- POSTNET
-
Value Encoding 1 
2 
3 
4 
5 
6 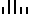
7 
8 
9 
0 
POSTNET (Postal Numeric Encoding Technique) is a barcode symbology that was used by the United States Postal Service to assist in directing mail. The ZIP Code or ZIP+4 code is encoded in half- and full-height bars[1]. Most often, the delivery point is added, usually being the last two digits of the address or PO box number.
The barcode starts and ends with a full bar (often called a guard rail or frame bar and represented as the letter "S" in one version of the USPS TrueType Font) and has a check digit after the ZIP, ZIP+4, or delivery point. The encoding table is shown on the right.
Each individual digit is represented by a set of five bars, two of which are full bars (i.e. two-out-of-five code). The full bars represent "on" bits in a pseudo-binary code in which the places represent, from left to right: 7, 4, 2, 1, 0. (Though in this scheme, zero is encoded as 11 decimal, or "binary" 11000.)
Contents
Example
The zip+4 of 55555-1237 yields a check digit of 2 for encoded data of 5555512372
Together with the initial and terminal frame bars, this would be represented as:Barcode formats
There have been four formats of Postnet barcodes used by the Postal Service:
A 5 digit (plus check digit) barcode, containing the basic ZIP Code only, referred to as the "A" code. 32 bars total.
A 6 digit (plus check digit) barcode, containing the last 2 digits of the ZIP Code and the 4 digits of the ZIP+4 Code, referred to as a "B" code. 37 bars total. In the early stages of Postal automated mail processing the B code was used to "upgrade" mail that had been coded only with a 5-digit "A" code. This barcode was only found on mail that received a 5-digit barcode on the initial coding by an OCR. Now obsolete.
A 9 digit (plus check digit) barcode, containing the ZIP Code and ZIP+4 Code, referred to as the "C" code. 52 bars total. The 9-digit barcode enabled the sorting of mail to the individual delivery carrier, and in some cases into a semblance of delivery sequence.
An 11 digit (plus check digit) barcode, containing the ZIP Code, ZIP+4 Code, and the delivery point code. 62 bars total. This is usually referred to as the DPBC, or Delivery Point Bar Code. This is the predominant barcode in use currently (as of 2005[update]), and it enables the Postal Service to sort mail into delivery point (address) sequence.[2]
Discontinuation
POSTNET is being retired,[3] and is being replaced by the Intelligent Mail barcode (also known as OneCode Solution) which combines all previous Postal Service barcodes and marking into a single barcode. The Intelligent Mail Barcode was originally supposed to be required beginning May 2011 however the USPS postponed the requirement date, allowing mailers to continue receiving automation discount rates using the Postnet Barcode after the May 2011 deadline.[4]
Checkdigit algorithm
The check digit is 10 minus (the digit-sum mod 10). That is, the check digit is calculated by:
- Add up the digits, including the delivery point code if it is being used. If you are sending a letter to somewhere in Young America, Minnesota, you might be sending to 55555-1237, which would have the sum of 38.
- Find the remainder of this number when it is divided by 10, in this case 8. This could also be called the sum modulo 10. (Note that when summing the digits, any leading 1 in the 10's column of the current sum may be discarded.)
- Subtract the sum modulo 10 from 10. Continuing with the example, 10 - 8 = 2. The check digit is therefore 2.
If calculated correctly, the sum of the ZIP, ZIP+4, or ZIP+4+delivery point digits and the check digit, modulo 10, will always be zero. Continuing with the example above, (5+5+5+5+5+1+2+3+7+2) mod 10 = 0.
Note that the Delivery Point is often added after the ZIP+4 and before the check digit, in which case the computation of the check digit includes the ZIP+4 and the Delivery Point.
See also
References
- ^ Publication 25, Designing Letter and Reply Mail. United States: United States Postal Service. July 2003. pp. 37-56. http://www.siemons.com/forms/pdf/designing_letter_reply_mail.pdf.
- ^ United States Postal Service, Domestic Mail Manual 708.4 - Special Standards, Technical Specifications, Barcoding Standards for Letters and Flats. http://pe.usps.com/cpim/ftp/manuals/dmm300/708.pdf
- ^ "USPS PCC Insider Q & A". http://www.usps.com/communications/pccinsider/2010/pcc_qa_1015.htm.
- ^ "Postal Service Relaxes Upcoming Requirements for Automation Prices". http://pe.usps.com/DMMAdvisory.asp?Dest=DMMAdvisory011311a.htm.
Barcodes Linear barcodes Automatic Car Identification - Code 39 - Code 93 - Code 128 - Codabar - European Article Number - GS1 DataBar - ITF-14 - MSI Barcode - Plessey - Telepen - UPC - Pharmacode

UPC-A MaxiCode Post office barcodes CPC Binary Barcode - Facing Identification Mark - PostBar - POSTNET - RM4SCC - Intelligent Mail barcode - PLANET2D barcodes (stacked) 2D barcodes (matrix) Polar coordinate barcodes Other Technological issues Other data tags RFID - BokodeRelated topics External links
Barcodes Linear barcodes Automatic Car Identification - Code 39 - Code 93 - Code 128 - Codabar - European Article Number - GS1 DataBar - ITF-14 - MSI Barcode - Plessey - Telepen - UPC - Pharmacode

UPC-A MaxiCode Post office barcodes CPC Binary Barcode - Facing Identification Mark - PostBar - POSTNET - RM4SCC - Intelligent Mail barcode - PLANET2D barcodes (stacked) 2D barcodes (matrix) Polar coordinate barcodes Other Technological issues Other data tags RFID - BokodeRelated topics Categories:- Barcodes
- Identifiers
- ZIP code
- United States Postal Service
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

