- Methyl bisulfate
-
Methyl bisulfate 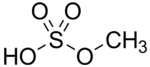 Other namesMethyl sulfate; Methylsulfuric acid; Methyl hydrogen sulfate; Monomethyl sulfate
Other namesMethyl sulfate; Methylsulfuric acid; Methyl hydrogen sulfate; Monomethyl sulfateIdentifiers CAS number 75-93-4 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - OS(OC)(=O)=O
Properties Molecular formula CH4O4S Molar mass 112.11 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Methyl bisulfate is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH3OSO3H. This compound is the mono-methyl ester of sulfuric acid. The significance of methyl bisulfate is that it is an intermediate in the hydrolysis of the important reagent dimethyl sulfate, (CH3)2SO4:[1]
- (CH3)2SO4 + H2O → (CH3)HSO4 + CH3OH
Methyl bisulfate is an acid:
- (CH3)HSO4 → (CH3)SO4- + H+
Methyl bisulfate came into the public view in 1993 with the discovery that certain mercury compounds catalyze the conversion of methane to methylbisulfate in good yields with excellent selectivity in concentrated sulfuric acid.[2] However, because of the toxicity and concerns with the use of mercury it wasn't until 1998 when platinum complexes were found that catalyze the reaction of CH4 by SO3 and O2 that it came into the limelight:[3][4][5]
- CH4 + SO3 + 1/2 O2 → (CH3)HSO4
This discovery pointed to a possible method for upgrading inexpensive and abundantly available methane (natural gas) into methanol, which is both a more useful chemical and more easily shipped than methane. The process is proposed to proceed via an intermediate containing the Pt-CH3 group.[6]
Salts of (CH3)SO4- are commercially available, e.g. tris(2-hydroxyethyl)methylammonium methylsulfate (CAS #29463-06-7).
References
- ^ Robertson, R. E.; Sugamon, S.E. (1966). "The Hydrolysis of Dimethyl Sulfate and Diethyl Sulfate in Water". Canadian Journal of Chemistry 44 (14): 1728–1730. doi:10.1139/v66-260.
- ^ Periana, R.A.; Taube, D.J.; Evitt, E.R.; Loffler, D.G.; Wentrcek, P.R.; Voss, G.; Masuda, T. (1993). "A Mercury-Catalyzed, High-Yield System for the Oxidation of Methane to Methanol". Science 259 (5093): 340–343. doi:10.1126/science.280.5363.493f. PMID 17832346.
- ^ Hristov, I. H.; Ziegler, T. (2003). "The Possible Role of SO3 as an Oxidizing Agent in Methane Functionalization by the Catalytica Process. A Density Functional Theory Study". Organometallics 22 (8): 1668–1674. doi:10.1021/om020774j.
- ^ Periana, R. A.; Mirinov, O.; Taube, D. J.; Gamble, S (2002). "High Yield Conversion of Methane to Methyl Bisulfate Catalyzed by Iodine Cations". Chemical Communications (20): 2376–2377. doi:10.1039/b205366g.
- ^ Wolf, D. (1999). "High Yields of Methanol from Methane by C-H Bond Activation at Low Temperatures". Angewandte Chemie, International Edition 37 (24): 3351–3353. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19981231)37:24<3351::AID-ANIE3351>3.0.CO;2-U.
- ^ Periana, R. A.; Taube, D. J.; Gamble, S.; Taube, H.; Satoh, T.; Fujii, H. (1998). "Platinum Catalysts for the High-Yield Oxidation of Methane to a Methanol Derivative". Science 280 (5363): 560–564. doi:10.1126/science.280.5363.560. PMID 9554841.
Categories:- Methyl esters
- Organosulfates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
