- Platinum(II) chloride
-
Platinum(II) chloride 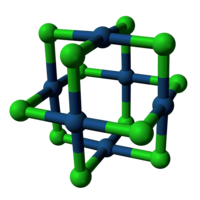 Other namesplatinous chloride
Other namesplatinous chlorideIdentifiers CAS number 10025-65-7 ChemSpider 2668 
ChEBI CHEBI:49801 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Cl[Pt]Cl
Properties Molecular formula PtCl2 Molar mass 265.99 g/mol Appearance olive green crystals Density 6.05 g/cm3, solid Melting point 581 °C
Boiling point decomposes
Solubility in water insoluble Solubility insoluble in alcohol
soluble in HCl, ammoniaHazards EU classification not listed Related compounds Other anions platinum(II) sulfide, platinum(II) iodide Other cations palladium(II) chloride, iridium dichloride Related compounds platinum trichloride  chloride (verify) (what is:
chloride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Platinum(II) chloride is the chemical compound PtCl2. It is an important precursor used in the preparation of other platinum compounds. It exists in two crystalline forms, but the main properties are somewhat similar: dark brown, insoluble in water, diamagnetic, and odorless.
Contents
Structure
The structures of PtCl2 and PdCl2 are similar. These dichlorides exist in both polymeric, or "α", and hexameric, or "β" structures. The β form converts to the α form at 500 °C. In the β form, the Pt-Pt distances are 3.32-3.40 Å, indicative of some bonding between the pairs of metals. In both forms of PtCl2, each Pt center is four-coordinate, being surrounded by four chloride ligands. Complementarily, each Cl center is two-coordinate, being connected to two platinum atoms.[1]
Preparation
β-PtCl2 is prepared by heating chloroplatinic acid to 350 °C in air.[2]
- H2PtCl6 → PtCl2 + Cl2 + 2 HCl
This method is convenient since the chloroplatinic acid is generated readily from Pt metal. Aqueous solutions of H2PtCl6 can also be reduced with hydrazinium salts, but this method is more laborious than the thermal route of Kerr and Schweizer.
Although PtCl2 must form when platinum metal contacts hot chlorine gas, this process suffers from over-chlorination to give PtCl4. Berzelius and later Wöhler and Streicher showed that upon heating to 450 °C, this Pt(IV) compound decomposes to the Pt(II) derivative:[3]
- PtCl4 → PtCl2 + Cl2
Transformations such as this are "driven" by entropy, the free energy gained upon the release of a gaseous product from a solid. Upon heating to still higher temperatures, PtCl2 releases more chlorine to give metallic Pt. This conversion is the basis of the gravimetric assay of the purity of the PtCl2 product.
Uses
Most reactions of PtCl2 proceed via treatment with ligands (L) to give molecular derivatives. These transformations entail depolymerization via cleavage of Pt-Cl-Pt linkages:
- PtCl2 + 2 L → PtCl2L2
Sometimes, such reactions can be deceptive. Addition of ammonia gives initially "PtCl2(NH3)2", but this material is in fact Magnus's green salt, [PtCl4][Pt(NH3)4].
Of the many such complexes that have been described, the following are illustrative:[4]
- pink K2PtCl4, a widely employed water-soluble derivative.
- colorless cis-PtCl2(NH3)2, better known as cisplatin.
- colorless cis-PtCl2(P(C6H5)3)2, a commonly employed, easily crystallized species that is widely employed as a precursor other complexes of the type PtX(Cl)(P(C6H5)3)2 (X = H, CH3, etc.).
- yellow trans-PtCl2(P(C6H5)3)2, a metastable relative of the cis- isomer.
- colorless dichloro(cycloocta-1,5-diene)platinum(II) (Pt(cod)Cl2), an "organic-soluble" compound containing a labile organic ligand.
Several of these compounds are of interest in homogeneous catalysis in the service of organic synthesis or as anti-cancer drugs.
See also
References
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Kerr, G. T.; Schweizer, A. E. (1980). "β-Platinum(II) Chloride". Inorg. Synth.. Inorganic Syntheses 20: 48–49. doi:10.1002/9780470132517.ch14. ISBN 9780470132517.
- ^ Wöhler, L.; Streicher, S. (1913). "Über das Beständigkeitsgebiet von vier wasserfreien Platinchloriden, über die Flüchtigkeit des Metalls im Chlorgas und die Darstellung sauerstoff-freien Chlors". Chem. Ber. 46 (2): 1591–1597. doi:10.1002/cber.19130460252.
- ^ Cotton, S. A. "Chemistry of Precious Metals," Chapman and Hall (London): 1997. ISBN 0-7514-0413-6
Categories:- Chlorides
- Platinum compounds
- Metal halides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

