- Control register
-
A control register is a processor register which changes or controls the general behavior of a CPU or other digital device. Common tasks performed by control registers include interrupt control, switching the addressing mode, paging control, and coprocessor control.
Contents
Control registers in x86 series
CR0
The CR0 register is 32 bits long on the 386 and higher processors. On x86-64 processors in long mode, it (and the other control registers) are 64 bits long. CR0 has various control flags that modify the basic operation of the processor.
Bit Name Full Name Description 31 PG Paging If 1, enable paging and use the CR3 register, else disable paging 30 CD Cache disable Globally enables/disable the memory cache 29 NW Not-write through Globally enables/disable write-back caching 18 AM Alignment mask Alignment check enabled if AM set, AC flag (in EFLAGS register) set, and privilege level is 3 16 WP Write protect Determines whether the CPU can write to pages marked read-only 5 NE Numeric error Enable internal x87 floating point error reporting when set, else enables PC style x87 error detection 4 ET Extension type On the 386, it allowed to specify whether the external math coprocessor was an 80287 or 80387 3 TS Task switched Allows saving x87 task context only after x87 instruction used after task switch 2 EM Emulation If set, no x87 floating point unit present, if clear, x87 FPU present 1 MP Monitor co-processor Controls interaction of WAIT/FWAIT instructions with TS flag in CR0 0 PE Protected Mode Enable If 1, system is in protected mode, else system is in real mode CR1
Reserved
CR2
Contains a value called Page Fault Linear Address (PFLA). When a page fault occurs, the address the program attempted to access is stored in the CR2 register.
CR3
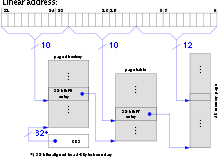
Used when virtual addressing is enabled, hence when the PG bit is set in CR0. CR3 enables the processor to translate virtual addresses into physical addresses by locating the page directory and page tables for the current task. Typically, the upper 20 bits of CR3 become the page directory base register (PDBR), which stores the physical address of the first page directory entry.
CR4
Used in protected mode to control operations such as virtual-8086 support, enabling I/O breakpoints, page size extension and machine check exceptions.
Bit Name Full Name Description 18 OSXSAVE XSAVE and Processor Extended States Enable 17 PCIDE PCID Enable If set, enables process-context identifiers (PCIDs). 14 SMXE SMX Enable 13 VMXE VMX Enable 10 OSXMMEXCPT Operating System Support for Unmasked SIMD Floating-Point Exceptions If set, enables unmasked SSE exceptions. 9 OSFXSR Operating system support for FXSAVE and FXSTOR instructions If set, enables SSE instructions and fast FPU save & restore 8 PCE Performance-Monitoring Counter enable If set, RDPMC can be executed at any privilege level, else RDPMC can only be used in ring 0. 7 PGE Page Global Enabled If set, address translations (PDE or PTE records) may be shared between address spaces. 6 MCE Machine Check Exception If set, enables machine check interrupts to occur. 5 PAE Physical Address Extension If set, changes page table layout to translate 32-bit virtual addresses into extended 36-bit physical addresses. 4 PSE Page Size Extensions If unset, page size is 4 KB, else page size is increased to 4 MB (ignored with PAE set). 3 DE Debugging Extensions 2 TSD Time Stamp Disable If set, RDTSC instruction can only be executed when in ring 0, otherwise RDTSC can be used at any privilege level. 1 PVI Protected-mode Virtual Interrupts If set, enables support for the virtual interrupt flag (VIF) in protected mode. 0 VME Virtual 8086 Mode Extensions If set, enables support for the virtual interrupt flag (VIF) in virtual-8086 mode. Additional Control registers in x86-64 series
EFER
Extended Feature Enable Register (EFER) is a register added in the AMD K6 processor, to allow enabling the SYSCALL/SYSRET instruction, and later for entering and exiting long mode.
Bit Purpose 63:12 Reserved 11 Execute-disable bit enable (NXE) 10 IA-32e mode active (LMA) 9 Reserved 8 IA-32e mode enable (LME) 7:1 Reserved 0 SysCall enable (SCE) See also
- Protected mode in x86 Assembly at Wikibooks
- General purpose registers
- Test register
- Debug register
- Flag byte
- Status register
References
External links
Categories:- Programming idioms
- Operating system technology
- Central processing unit
- Digital registers
- Operating system stubs
- Computer science stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.