or thermals underneath.[5]
Forecast
Cumulus humilis clouds, appearing as small- or medium-sized puffy shapes in the sky, often occur in times of fair weather.[9] However, cumulus clouds can grow into cumulonimbus clouds which may produce heavy rain, lightning, severe and strong winds, hail, and even tornadoes.[10][11] Cumulus congestus clouds, which appear as towers, will often grow into cumulonimbus storm clouds.
 Cumulonimbus Cloud Formation Over Central Florida
Cumulonimbus Cloud Formation Over Central Florida
References
- ^ Cumuliform clouds: some examples. Accessed 2009-11-08.
- ^ "BBC - Cumulus Clouds". http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/features/cumulus.shtml. Retrieved 2008-08-15.
- ^ Brunt, D (1939). Physical and Dynamical Meteorology. London: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Mossop, S C; Hallett J (November 1974). Ice Crystal Concentration in Cumulus Clouds: Influence of the Drop Spectrum: Science. AAAS.
- ^ a b "Pilot Outlook - Cloud Streets". http://www.pilotoutlook.com/glider_flying/cloud_streets. Retrieved 2008-08-13.
- ^ "Wave Soaring Over the British Isles". http://www.go.ednet.ns.ca/~larry/bsc/articles/wave/wavesoar.html. Retrieved 2008-10-02.[dead link]
- ^ Russell, Sharman. "The Language of Clouds". Natural Resources Defense Council. http://www.nrdc.org/OnEarth/03fal/openspace.asp. Retrieved 2008-10-14.
- ^ "ARIC - Cumulus Clouds". http://www.ace.mmu.ac.uk/eae/weather/older/Cumulus_Clouds.html. Retrieved 2008-08-16.
- ^ "Michigan Tech - Cumulus Clouds". Archived from the original on 2008-06-18. http://web.archive.org/web/20080618075254/http://www.geo.mtu.edu/department/classes/ge406/tjbrabec/cumulus.html. Retrieved 2008-08-13.
- ^ Palmer, Chad (2005-10-16). "USA Today - Cumulus Clouds". http://www.usatoday.com/weather/wcumulus.htm. Retrieved 2008-08-13.
- ^ Thompson, Philip; Robert O'Brien (1965). Weather. New York: Time Inc.. pp. 86–87.
External links
- AMS Glossary of Meteorology
- Cumulus cloud at BBC Weather
- Cumulus cloud page at University of Richmond internal site
- Time-lapse of the formation of Cumulus clouds
Cloud genuses Extreme-level High-level Medium-level Low-level Fog · Stratus (St) · Cumulus (Cu) · Stratocumulus (Sc) · Arcus (Roll) · Fractus · Funnel · Nimbostratus (Ns) · Shelf · Wall · Actinoform cloud · Undulatus asperatusVertical Cumulonimbus (Cb) · Cumulonimbus mammatus · Pyrocumulus · Pyrocumulonimbus · Overshooting top · AccessoryCategories: -
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.