- Chebyshev function
-
In mathematics, the Chebyshev function is either of two related functions. The first Chebyshev function ϑ(x) or θ(x) is given by
with the sum extending over all prime numbers p that are less than or equal to x.
The second Chebyshev function ψ(x) is defined similarly, with the sum extending over all prime powers not exceeding x:
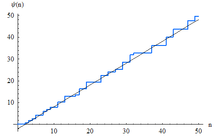
where Λ is the von Mangoldt function. The Chebyshev function is often used in proofs related to prime numbers, because it is typically simpler to work with than the prime-counting function, π(x). Both Chebyshev functions are asymptotic to x, a statement equivalent to the prime number theorem.
Both functions are named in honour of Pafnuty Chebyshev.
Contents
Relationships
The second Chebyshev function can be seen to be related to the first by writing it as
where k is the unique integer such that pk ≤ x but pk+1 > x. A more direct relationship is given by
Note that this last sum has only a finite number of non-vanishing terms, as
The second Chebyshev function is the logarithm of the least common multiple of the integers from 1 to n.
Asymptotics and bounds
The following bounds are known for the Chebyshev functions:[1][2] (in these formulas pk is the kth prime number p1 = 2, p2 = 3, etc.)
 for
for 
 for k ≥ 198,
for k ≥ 198,
 for x ≥ 10,544,111,
for x ≥ 10,544,111,
 for x ≥ exp(22),
for x ≥ exp(22),
![0.9999\sqrt x<\psi(x)-\vartheta(x)<1.00007\sqrt x+1.78\sqrt[3]x](8/a88ed178b9365f24723fc34eb6812baa.png) for
for 
Further, under the Riemann hypothesis,

- | ψ(x) − x | = O(x1 / 2 + ε)
for any

The exact formula
In 1895, Hans Carl Friedrich von Mangoldt proved[3] an explicit expression for ψ(x) as a sum over the nontrivial zeros of the Riemann zeta function:
(The numerical value of ζ'(0)/ζ(0) is log(2π).) Here ρ runs over the nontrivial zeros of the zeta function, and ψ0 is the same as ψ, except that at its jump discontinuities (the prime powers) it takes the value halfway between the values to the left and the right:
From the Taylor series for the logarithm, the last term in the explicit formula can be understood as a summation of xω / ω over the trivial zeros of the zeta function,
 , i.e.
, i.e.Similarly, the first term, x = x1/1, corresponds to the simple pole of the zeta function at 1. Its being a pole rather than zero accounts for the opposite sign of the term.
Properties
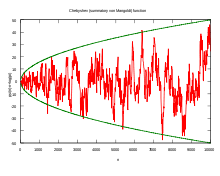
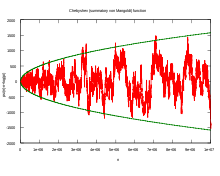
A theorem due to Erhard Schmidt states that, for some explicit positive constant K, there are infinitely many natural numbers x such that
and infinitely many natural numbers x such that
In little-o notation, one may write the above as
Hardy and Littlewood[6] prove the stronger result, that
Relation to primorials
The first Chebyshev function is the logarithm of the primorial of x, denoted x#:
This proves that the primorial x# is asymptotically equal to exp((1+o(1))x), where "o" is the little-o notation (see Big O notation) and together with the prime number theorem establishes the asymptotic behavior of pn#.
Relation to the prime-counting function
The Chebyshev function can be related to the prime-counting function as follows. Define
Then
The transition from Π to the prime-counting function, π, is made through the equation
Certainly
 , so for the sake of approximation, this last relation can be recast in the form
, so for the sake of approximation, this last relation can be recast in the formThe Riemann hypothesis
The Riemann hypothesis states that all nontrivial zeros of the zeta function have real part 1/2. In this case,
 , and it can be shown that
, and it can be shown thatBy the above, this implies
Good evidence that RH could be true comes from the fact proposed by Alain Connes and others, that if we differentiate the von Mangoldt formula with respect to x make x = exp(u). Manipulating, we have the "Trace formula" for the exponential of the Hamiltonian operator satisfying
where the "trigonometric sum" can be considered to be the trace of the operator (statistical mechanics)
 ,which is only true if ρ = 1 / 2 + iE(n).
,which is only true if ρ = 1 / 2 + iE(n).Using the semiclassical approach the potential of H = T + V satisfies:
with Z(u) → 0 as u → ∞.
solution to this nonlinear integral equation can be obtained (among others) by
 in order to obtain the inverse of the potential : πN(E) = Argξ(1 / 2 + iE)
in order to obtain the inverse of the potential : πN(E) = Argξ(1 / 2 + iE)Smoothing function
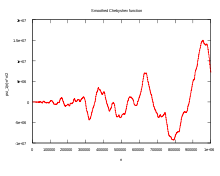
The smoothing function is defined as
It can be shown that
Variational formulation
The Chebyshev function evaluated at x = exp(t) minimizes the functional
so
for c > 0.
Notes
- ^ Pierre Dusart, "Estimates of some functions over primes without R.H.". arXiv:1002.0442
- ^ Pierre Dusart, "Sharper bounds for ψ, θ, π, pk", Rapport de recherche n° 1998-06, Université de Limoges. An abbreviated version appeared as "The kth prime is greater than k(ln k + ln ln k − 1) for k ≥ 2", Mathematics of Computation, Vol. 68, No. 225 (1999), pp. 411–415.
- ^ Erhard Schmidt, "Über die Anzahl der Primzahlen unter gegebener Grenze", Mathematische Annalen, 57 (1903), pp. 195–204.
- ^ G.H. Hardy and J.E. Littlewood, "Contributions to the Theory of the Riemann Zeta-Function and the Theory of the Distribution of Primes", Acta Mathematica, 41 (1916) pp. 119–196.
- ^ Davenport, Harold (2000). In Multiplicative Number Theory. Springer. p. 104. ISBN 0-387-95097-4. Google Book Search.
References
- Apostol, Tom M. (1976), Introduction to analytic number theory, Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics, New York-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-90163-3, MR0434929
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Chebyshev functions" from MathWorld.
- Mangoldt summatory function on PlanetMath
- Chebyshev functions on PlanetMath
- Riemann's Explicit Formula, with images and movies
Categories:- Arithmetic functions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


























![J[f]=\int_{0}^{\infty}\frac{f(s)\zeta' (s+c)}{\zeta(s+c)(s+c)}\,ds-\int_{0}^{\infty}\!\!\!\int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-st}f(s)f(t)\,ds\,dt,](d/8fd9f1d1db36a04cd02ddbcdc04aaebb.png)
